 Nonblanchable erythema of intact skin
Nonblanchable erythema of intact skin
What is Stage 1 pressure injury?
Wound healing is a process of tissue response to..
What is injury?
Use for small wounds; remain in place for 4-7 days; stage 1 pressure injuries; wounds with minimal drainage; cover dressings for gels, foams, and gauze
What is transparent films? (3M medipore,3M tegaderm, Bioclusive, clearsite, dermaview, opsite, suresite)
Sample collection of an infected wound.
What is a wound culture?
A localized mass of usually clotted blood.
What is hematoma?
 Partial-thickness skin loss with exposed dermis; intact or ruptured serum-filled blister.
Partial-thickness skin loss with exposed dermis; intact or ruptured serum-filled blister.
What is Stage 2 Pressure Injury?
Occurs immediately after the initial injury;Involved blood vessels constrict and blood clotting begins through platelet activation and clustering. Forming a liquid which consist of plasma and blood components called exudate.
What is hemostasis?
Used for partial and full-thickness wounds; stage 2 & 3 pressure injuries; prevention at high risk friction areas; wounds with light to moderate drainage; wounds with necrosis or slough; first or second degree burns; not for use with wounds that are infected.
What is Hydrocolloid dressings?
Comfeel
Droderm
exuderm
primacol
ultec
The application of ___________ accelerates the inflammatory response to promote healing.
What is heat therapy?
A partial or total separation of wound layers as a result of excessive stress on wounds that are not healed.
What is dehiscence?
 Full thickness skin loss; adipose tissue visible, granulation;rolled wound edges.
Full thickness skin loss; adipose tissue visible, granulation;rolled wound edges.
What is Stage 3 pressure injury?
Last about 2 to 3 days. White blood cells, predominantly leukocytes and macrophages, move to the wound. Leukocytes arrive first to ingest bacteria and cellular debris. Macrophages (essential to healing) occurs 24 hours after injury.
What is inflammatory phase?
Partial and full-thickness wounds; stages 2-4 pressure injuries;necrotic wounds;first and second degree burns;dry wounds;wounds with minimal exudate;infected wounds;radiation tissue damage.
What is hydrogels?
Aquasorb
Dermagauze
flexigel
hypergel
instrasite gel
The local application of ____________constricts peripheral blood vessels, reduces muscle spasms, and promotes comfort.
What is cold therapy?
Most serious complication of dehiscence. It occurs primarily in abdominal wounds. The abdominal wound completely separates, with protrusion of viscera (internal organs) through the incisional area.
What is evisceration?
 Full thickness skin and tissue loss; exposed fascia, muscle, tendon, ligament, cartilage or bone. Undermining and/or tunneling often occur.
Full thickness skin and tissue loss; exposed fascia, muscle, tendon, ligament, cartilage or bone. Undermining and/or tunneling often occur.
What is stage 4 pressure injury?
follows the proliferation phase A.K.A fibroblastic, regenerative, or connective tissue phase. Last for several weeks. New tissue is built to fill the wound space through the actions of fibroblasts. New tissue is called granulation tissue (vascular, red, and bleeds easily), forms the foundation for scar tissue development.
What is proliferation phase?
Partial and full thickness wounds;may remain inplace for 1-3 days; stage 3 and stage 4 pressure injuries;infected and noninfected wounds;wounds with moderate to heavy exudate;tunneling wounds;undermining; moist red and yellow wounds; not for use with wounds with minimal drainage or dry eschar.
What is alginates?
Algicell
Aquacel
Curasorb
Kalginate
The process of removing microorganisms and debris with as little chemical and mechanical force as possible, and protect healthy granulation.
What is wound cleaning?
AN abnormal passage from an internal organ or vessel to the outside of the body or from one internal organ or vessel to another.
What is fistula?
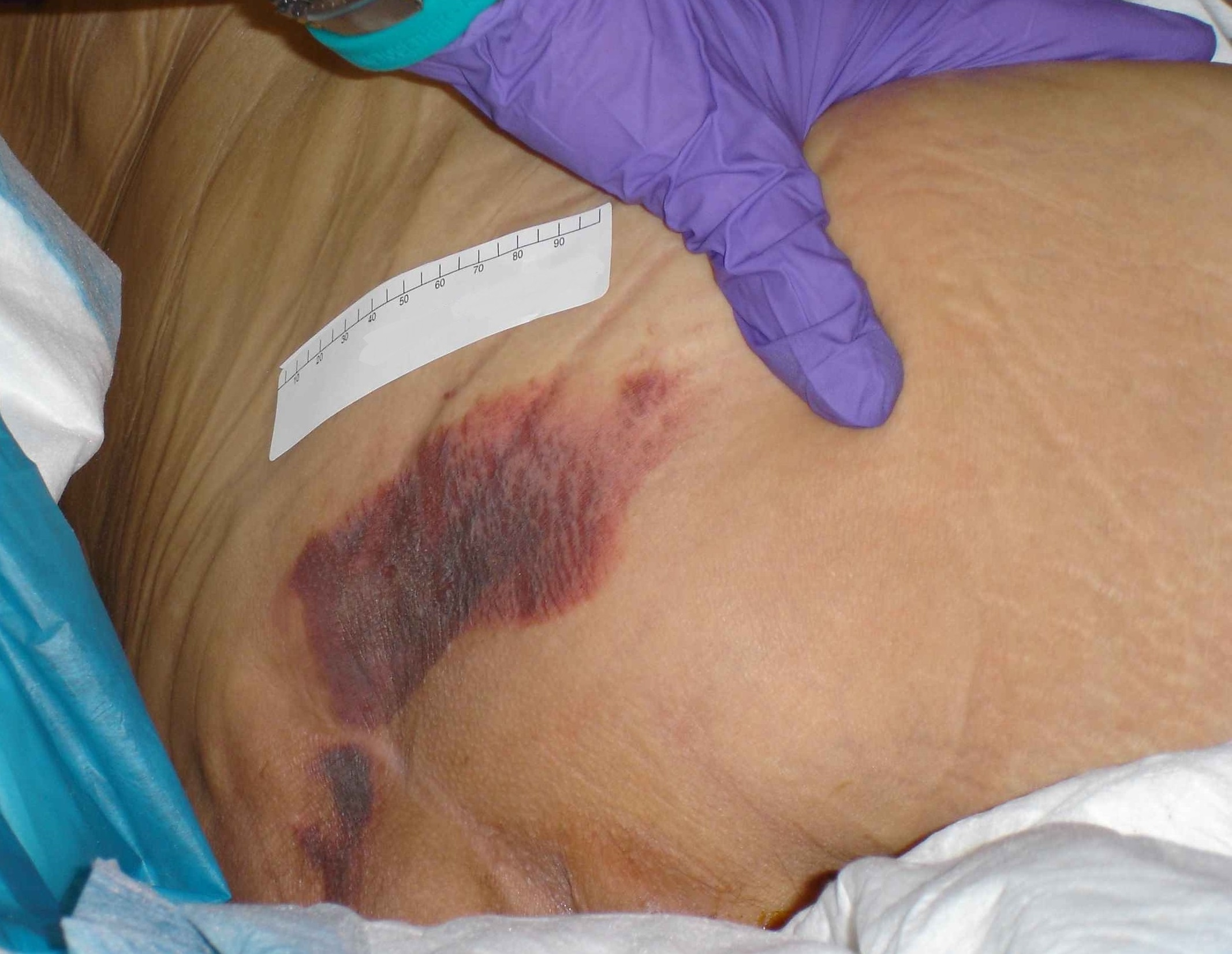 Persistent nonblanchable deep red,maroon or purple discoloration
Persistent nonblanchable deep red,maroon or purple discoloration
What is deep tissue pressure injury?
The final stage of healing, maturation (or remolding) begins about 3 weeks after the injury, possibly continuing for months or years. Collagen is remoldeled, making the healed wound stronger and more like adjacent tissue. Scar tissue develops and the skin is less elastic than the uninjured tissue.
What is maturation phase?
Partial and full-thickness wounds;may remain inplace 3-5 days (7days for foams with silver). depending on exudate, stages 2-4 pressure injuries; surgical wounds;absorbs light to heavy amounts of drainage;use around tubes and drains;not for use with wounds with dry eschar.
What is foams?
Lyofoam
Mepilex
Optifoam
Polyderm
Xusorb
Promotes wound healing and wound closure through the application of uniform negative pressure on the wound bed,reduction in bacteria in the wound, and the removal of excess wound fluid, while providing a moist wound healing environment.
What is negative pressure wound therapy? (NPWT)
A collection of infected fluid that has not drained.
What is an abscess?