The Reyner & Horne (2013) looked at the impact of sleep restriction on tennis performance, and whether caffeine helped tobolster performance after sleep restriction.
Did sleep restriction lead to detriments in performance?
Did consuming caffeine improve performance?
Sleep restriction did lead to reduced performance.
Caffeine did not help improve performance.
In the Mitler et al. (1998) article, sleep research experts discussed the impact of sleepiness and sleep loss on performance that can lead to catastrophes.
What are the three most significant catastrophes discussed where sleep-related human error was involved in the catastrophe?
Three Mile Island, Chernobyl, and Challenger disasters
In the "Debate" article, a series of public debate about the role of sleep in memory processing were published as editorials in the journal SLEEP.
What were the two sides of the debate and their arguments?
Robert Vertes and Jerome Siegel argued that sleep did not play a role in memory encoding and consolidation processes.
Robert Stickgold and Matthew Walker argued that sleep does play a role in memory encoding and consolidation processes.
The Cartwright et al. (1998) article examined how REM sleep and dreams contributed to mood regulation.
True or False: Individuals who reported more negative dreams at the beginning of the night and fewer at the end of the night were more likely to be in remission 1 year later?
True.
Subjects reporting more negative dreams at the beginning and fewer at the night’s end were more likely to be in remission 1 year later than were those with fewer negative dreams at the beginning and more at the end of the night.
Ju et al. (2017) examined how slow wave sleep disruption impacted cerebrospinal fluid amyloid beta levels. They found that SWS disruption led to increased amyloid levels.
What do the findings indicate about the relationship between sleep and amyloid beta/tau levels?
Both of these findings support the hypothetical cascade in which decreased SWA leads to increased soluble amyloid beta and tau levels, which eventually increase risk of amyloid plaques and tau tangle pathology, and subsequent development of symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease.
In the Frenda et al. (2015) article, they examined how sleep deprivation impacted the decision to make a false confession as part of one of the tasks they completed in the lab.
What was their primary finding?
Sleep deprivation led to a 4.5-fold increase in making a false confession of pressing the escape key to exit a task during the laboratory visit compared to well-rested participants.
In the Prather et al. (2015) article, participants underwent actigraphy and sleep monitoring after being exposed to the common cold.
What were the primary findings of the study?
Short sleep duration was associated with a greater likelihood of developing the common cold compared to individuals sleeping 7 hours or more.
Why do we not remember waking up in the middle of the night or falling asleep?
Mesograde amnesia
In Voss et al. (2014), the authors stimulated gamma band activity during REM sleep and induced self-awareness in dreams.
What is a possible clinical application for this finding?
Frontotemporal tACS might facilitate reemergence of intrinsic cerebral rhythms and reset thalamocortical oscillators, which may be able to restore dysfunctional network connectivity, such as the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) in
schizophrenia, activate the PFC in schizophrenia with predominating negative symptoms, or synchronize or suppress basal ganglia activity in, for example, obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Finally, promoting gamma oscillations during REM sleep in post-traumatic stress disorder with reemerging nightmares might trigger lucid dreaming
and eventually enable active changes in dream content.
In the Mindell et al. (2009) article, the authors examined whether the implementation of a nightly bedtime routine impacted the sleep of young children and maternal mood.
What were their primary findings?
They found the routine led to improvements in sleep onset latency and a fewer number of awakenings in the children. There were less problematic sleep behaviors reported. Improvements in sleep continuity.
Maternal mood state improved.
In the Alkozei et al. (2017) article, they examined whether chronic sleep restriction over 3 weeks affects implicit attitudes.
What were their primary findings?
They found evidence for an increased negative implicit bias towards Arab Muslims.
No indicators of an implicit bias were found in these same individuals when they were rested (during a counterbalanced 3-week period of 8 hours time in bed per night).
These findings suggest that chronic sleep restriction
may “unmask” implicit racial or ethnic biases that are otherwise inhibited when in a rested state.
Two or more SOREMPs (sleep onset REM periods) on the Multiple Sleep Latency Test indicate what condition?
Narcolepsy
Who did the first empirical study of memory?
What did they think of the lack of drop-off in memory performance after a night of sleep?
Hermann Ebbinghaus
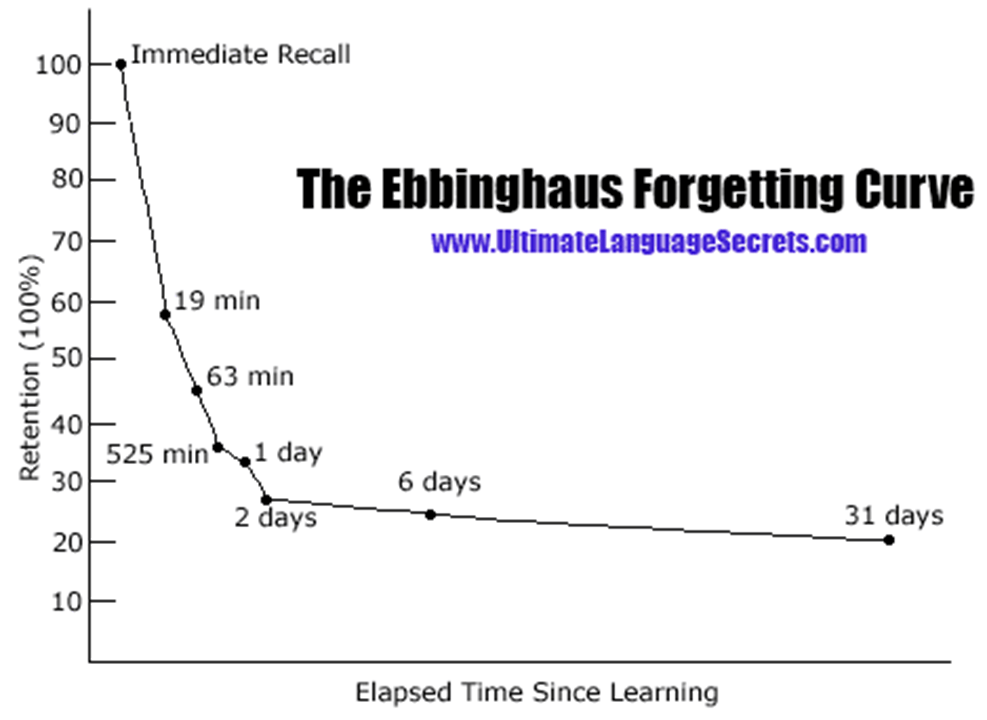
"not credible; least satisfying result"
How do you study or measure lucid dreams?
Teaching the lucid dreamer to perform a distinct eye movement pattern to signal when they become lucid on the dream.
This can be observed with polysomnography (EOG).
When is the peak delay of the midpoint of sleep?
18-21 years of age (college-age)
Based on previous research, how long can you survive without sleep?
11-32 days
Animal studies sleep deprived rodents and they died within 11-32 days without sleep
What is the disease characterized by progressive insomnia, autonomic dysfunction, and eventual death.
Fatal familial insomnia
How do our brains choose amongst all the experiences and things we learn during the day which things to consolidate?
Selective consolidation theory
•When explicitly instructed to expect a later test
•For “remember” but not “forget” items in directed forgetting lists
•Memories for future actions
•Highly rewarded memories
•Emotional content
What are the differences between nightmares and night terrors?
Nightmares can occur at any age, while night terrors primarily occur during childhood.
Nightmares primarily occur during REM sleep, while night terrors occur during NREM sleep.
People who experience nightmares usually remember the details of the dream vividly. People who experience night terrors often have no memory of the event.
During a nightmare, individuals may sit up, scream, or cry, but they are usually aware of their surroundings and can be easily awakened. During a night terror, individuals may appear wide-eyed, sit up, or scream, but they are not aware of their surroundings and are difficult to wake up
What is nocturia?
Nocturia is a condition that often develops with age. Its characterized by waking up to go to urinate during the night. It is defined by needing to wake up more than once to go to the bathroom.
Can you train someone to sleep less?
What are other factors that impact how resistant someone is to sleep loss?
Yes, you can train individuals to sleep less (can be hard to do)
Genetic mutations (mutation P384R in DEC2 gene) is associated with the ability to sleep less 4-6 hours without impairment.
How do you measure:
introspective sleepiness
physiological sleepiness
manifest sleepiness
Introspective sleepiness: self-report questionnaires like the ESS, Karolinska Sleepiness Scale, or Stanford Sleepiness Scale
Physiological: the Multiple Sleep Latency Test
Manifest (behavioral): the Psychomotor Vigilance Task (PVT)
What are the three phases of the systems memory consolidation theory?
Encoding, Storage, Retrieval
Initial Encoding:
When a new experience is learned, memories are rapidly stored in the hippocampus and associated neocortical regions.
Replay and Storage:
Over days or weeks, the hippocampus reactivates the original experience, linking together its various representations and strengthening connections between different cortical areas. This process, known as "neural replay," happens during sleep and other offline periods. As these cortico-cortical connections grow stronger, the memory becomes less reliant on the hippocampus.
Permanent Storage and Retrieval:
Eventually, the memory is fully transferred to the neocortex, becoming a stable, long-lasting trace that can be retrieved without the hippocampus.
ns
Why do we forget that we dream?
Norepinephrine is low (and acetylcholine is high)
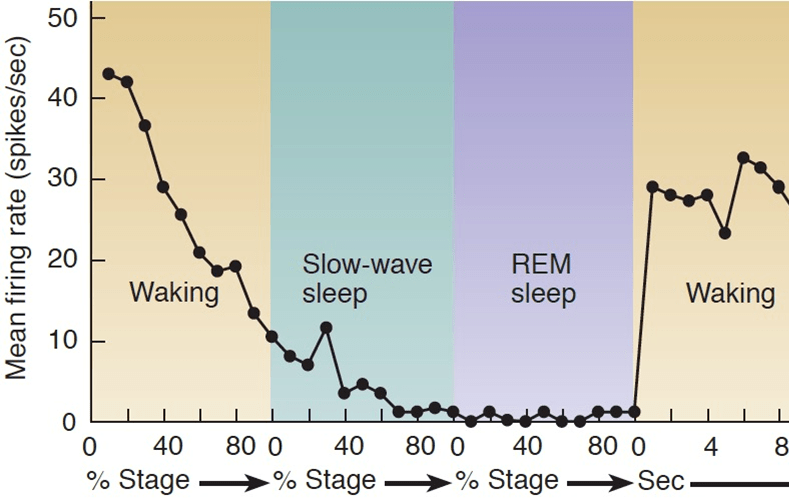
This combination of high acetylcholine and low norepinephrine makes it difficult to consolidate the experiences of the dream.
What are major obstacles to delaying school start times?
•Transportation
•After School Activities
•Effects on younger students and childcare programs
•Reduced time to access the library and other public resources
•Might affect time teachers have with their families
•Might cause stress for families to alter routine
•Community is uneducated about sleep health
•Students might resist the change