What type of electromagnetic wave can humans see?
Visible light
Glowsticks are an example of this type of light source.
Chemiluminescence
Name the two processes that allow light to change direction.
Reflection and refraction
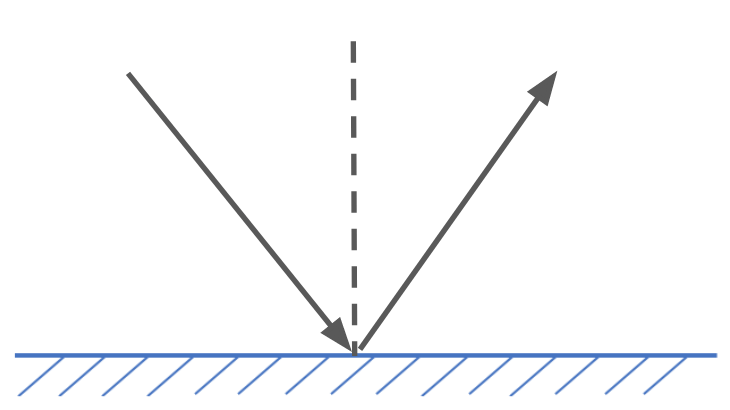
Draw an incident ray and a reflective ray hitting a plane mirror. Please include the normal.
Makeup mirrors are often _____________________ mirrors.
Converging
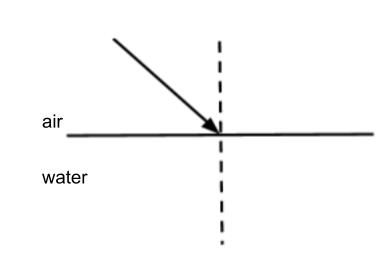 Will the refracted ray bend towards or away from the normal?
Will the refracted ray bend towards or away from the normal?
Towards the normal
(angle of refraction < angle of incidence)
The colours in the visible spectrum combine to form ________ light.
white
What type of of light source would cease to glow immediately after the radiation source (UV light) is removed?
Fluorescence
A ray aimed parallel to the principal axis will reflected through here
Focal Point
State the two laws of reflection:
1) θi = θr
2) Incident ray, normal and reflected ray all line in the same plane
Large hospitals, offices or stores sometimes make use of _____________________ mirrors in order to let people see what is around a corner to avoid people running into each other and prevent minor/major collisions.
Convex (Diverging)
What happens to the speed of light when it enters glass, causing the refraction of light?
the speed slows down.
What is a wavelength?
The space between 2 crests (i.e. the distance from the top of one wave to the top of the adjacent wave)
This type of light bulb is the most efficient kind you can buy in the store.
LED (light-emitting diode)
The critical angle is just what?
90°
Using SALT, describe an image in a plane mirror.
Size - Same
Attitude - Upright
Location - Behind Mirror
Type - Virtual
A ___________________ mirror is a reflective surface that curves outwards (like the outside bowl of a spoon)
Convex (Diverging)
Curved Mirror Diagrams Rules
1.Parallel to principle axis, reflects though F
2.Through F, reflects parallel to principle axis
Give an example of something that is luminous and something that is non-luminous.
(luminous – sun, flashlight, a lit match; non-luminous – almost everything)
A hot light bulb is an example of what kind of light source.
Incandescence
In what type of reflection do light rays no longer remain remain parallel after striking the surface of the reflective medium?
Diffuse Reflection
What is the point when the rays meet after reflection or refraction?
Focal Point
Describe the image (using SALT) that is produced when the object is located between the focal point and a concave mirror.
Size - Larger
Attitude - Upright
Location - Behind Mirror
Type - Virtual
A light ray is bending away from the normal when it passes from medium A to medium B. In which medium does light travel faster?
Medium B
List the colours of the visible light spectrum from longest to shortest wavelength
ROYGBIV
A firefly is an example of this light source.
If the index of refraction is 1.78, this is the speed of light in that medium
What is 1.685 x 10^8 m/s?
What is the name for the type of reflection of light off a smooth, shiny surface, like a plane mirror?
Specular Reflection
Describe using SALT any image produced in a convex mirror.
Size - smaller
Attitude - Upright
Location - Behind mirror
Type - Virtual
What two conditions must be met for total internal reflection to occur?
1) light must be going from a slower medium to a faster medium
2) the angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle.