Decreased O2 to the brain that could be of clot or narrowed blood vessels which result in tissue death
What is Stroke?
After a TBI, you find several abnormalities while doing your Head, Face, and Neck assessment. What would be an emergent priority finding as you are checking Cranial Nerve 8:
decreased hearing to left ear, otorrhea bilaterally or Battle sign (bruising behind ear and around eyes)
What is Otorrhea?
Leak in CSF system!
What are the common types, routes, vaccines available for Hepatitis, an inflammation of the liver caused by viral infection, alcohol use or autoimmune disease
What is 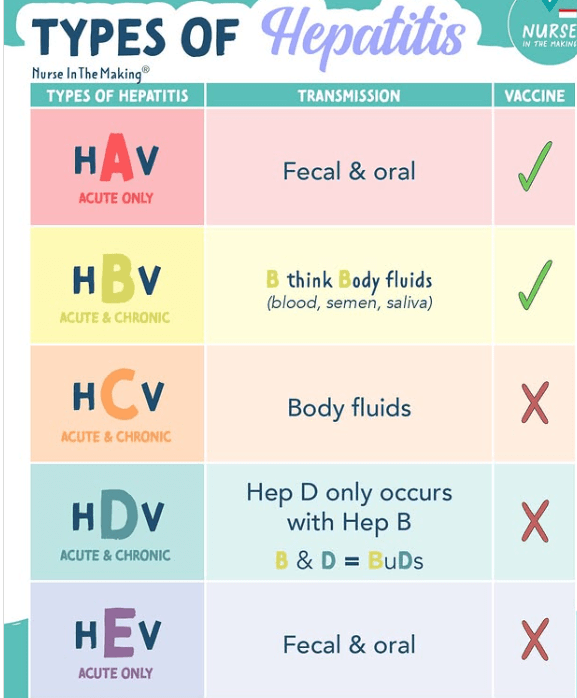
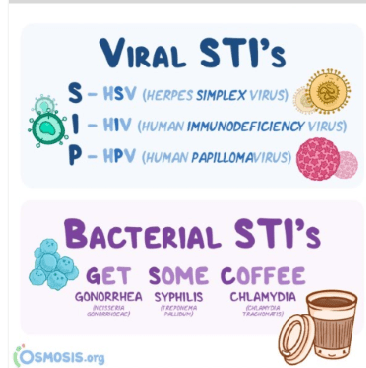
3 viral STIs
3 bacterial STIs
The first is specialized medical care providing physical, emotional, and spiritual support for people living with chronic conditions or serious illness.
The second term is currently used for issues related to death and dying, as well as services provided to address these issues.
What is Palliative vs End-of Life Care?
The number one cause and risk factor for stroke?
What is Hypertension?
Headache, facial flushing, and sweating above the site of injury are signs of this life-threatening complication of SCI
What is AD (autonomic dysreflexia )
Think pressure from bowel, bladder, or bed sheets! Remove pressure is a priority!
Contaminated food, milk, water, shellfish ,Crowded conditions (e.g., day care, nursing home), Persons with subclinical infections, infected food handlers, sexual contact, IV drug users , Poor personal hygiene
What are risks for Hepatitis A?
prostate gland enlargement caused by hyperplasia
of prostate cells.
What is BPH?
Blood cancer that poses the greatest risk for infection due to neutropenia
What is Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia ?
It is cause by bleeding in the brain with an increase ICP?
What is Hemorrhagic stroke?
What are signs and symptoms of Parkinson's
Epigastic pain, severe LUQ pain, turners flank, Cullen's sign and jaundice
What is Pancreatitis?

painful small blisters, influenza-like symptoms, enlarged lymph nodes, transmitted with skin to skin contact
What is HSV ?
Tumors that are well differentiated
What is Benign Neoplasms?
Poorly differentiated are Malignant neoplasms
It is a thrombolytic that needs to be administered within 4.5 hours of the onset of symptoms.
What is Alteplase?
Reminders and memory aids to show which date, month and day of the week, educating caregivers how to keep client safe in their environment and encourage the client to make their medical decisions and advanced directives before cognitive decline.
What is Early Stage dementia?
NPO, , cholecystectomy, low fat diet
What are pre-, intra, and post-op interventions for cholecystitis?
menses before 12 yo, long menstrual history, menses > 55 , and family history of this increases risk
What is Ovarian Cancer?
mutation in the cell’s DNA genetic structure
following exposure to a chemical, radiation, or viral agent. The mutation may also
be inherited
What is the Initiation stage of cancer?
Hemiparesis with arm drift, facial and smile droop, speech impairment, sever headache
What are the signs and symptoms of stroke?
set routines, familiar activities, low-stimuli, and distraction should be used for agitated behavior for this stage and condition
What is Late stage Dementia
Increase ammonia build up causing brain fog
What is Hepatic Encephalopathy?
caused by Treponema pallidum and may be spread through contact with infectious lesions and the sharing of needles among IV drug users. Treatment will not cure previous damage
What is Syphilis?
multistep process in which tumor cells travel to distant sites via lymphatic and hematogenous routes.
What is Metastasis?
Elements of Cushing's Triad from increased ICP
Bonus points- priority interventions for these clients to reduce negative outcomes
Interventions- low stimuli environment, seizure precautions ( padding bed and rails), managing pain, suction available, oxygen
In this disorder, the priority is reducing falls as the client experiences gait disturbances and postural instability.
Anticholinergic drugs like benztropine and dopamine agonists like levodopa aid in reducing extrapyramidal effects and improving neurotransmission.
What is Parkinson's Disease?
Lactulose removes what toxin from the body by inducing diarrhea.
Bonus points- Which organ is not functioning properly
What is Ammonia and The liver
After a TURP, What exercises help with post-surgery voiding and what foods should you avoid post-operatively?
What is Kegel exercises which strengthen the contractions of the pelvic floor muscles?
What are Avoiding drinks containing caffeine (coffee, tea, cola), fizzy drinks, green tea, tomatoes, hot chocolate, alcohol and acidic fruits/fruit juices (such as orange juice).
Stages of Grieving
Denial
Anger
Bargaining
Depression
Acceptance
