The term for a fracture where the bone breaks but doesn't penetrate the skin.
What is a closed/simple fracture?
The three layers of skin from superficial to deep
What are epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue?
The primary purpose of a traction splint in femur fractures.
What is to reduce pain and bleeding by realigning bone fragments?
This type of fracture occurs when a bone is partially bent and partially broken, typically seen in children.
What is a greenstick fracture?
Used to treat life threatening extremity bleeding.
What is a tourniquet?
This type of fracture results in multiple bone fragments at the fracture site.
What is a comminuted fracture?
The amount of blood each femur can bleed out.
What is 1.5 liters?
The recommended initial field treatment for an open fracture with visible bone.
What is cover with sterile dressing, control bleeding, and splint without reducing?
A painful or grotesque injury that can mask a more serious underlying injury.
What is a distracting injury?
Excessive scar tissue; extends beyond boundaries of wound
What is a keloid?
This is the classification system for pediatric joint fractures
What is the Salter-Harris System
This condition occurs when increased pressure within a muscle compartment compromises blood flow and function, often requiring emergency intervention.
What is Compartment Syndrome?
The surgical procedure that must be performed to definitively treat compartment syndrome.
What is fasciotomy?
Partial bone end displacement from position within joint capsule
What is subluxation?
Encloses the muscle compartments.
What is the fascia?
This "P" term means cool to the touch
What is Poikilothermia
This serious wound contamination can occur when soil containing bacterial spores enters deep wounds.
What is tetanus?
In managing severe soft tissue injuries, paramedics may apply this type of dressing to control bleeding and promote clotting.
What is a hemostatic dressing?
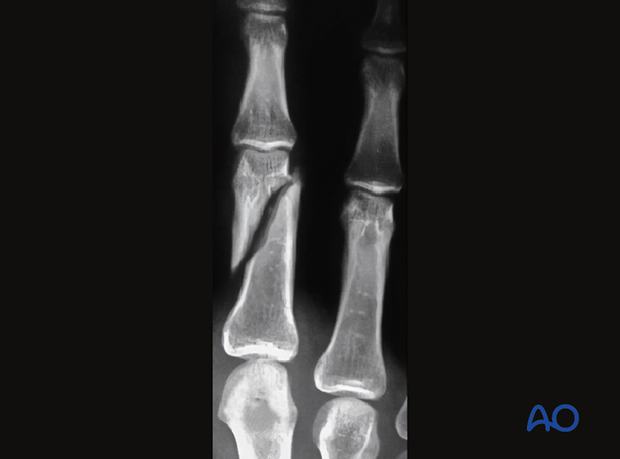
What is an oblique fracture?
Red streaks on the skin that can be indicative of infection.
What is Lymphangitis?
This "6 P's" assessment mnemonic is used to evaluate neurovascular status in extremity injuries.
What are Pain, Pallor, Pulse, Paresthesia, Pressure, and Paralysis?
This injury pattern where skin separates from underlying tissues in degloving injuries.
What is Avulsion?
The specific anatomical landmark used for proper placement of a pelvic binder in cases of suspected pelvic fracture.
What is the greater trochanter/over the trochanters?
Natural condition; bone deterioration with age
What is osteopenia?
Skeletal muscle destruction that releases toxins in a crush injury.
What is Rhabdomyolysis?