Salt is an example of this when added to water.
solute
Name the solutes and solvents that make up vinegar.
Acetic Acid 5%
Water 95%
Solute: Acetic Acid
Solvent: Water
List two variables that can affect a solute's solubility
temperature and pressure
Which property describes the water's simultaneous negative and positive charge?
a) cohesive
b) adhesive
c) polar
d) ionic
c) polar
Two or more elements chemically combined is called a _______
compound
A solution that could hold more solute is called
unsaturated
Name the solutes and solvents that make up the air (solution)
21% of Oxygen
0.9% Argon
0.03% Carbon dioxide
78% of Nitrogen
Oxygen, argon and carbon dioxide (solutes) dissolve in Nitrogen (solvent)
Types of Solutions
a. Points that collectively make up the
solubility curve (points ON the curve)
represent _____________ solutions.
saturated
1) Which property describes the water molecule's ability to stick to another water molecule?
a) cohesive
b) adhesive
c) polar
d) surface tension
2) Which property describes the water molecule's ability to stick to other materials?
a) cohesive
b) adhesive
c) polar
d) surface tension
1) cohesive
2) adhesive
A seedless watermelon is an example of this type of mixture
homogenous mixture
The variable that must be carefully controlled in order for more solute to be added to a solution in order to create a supersaturated solution is ____
temperature
Brass is a solid solution of metals, principally Copper and Zinc.

In brass, the solute is zinc and copper is the solvent.
b. Points that are BELOW the curve
represent__________________
solutions.
unsaturated
1) Which word describes the water's high cohesive properties that allow this water strider to stride?
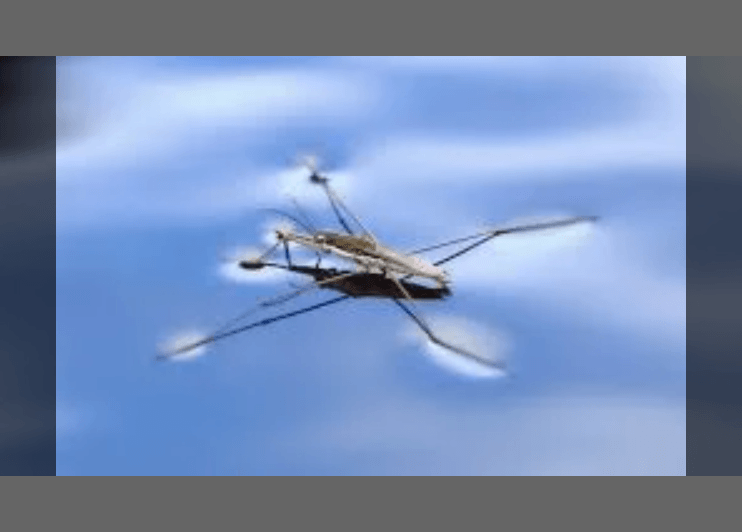

a) Adhesion
b) Surface Tension
c) Capillary Action
d) High Heat of Vaporization
2) Which properties of water help a plant get water to the tops of it's leaves?
a) Capillary action
b) Surface tension
c) High heat of vaporization
d) High specific heat
1) b) surface tension
2) a) capillary action
A salad would be an example
heterogenous mixture
Where as a solutes solubility _____ in a liquid when the temperature rises, a gas's solubility ______ in a liquid when the temperature rises.
increases decreases
Typically there is less than 0.40%-4% carbon in steel. The rest is iron.
.jpg)
Steel is another example of a solid–solid solution. It is an iron solvent with a carbon solute.
c. Points ABOVE the solubility curve
represent ___________________
solutions, and the difference between the point above the curve and on the curve represents the amount of solute which will precipitate out.
supersaturated
It takes a lot of energy to heat and cool water, this is important because...
a) Water helps keep our climate from fluctuating violently
b) It takes me forever to boil water for pasta
c) Surface Tension
d) Polar
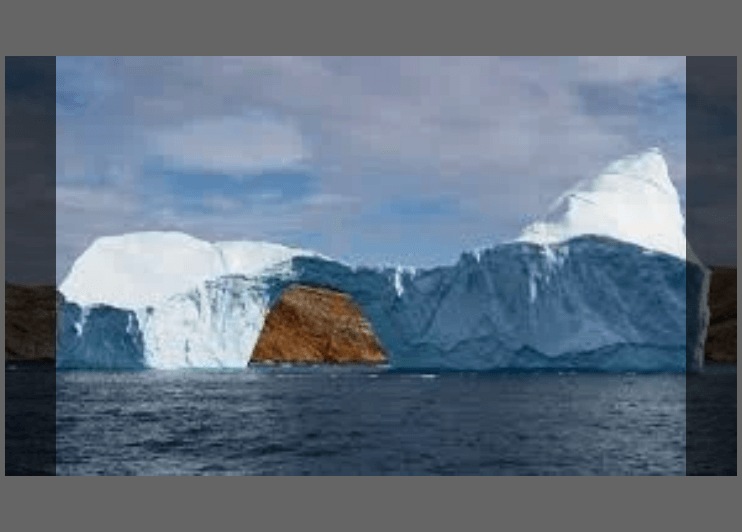

a) Water helps keep our climate from fluctuating violently
Pure substances can not be separated _.
a) physically
b) chemically
a) physically
A solute's __________ is referred to the amount of solute per unit solvent required to form a saturated solution
solubility
Air conditioners, brewing coffee, your kidneys are examples of ...
Filtration

a) 130g/100g water
b) 40g/100g water
c) 70g/100g water
d) NaCl
When water is a solid (ice) it:
a) sinks
b) floats
c) suspends in the middle
why?
b) It floats because ice is less dense than liquid water.
Aluminum is _______________
an element
What is the percent by mass of potassium iodide, KI, in 2.24 g of KI dissolved in 10.0 g of water.
18.3%
Mass%= (2.24g/12.24g)x100 = 18.3%
Asphalt comes from petroleum. The petroleum undergoes _______________________ whereby the petroleum is liquified and the parts are separated using various boiling points.
Fractional Distillation
b. At what temperature is the solubility of potassium nitrate (KNO3) equal to 40 g/100 g of water? 
25C?
It takes a lot of energy to heat up water, this is called:
a) High heat capacity
b) Low heat capacity
c) Polarity
d) Surface Tension

a) high heat capacity
Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) is a
compound
How many grams of KBr are contained in 125 g of a 6.25% KBr solution?
7.81 g KBr
%mass = (x/125g) x100 = 6.25%
100x= 6.25*125
100x = 781.25
x = 781.25/100
x = 7.81
What is the maximum amount of sodium chloride (NaCl) that can be dissolved in 150g of water at 80ºC ? 
At 80C, the solubility of NaCl is 40g/100g water
therefore in 150g of water, the solubility of NaCl is
60g/150g water?
Sweet tea is ________________
a solution