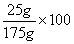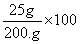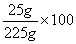State the solubility of limestone (CaCO3) in water.
Insoluble
Based on Table G, describe what happens to the solubility of SO2(g) as the temperature increases from 10.oC to 30.oC at standard pressure.
The solubility of SO2 decreases
The solubility of KCl(s) in water depends on the
- pressure on the solution
- rate of stirring
- size of the KCl sample
- temperature of the water
(D.) temperature of the water
Which unit can be used to express the concentration of a PbCl2(aq) solution?
ppm or Molar
Compared to the freezing point and boiling point of water at 1.0 atm, a 0.5 M aqueous solution of NaCl at 1.0 atm has
a lower freezing point and a lower boiling point
a lower freezing point and a higher boiling point
a higher freezing point and a lower boiling point
a higher freezing point and a higher boiling point
(B) a lower freezing point and a higher boiling point
Explain, in terms of molecular polarity, why oxygen gas has low solubility in water. Your response must include both oxygen and water.
Oxygen gas is nonpolar and water is polar
According to Table F, which ions combine with chloride ions to form an insoluble compound?
- Fe2+ ions
- Ca2+ ions
- Li+ ions
- Ag+ ions
(D.) Ag+ ions
Based on Table G, determine the mass of KClO3(s) that must dissolve to make a saturated solution in 100. g of H2O at 50.0oC.
Approximately 22g
Describe what happens to the solubility of SO2(g) when the pressure is increased at constant temperature.
The solubility increases
What is the molarity of 2.0 liters of an aqueous solution that contains 0.50 mole of potassium iodide, KI?
0.25M
Compared to the freezing point of 1.0 M KCl(aq) at standard pressure, the freezing point of 1.0 M CaCl2(aq) at standard pressure is
- lower
- higher
- the same
(A.) lower
A 2.0-liter aqueous solution contains a total of 3.0 moles of dissolved NH4Cl at 25°C and standard pressure. Identify the two ions present in the solute.
NH4+1 and Cl-1
Which ion combines with Ba2+ to form a compound that is most soluble in water?
- S2−
- OH−
- CO32−
- SO42−
(B.) OH−
Determine the mass of NH4Cl that must be dissolved in 200. grams of H2O to produce a saturated solution at 70.°C.
Approximately 62g x 2= 124g
Describe the effect on the solubility of KNO3(s) in this solution when the pressure on the solution increases.
No Effect
(Pressure only affects gases)
A 150.-gram sample of this tap water contains 0.00075 gram of CaCO3(aq). Determine the concentration in ppm.
5 ppm
Four flasks each contain 100 milliliters of aqueous solutions of equal concentrations at 25°C and 1 atm.
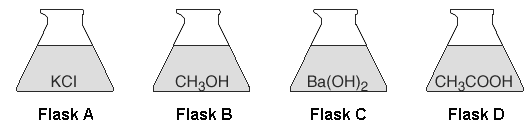
Which flask has the solution with the lowest freezing point?
Flask C (It produces the most ions)
A solution contains 25 grams of KNO3 dissolved in 200. grams of H2O. Which numerical setup can be used to calculate the percent by mass of KNO3 in this solution?
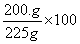
Choice D
Pb(NO3)2 + 2NaI → PbI2 + 2NaNO3
Identify the compound produced that is insoluble in water.
PbI2
Based on Table G, which sample, when added to 100. grams of water and thoroughly stirred, produces a heterogeneous mixture at 20.°C?
20. g of KCl C. 20. g of KI
80. g of KCl D. 80. g of KI
(B) 80. g of KCl
Explain, in terms of the molecular polarity, why hexane is nearly insoluble in water.
Hexane is nonpolar and water is polar. Only "like dissolves like".
What is the concentration of an aqueous solution that contains 1.5 moles of NaCl in 500. milliliters of this solution?
3.0 M
Which aqueous solution has the highest boiling point at standard pressure?
- 1.0 M KCl(aq)
- 1.0 M CaCl2(aq)
- 2.0 M KCl(aq)
- 2.0 M CaCl2(aq)
(D.) 2.0 M CaCl2(aq)
State, in terms of the concentration of ions, why the 6.0 M HCl(aq) is a better conductor of electricity than the 0.1 M HCl(aq).
The 6.0 M HCl(aq) has a greater concentration of ions
Which compound is soluble in water?
- PbS
- BaS
- Na2S
- Fe2S3
c) Na2S
A scientist makes a solution that contains 44.0 grams of hydrogen chloride gas, HCl(g), in 200. grams of water, H2O(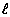 ), at 20.°C. Identify, in terms of saturation, the type of solution made by the scientist.
), at 20.°C. Identify, in terms of saturation, the type of solution made by the scientist.
Unsaturated
Explain, in terms of molecular polarity, why the solubility of methanol in water is greater than the solubility of methane in water.
Methanol is polar. Methane is nonpolar.
A 2400.-gram sample of an aqueous solution contains 0.012 gram of NH3. What is the concentration of NH3 in the solution, expressed as parts per million?
5.0 ppm
State, in terms of freezing point, why sodium chloride is part of the mixture put on icy roads.
Sodium Chloride lowers the freezing point
In an investigation, aqueous solutions are prepared by completely dissolving a different amount of NaCl(s) in each of four beakers containing 100.00 grams of H2O(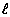 ) at room temperature. Identify the solute and the solvent used in this investigation.
) at room temperature. Identify the solute and the solvent used in this investigation.
Solute- NaCl
Solvent- Water