State the solubility of limestone (CaCO3) in water.
Insoluble
Based on Table G, describe what happens to the solubility of SO2(g) as the temperature increases from 10.oC to 30.oC at standard pressure.
The solubility of SO2 decreases
Which unit can be used to express the concentration of a PbCl2(aq) solution?
mol/L or Molar (M)
What is a Bronsted-Lowery Acid?
Donates a H+
Write the general equation for a neutralization reaction.
Acid + Base --> Salt + water
According to Table F, which ions combine with chloride ions to form an insoluble compound?
- Fe2+ ions
- Ca2+ ions
- Li+ ions
- Ag+ ions
(D.) Ag+ ions
Based on Table G, determine the mass of KClO3(s) that must dissolve to make a saturated solution in 100. g of H2O at 50.0oC.
Approximately 22g
What is the molarity of 2.0 liters of an aqueous solution that contains 0.50 mole of potassium iodide, KI?
0.25M
______ turn red litmus paper to Blue.
Bases
A 9.0-milliliter sample of HCl solution is exactly neutralized by 6.0 milliliters of a 3.0M NaOH solution. What is the concentration of the HCl solution?
2.0M
Which ion combines with Ba2+ to form a compound that is most soluble in water?
- S2−
- OH−
- CO32−
- SO42−
(B.) OH−
An unsaturated aqueous solution of NH3 is at 90°C in
100. grams of water. According to Reference Table G,
how many grams of NH3 could this unsaturated
solution contain?
Anything 104g or less
How many total moles of KNO3 must be dissolved in
water to make 3.0 liters of a 4.0 M solution?
12 Moles
The pH of a solution is 7. When acid is added to the
solution, the hydronium ion concentration becomes
10 times greater. What is the pH of the new
solution?
6 pH
A student recorded the following buret readings during a titration of a base with an acid. What is the molarity of KOH?
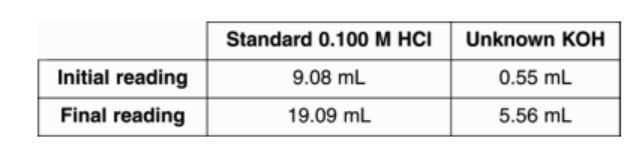
0.200M
Which compound is soluble in water?
- PbS
- BaS
- Na2S
- Fe2S3
3) Na2S
Based on Table G, which sample, when added to 100. grams of water and thoroughly stirred, produces a heterogeneous mixture at 20.°C?
20. g of KCl C. 20. g of KI
80. g of KCl D. 80. g of KI
(B) 80. g of KCl
What is the concentration of an aqueous solution that contains 1.5 moles of NaCl in 500. milliliters of this solution?
3.0 M
Any base
CaOH, NaOH, etc.
What is the molarity of an 84mL solution of HCl that is needed to completely neutralize 0.20L of a 3.2-molar solution of NaOH?
7.6M
Pb(NO3)2 + 2NaI → PbI2 + 2NaNO3
Identify the compound produced that is insoluble in water.
PbI2
Explain, in terms of molecular polarity, why oxygen gas has low solubility in water. Your response must include both oxygen and water.
Oxygen gas is nonpolar and water is polar
What is the molarity of 2.0 liters of an aqueous
solution that contains 82 grams of lithium fluoride,
LiF?
1.6M
What are the two acids in the reaction
H2O + HI --> H3O+ + I-
HI and H3O+
What is equal when a titration reaches its equivalence point?
Moles of Acid is equal to the Moles of the Base.