The formula for calculating molarity
M = n/V
a homogenous mixture made up of 2 or more components
solution
Calculate the pH of a HCl solution with [H+] = 0.002M.
pH = -log(0.002)=2.70
a substance that changes color after coming in contact with an acid or base.
indicator
M = n/V = (4.5mol)/(6.0L)
=0.75M
solubility
What is the [OH-] of a solution with pOH = 12.7?
[OH^-]=10^(-12.7)=2.0*10^(-13)M
an acid donates one of these ions when dissolved in solution
H+
calculate the number of moles dissolved in 2.1 L of 1.3 M solution.
n = M x V = (1.3 M)(2.1 L) = 2.73 moles
this type of intermolecular force is the reason why water is known as the universal solvent
hydrogen bonding
pH = -log(1.3*10^-9)=8.89
basic
a solution that contains more solute than predicted at a given temperature/pressure is said to be
supersaturated
A student wishes to dilute 100 mL of 2.0 M solution. The desired concentration of the new solution is 0.5 M. What is the volume of the new solution?
M1V1=M2V2;
(100mL*2.0M)/(0.5M)=400mL
The solubility of a gas _______ as temperature increases.
decreases
pOH = 14 - 4 = 10
[OH-] = 10-pOH = 1 x 10-10 M
name 2 examples of colligative properties
freezing point and boiling point
A 3.8 M solution of CuCl2 is diluted to 2 times its original volume. What is the molarity of the diluted solution?
(3.8)/2=1.9M

At 20 degrees C 200mL saturated solution of sugar contains this many grams of solute.
400 grams
the graph shows 200 g dissolved in 100 mL at 20 degrees C. Multiply this by 2 to get 400 g.
Calculate the pH of a solution with [OH-] = 2.3 x 10-5 M.
pOH = -log(2.3*10^-5)=4.64
pH = 14-4.64=9.36
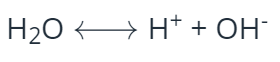
Write a chemical equation for the autoionization of water.