This refers to the capacity at which a solute can dissolve in a solvent and form a solution.
What is Solubility?
What is Aggravating a Solution & Temperature?
Nanoparticles between 1 - 1,000 nm
What is Colloids?
This is what Molarity measures of a solution.
What is Concentration of a Solution?
This is the compound name for Fe2O
What is Iron(II) Oxide?
This is a quantitative measure of how much solute is dissolved in a solvent.
What is Concentration?
This refers to the electrically charged, dissolved ions that can carry electricity through a solution.
What is Electrolytes?
Particles less than 1 nm
What is Solution?
Convert 16 grams of sulfur dioxide into moles. (Round you answer to the first two units after the decimal).
What is 0.25 moles?
N2 is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere. N2 is this type of chemical bond (include polarity).
What is Non-Polar Covalent bond?
What electrolyte is lost most from sweat during strenuous exercise?
What is Na+?
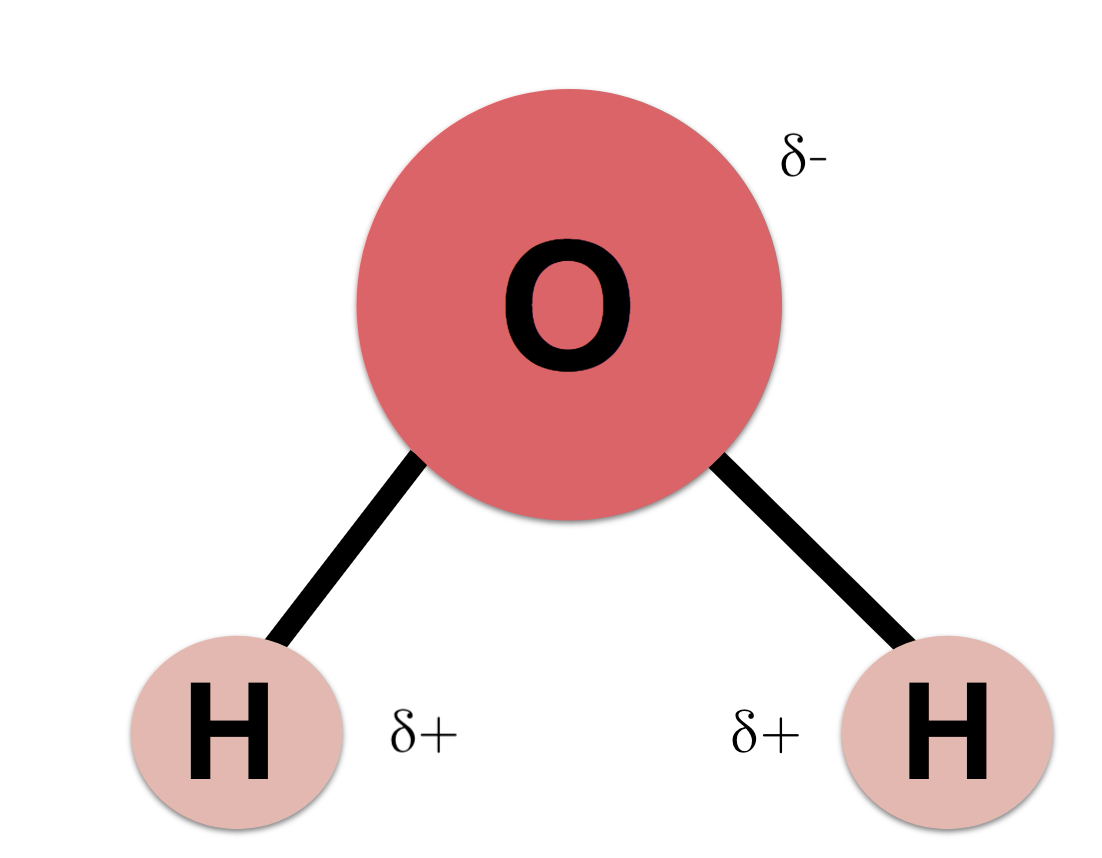
This is the chemical property of water that renders it the universal solvent. It is a key component to the dissolving process in solutions.
What is Polarity?
The largest heterogenous mixture of the two, and largest particle size of the three mentioned, this is the particle size of suspensions.
What is greater than 1,000 nm?
You have an aqueous solution in a large container in which you have dissolved 82 moles of NaF in 42 L of water. This is the molarity of the solution. (round your answer to two units after the decimal).
What is 1.95 M
These are the five types of chemical reactions.
What is:
- Synthesis
- Decomposition
- Single-Displacement
- Double-Displacement
- Combustion
This is a solution in which the metal of highest concentration is the solvent and the metal(s) of lowest concentration are the solutes.
What is Alloy?
The shell of water molecules that surrounds an ion and pulls it away from its original ionic compound is called this.

What is Hydration Shell?
This mixture's particles are affected by gravitation force due to their size and can be settled out at the bottom of a container.
What is Suspensions?
You have a solution of HCl that is 6 M. If you have 19 L of said solution, this is how many moles of HCl you have.
What is 114 moles HCl
This is a chemical reaction that involves the absorbing of heat, such as baking bread or photosynthesis.
What is Endothermic Chemical Reaction?
This is the way you would describe a solution when it possess more than its maximum dissolving capacity, having a number of solutes that are recrystallizing as solids.
What is Supersaturated?

This is when recrystallization of a solute and dissolution of a solute occur at equal rates. Therefore the ratio of the two is constant.
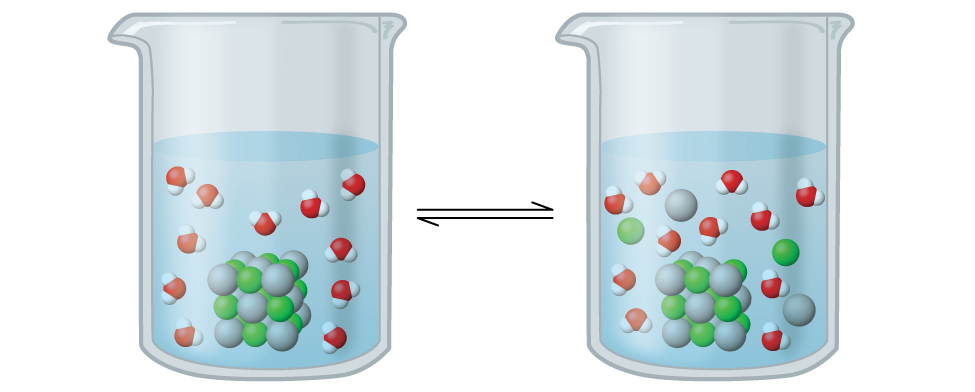
What is Solution Equilibrium?
What is Colloids?
With a solution of coffee, caffeine (C8H10N4O2) is a solute. Let's say you are making coffee for a large party so you put a bunch in a giant dispenser. You mix together enough coffee that you have 4.5 grams (4,500 mg) of caffeine. The molarity of the solution when considering caffeine is 0.4 M. This is the volume of the solution.
What is 11.25 L
This is the electron carrying capacity of the four inner most electron shells.
What is
1st - 2 electrons
2nd - 8 electrons
3rd - 18 electrons
4th - 32 electrons
