Sound reaches our ears as:
A. waves B. electric impulses
C. particles D. radiation
A. waves
What does light do when it strikes a window?
A. reflection B. refraction C. absorption D. transmission
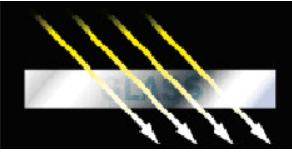
D
No matter how different they are, all sounds are created by __.
A. collisions of solid matter B. electromagnetism
C. air moving over solid mater D. vibrations
D
What is light doing in this mountain lake?
A. reflection B. refraction C. absorption D. transmission

A
A bird flies at a constant speed of 2 m/s for 15 seconds. What is the distance the bird flew?
Distance = speed X time time = Distance / speed
speed = Distance / time
30 meters
As wavelength increases, what decreases?
A. wave speed B. frequency
C. amplitude D. wave speed
frequency

Why does a pencil in a glass of water seem to be bent?
[One click for the one word answer. Three clicks for the long sentence answer.]refraction
The light is first traveling through the air, and then it passes through the water. Since the water is more dense than the air, the light rays bend in the water. This makes the pencil seem to bend as well. The process of light bending is called refraction.
What is B?

a compression
What materials do not transmit any light because they absorb light, or reflect it, or both?
A. solid materials B. opaque materials
C. translucent material D. transparent
B
Which characteristic distinguishes an electromagnet from a bar magnet?
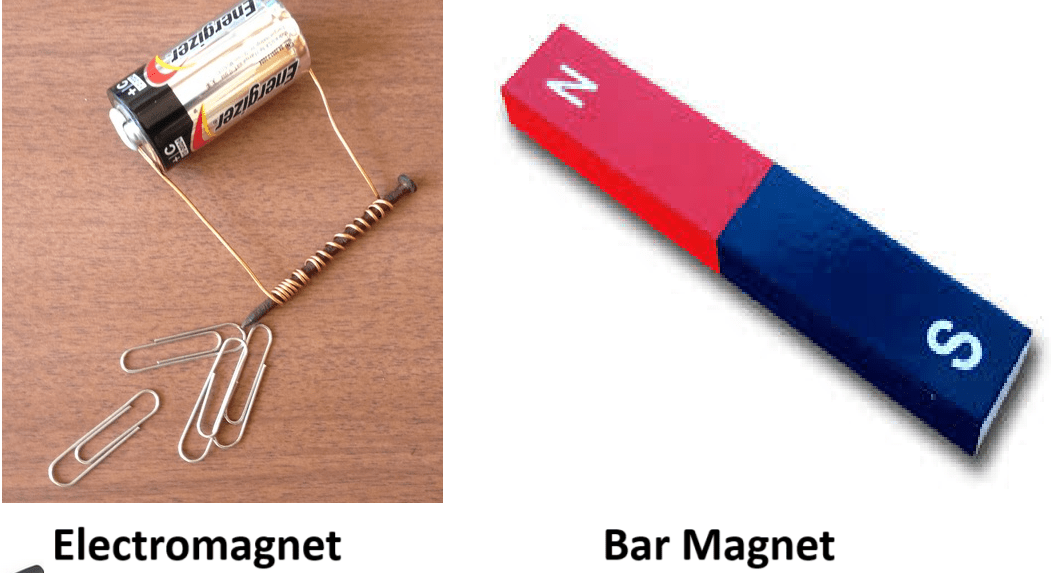
B Only a bar magnet attracts iron filings. C Only an electromagnet requires a current. D Only an electromagnet has opposite poles.
C
Which of these best explains why a student hears the noises from the hall but cannot see into the classroom?
B. Sound waves are transmitted through the wall, and visible light waves are reflected by the wall.
C. Sound waves are reflected by the wall, and visible light waves are refracted by the wall.
D. Sound waves are reflected by the wall, and visible light waves are absorbed by the wall.
B
Can sound travel through outer space?
A. No, sound is a mechanical wave and must travel through a medium.
B. Yes, it can travel through transparent media as well as a vacuum because sound is electromagnetic.
C. Yes, sound can only travel through a vacuum because sound is a transverse wave.
D. No, sound travels better through matter, but can move through outer space at slower speeds.
A
What is C?

a rarefaction
What is light doing when it strikes an black material?

absorption
What is the net force in this picture?
[Give units and direction.]
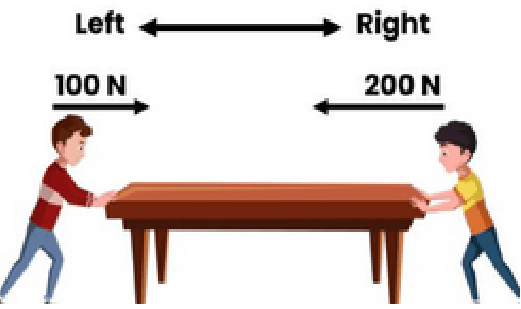
100 N left [Subtract and go the direction of the largest.]
Cicadas produce a buzzing sound that has a wavelength in air of 2.69 m. If the speed of
sound in air is 346 m/s, what is the frequency of the sound produced by a cicada?
frequency = wave speed / wavelength wave speed = frequency X wavelength wavelength = wave speed / frequency
2.69 / 346 = .0078 Hz
!DAILY DOUBLE!
What will Observer A hear?
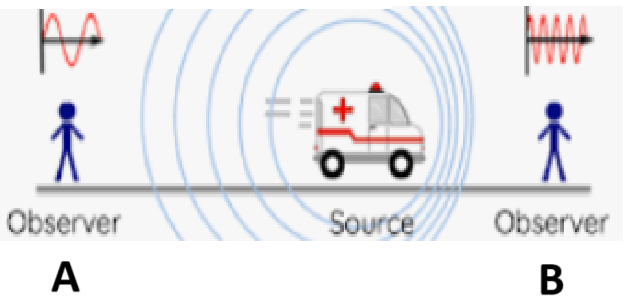
a lower pitch sound
Name the measurements and parts of the longitudinal wave.
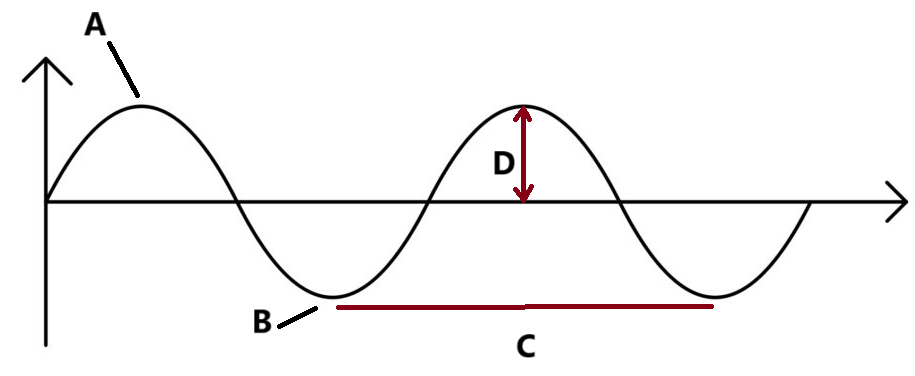
A. crest
B. trough
C. wavelength
D. amplitude
What do we call sounds that are too high for us to hear?
ultrasound
Which of the following is/are showing magnetic repulsion?
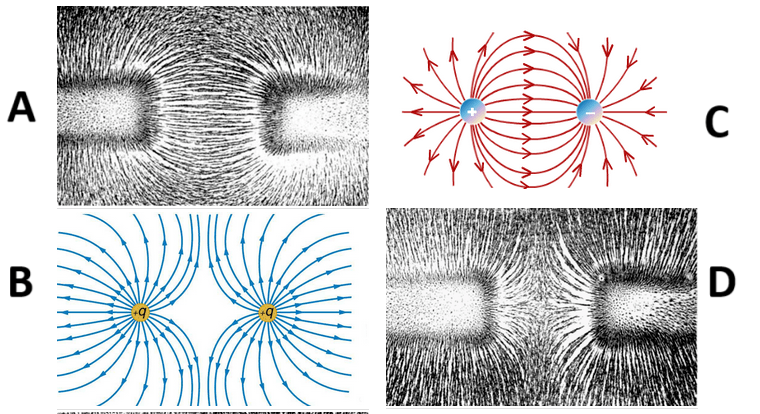
B and D
The diagram shows how light in front of a sound source is compressed and so has a higher pitch than light behind the source. What is this principle called? 
the Doppler effect
What is light doing when it strikes a prism?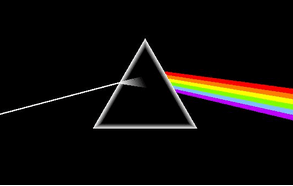
refraction
The diagram below shows how a convex lens focuses light so that a farsighted person can see clearly.
What is light doing in this situation?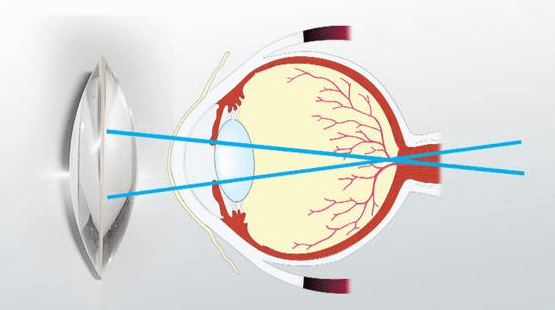
refraction
A single beam of light is shown into a container of milky water. Why does the beam bend downwards?
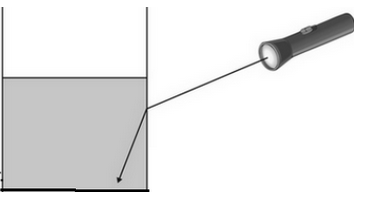
The light is moving into a different medium [not a denser medium, just a different one].
A college student designed and constructed an electric generator in his physics class to investigate cause and effect connections about magnetism and electricity.
When he first tested this generator, it only produced 50 amps. However, his goal was for this generator to induce 100 amps.
What is one action that he could do to make this happen?
Any of these:
move the magnet faster
use more or stronger magnets
use more coils of wire