Name label A.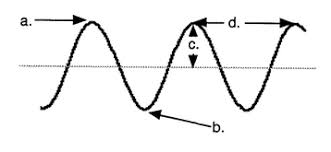
Crest or peak
What term is defined here:
Determined by amplitude.
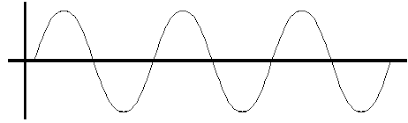 What is the frequency for this wave?
What is the frequency for this wave?
3 Hz
This demonstration showed us that sound vibrates.
The drum and lasers.
Name number 3.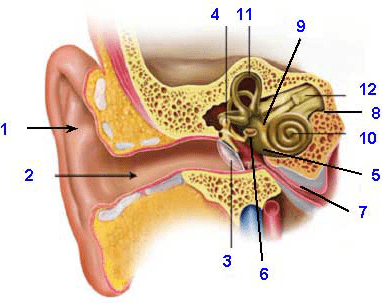
Eardrum
Name label B.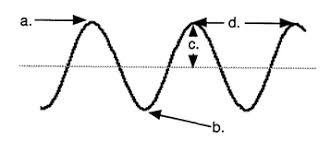
Trough
What term is defined here:
The unit used to measure frequency
Hertz (Hz)
What is the frequency of this wave?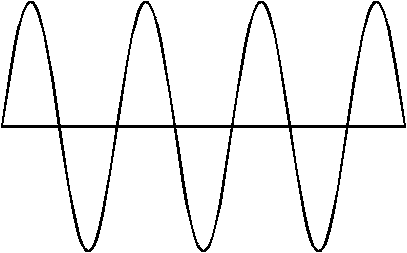
3.5 Hz
The lab with the marbles and a marker showed ...
That amplitude transfers more energy than frequency
Name number 10.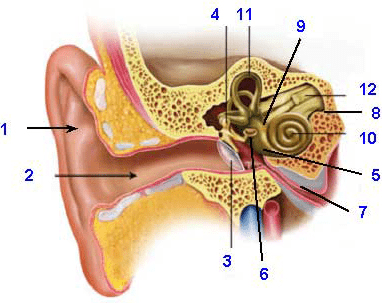
Cochlea
Did you say it right? (coke-lee-uh)
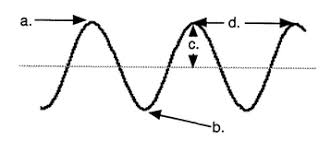 Name label D.
Name label D.
Wavelength
What is the term that matches this definition:
The number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
Frequency
What is the amplitude?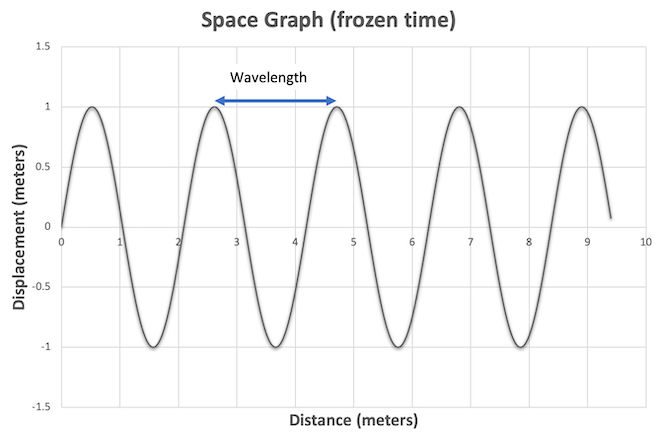
1 meter
The demonstration with the bell vacuum jar showed us that...
...sound needs matter to travel through.
What is the correct sequence of events:
a. sound enters ear canal, vibrates eardrum, bones move back and forth, sending vibrations to the cochlea, then to the basilar membrane, then to signals in our brain
b. sound enters ear canal, bones move back and forth, then vibrates the basilar membrane, then the eardrum, then sends signals to our brain
c. sound enters ear canal, vibrates the eardrum, vibrates the basilar membrane, then moves the bones back and forth, which then sends signals to our brain
A. sound enters ear canal, vibrates eardrum, bones move back and forth, sending vibrations to the cochlea, then to the basilar membrane, then to signals in our brain
 The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles are close together.
The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles are close together.
Compression
What is the term that matches the definition:
A wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of wave motion (sound)
Longitudinal wave
What is the wavelength? (in numbers)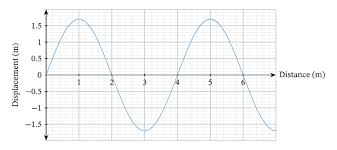
4 meters
The slinky demonstration showed us that...
...sound waves do not transfer matter, but transfers energy through matter.
Can we see the basilar membrane in this diagram? If so, what number is it? If we can't see it, why not?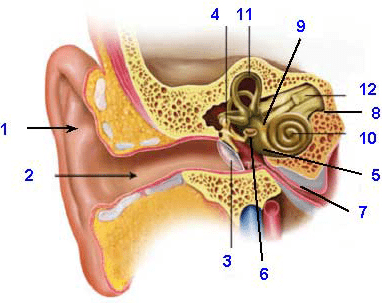
We cannot see it in the diagram because it is a layer inside the cochlea.
What is the name of the part of the wave depicted by the spread out section:
Rarefaction
What is the definition that matches the term:
Rarefaction
The part in a longitudinal wave where the particles are spread apart
DAILY DOUBLE!!!
At 680F, a sound wave will travel through the air at 343m/s (velocity). This specific wave has a frequency of 100Hz. Calculate the wavelength using the formula shown: 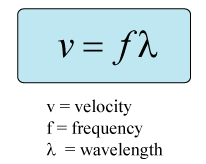
3.43 meters
The speaker and laser pointer showed us that ...
... every wave has a different pattern depending on pitch and that you can in fact see sound.
How does the basilar membrane work in order for humans to hear?
The basilar membrane vibrates in different places so that we are able to hear different pitches.