Define: Sound
Vibrations that travel through a medium to someone's ear
Which wave has a higher frequency?
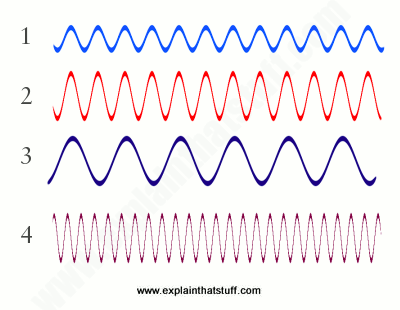
Wave 4
In sound waves, the amplitude of the wave determines this characteristic of the sound.
What is loudness (or volume)
Name the 3 mediums that sound can travel through.
Solid, liquid, gas
What is #4?
Crest
Define: Frequency
Number of waves that pass a point in a second
What is the word we use to describe how high or low a sound is?
Pitch
True or False: A wave with larger amplitude carries more energy than a wave with a smaller amplitude
What is True
Which affects energy the most: frequency or amplitude?
Amplitude! Frequency also affects energy, but not as much as amplitude does.
What is #3?
Amplitude
Define: Amplitude
Distance between the middle (equilibrium) and crest or trough of a wave
What is the unit used to measure the frequency of a wave
Hz (Hertz)
A sound wave with a very small amplitude would be described as sounding as this
What is quiet
You want to send a sound wave message as quickly as possible. Should you send it through air, water, or brick?
Brick. Sound waves travel fastest through solids.
What is #2?
Trough
What is the name of the small electronic device that provides a sense of sound to people? One part goes on the outside of the ear, one part goes on the inside.
Cochlear Implant
As frequency increases, what happens to the wavelength?
The wavelength decrease (Inverse Relationship)
Which wave is louder?
Wave 2
Sound #1 is low frequency, high amplitude.
Sound #2 is high frequency, low amplitude.
Which sound wave has more energy?
Sound #1 because amplitude causes the energy to increase MORE.
What is #1?
Wavelength
Define: Rarefaction
A part of a mechanical sound wave where the particles are furthest apart.
As frequency decreases, what happens to the amplitude?
Nothing. Frequency and Amplitude are independent of each other. There is no connection!
How can you find the amplitude of a wave?
Measure the height from the middle of the wave to the top (crest) or the bottom (trough)
Bonus Points: The difference in pressure between rarefaction and compression points
Why do sound waves travel fastest through solid? Use the words 'particles', 'speed', 'bonds' and 'density'.
Bonus 100 points if you can think of an accurate analogy for this phenomenon.
In solids, the particles have stronger bonds and are more dense. Sound waves travel faster because the particles transfer vibrations more efficiently than in a gas, where the particles are spread a part.
Analogy: In a relay race if the runners are closer together, they can hand off the baton quickly.
If dominoes are stacked closer together, they fall quickly.
What do you call the part of this wave where particles are very close together?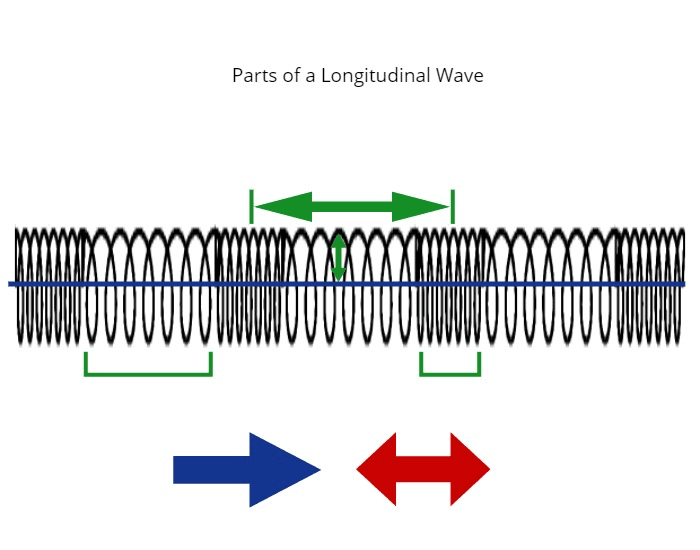
Compression