What is frequency?
The number of complete waves that pass a point in a given time.
How do sound waves transfer energy?
By vibrating particles in the medium they travel through.
What phase of matter does sound travel faster in?
Travels faster in solids due to closely packed particles.
Decreasing "b" will cause what to happen to the sound?
?
The pitch (and frequency) will increase. It would sound like a higher note.
What is the formula for calculating the frequency of a wave?
f = 1/(time it takes to complete one cycle)
or
Frequency = Number of vibrations ÷ Time
What is amplitude?
The height of a wave from the rest position to its crest.
Role of amplitude in energy transfer?
Higher amplitude means more energy transfer.
Compare the speed of sound in liquids and gases.
Sound travels faster in liquids than gases due to particle density.
How does the amplitude of a sound wave relate to the loudness of the sound?
The amplitude of a sound wave is related to the loudness of the sound; larger amplitudes correspond to louder sounds.
What is the amplitude of this wave?

1000mm
Define wavelength
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave.
Frequency's effect on energy transfer?
Higher frequency can increase energy transfer, but much LESS than amplitude.
Describe how particle collisions are involved in sound?
Sound travels through particle collisions in the medium, creating areas of high-density particles and areas of low-density particles.
Explain how sound travels through different mediums (like air, water, and solids) and how this affects sound quality.
Sound travels through different mediums at different speeds; it travels fastest in solids, slower in liquids, and slowest in gases. This affects sound quality, as some materials can absorb or reflect sound differently.
You also lose energy as it transfers between mediums which is why sounds will sound muffled when you hear it through a wall.
Explain the differences between analog and digital signals in transmitting sound information.
Analog signals transmit sound information as continuous waves, while digital signals represent sound as discrete values or samples, allowing for clearer sound quality and easier manipulation. But while digital signals are more clear they actually have less information and are an approximation of the analog wave.
Relationship between frequency and pitch?
Higher frequency results in a higher pitch.
What will have more energy, a wave where you double the frequency or a wave where you double the amplitude?
Higher amplitude.
As frequency doubles the energy transferred increases 2x
As amplitude doubles the energy transferred increases 4x
Describe the properties of a medium that have an effect on sound speed?
The denser the medium, the faster the sound travels.
What happens to the sound waves when more force is applied to an object?
When more force is applied to an object, it causes bigger vibrations, which results in louder sounds.
How does the length of an object affect its vibration frequency?
The length of an object affects its vibration frequency; shorter objects vibrate at higher frequencies and produce higher pitches, while longer objects vibrate at lower frequencies and produce lower pitches.
If you change amplitude, what does that do to the frequency?
Nothing! Frequency and amplitude are not related at all!
Example of energy transfer in sound waves?
Vibrations from a speaker transferring energy to air particles. These particles can make other things vibrate, eardrums, windows, etc.
Why is the expression, "in space no one can hear you scream", accurate?
Sound cannot travel in a vacuum as there are no particles to transmit it.
Sound needs a medium to travel in/on or through. The energy needs to be physically passed to something else to make it vibrate for sound to move (propagate).
Describe how the cochlea and hair cells in the ear detect sound and send signals to the brain.
The cochlea is a spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear that contains hair cells. These hair cells detect sound vibrations and convert them into electrical signals that are sent to the brain.
Which sound waves is the softest? How can you tell?
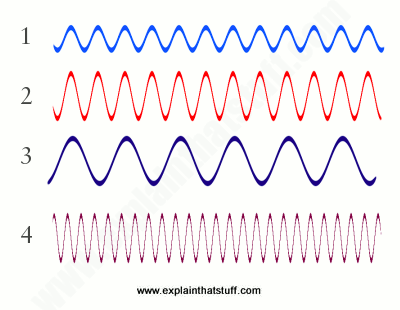
#1 has the smallest amplitude of the options.
Smaller amplitudes correspond to softer sounds.
