This statistical measure tests whether cases are more clustered or dispersed in space than expected by chance.
What is Moran’s I (spatial autocorrelation)?
This one-dimensional ecological study design focuses leverages multiple time periods across 1 spatial unit.
What is ecological time series studies?
Both nesting and spatial autocorrelation violate this fundamental statistical assumption required for standard regression models.
What is unit independence?
Developed by this psychologist, this theoretical model posits ecological systems theory of human
development, defined as “lasting change in the
way in which a person perceives and deals
with his environment.” It describes a sequence of nested ecological structures.
What is the Bronfenbrenner ecological model?
A modeling approach that accounts for both space and time to better predict disease spread is called this.
What is a spatiotemporal model?
This concept involves data organized at multiple hierarchical levels, such as individuals nested within neighborhoods.
What is nesting (or hierarchical structure)?
This phenomenon occurs when an event, intervention, or condition in one location is influenced by the presence of these exposure in nearby locations.
What is a spillover effect?
This first law is the foundation of the fundamental concepts of spatial dependence and spatial autocorrelation.
What is Tobler's First Law of Geography, which states: "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things."
This concept refers to the distortion of statistical relationships when data is aggregated over different spatial scales.
What is the Modifiable Areal Unit Problem (MAUP)?
A quasi-experimental design often used to evaluate the effect of interventions over time while controlling for trends in untreated areas.
What is a difference-in-differences design?
In spatial epidemiology, this method estimates disease risk for unsampled locations using observed data points.
What is spatial interpolation (e.g., kriging)?
This key assumption of DiD states that outcome trends in treatment and control groups would have followed the same trajectory in the absence of treatment.
What is the parallel trends assumption?
The topological relationship of adjacency occurs when two polygons share a boundary segment
What is Adjacency-Based Measure? (Will also accept Rook's Contiguity)
If we know the point or polygon of residence for
individuals, there 3 main approaches to constructing
residence-based measures (Sacks, 2019). Name at least one approach.
What is:
– Container-based (e.g. simple aggregations within polygons)
– Distance-based (e.g. average distance)
– Spatial access-based (e.g. weighted distance)
Aggregating within polygons misses variation within
polygons leads to loss of variation and smoothes the data, which inflating standard errors and attenuates point estimates.
What is Aggregation Bias?
This term describes abrupt policy or environmental changes that allow researchers to study their effects even though they were not randomly assigned.
What is a natural experiment?
This is an image of what type of clustering analysis? Define it. 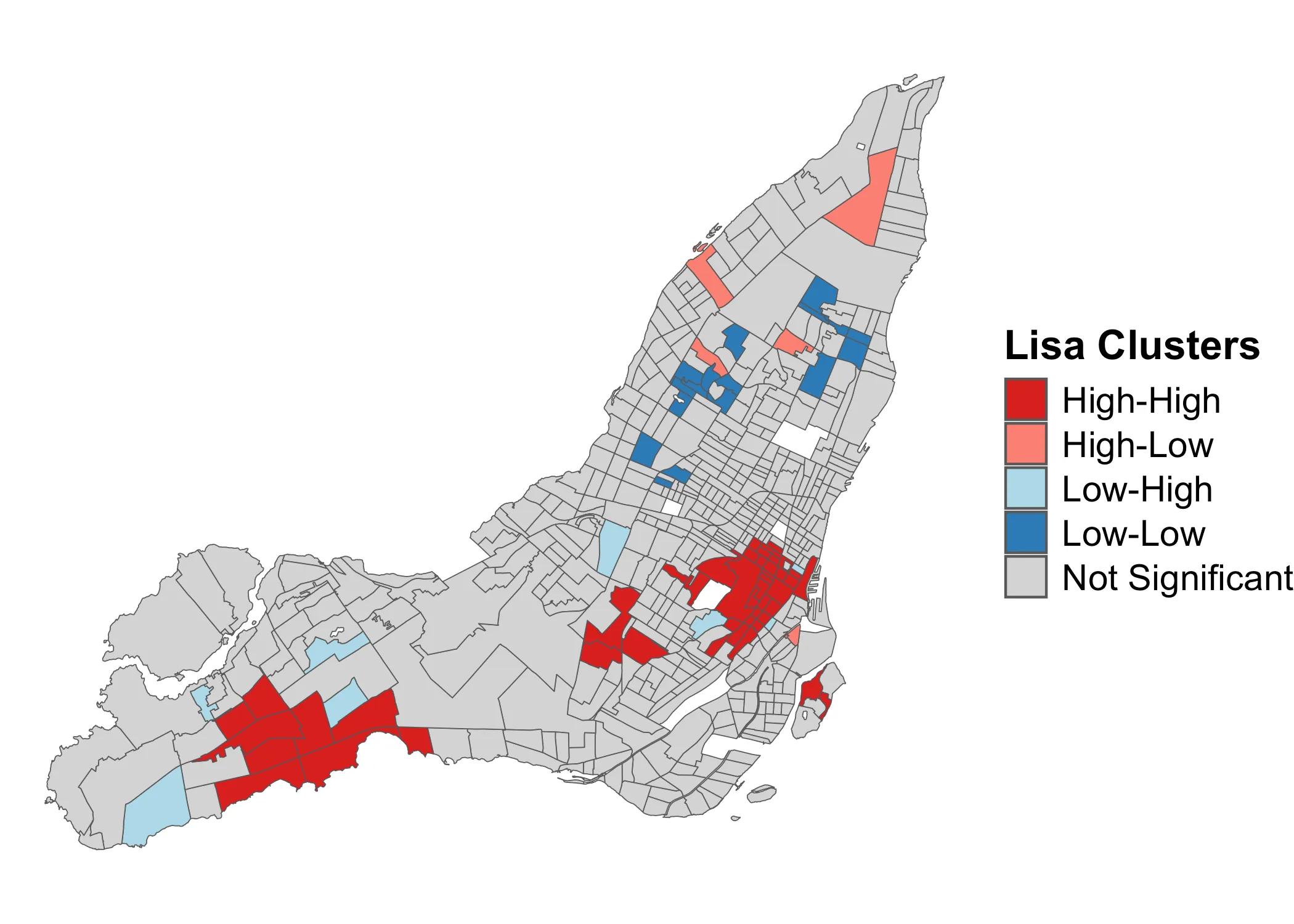
What is a local test for spatial autocorrelation, which tells us where there is clustering?
According to Dormann (2007), one way to reduce bias due to spatial autocorrelation is to randomly sample a smaller portion of all available geographic units. This comes at the expense of sample size.
What is a methodological solution to dismantle spatial structure?
Occurs when researchers want to compare data
with different geographies.
What is Spatial Misalignment?
To perform space-time analysis, your dataset must be organized so that each location has multiple rows across time.
What is long format?