What does IEP stand for?
What is Individual Education Plan
The written plan identifying the modified or alternative learning expectations and the accommodations or services needed to assist a student in achieving success
Why are advocates and educators promoting the use of "person-first" language.
Example: Instead of stating 'Sherry is autistic,' you would say, 'Sherry is a student with WITH AUTISM'
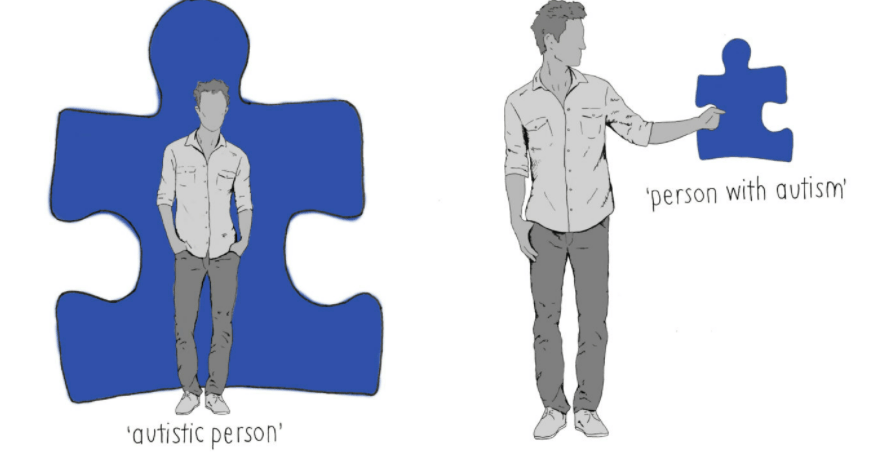
It puts the person before the exceptionality
It is the Educational Assistants role to modify/accommodate IEPs
True or False?
False - it is the teachers role to modify and/or accommodate all IEPs based upon the suggestion of each report

What does IPRC stand for? What does it do?

Identification, Placement and Review Committee (IPRC)

In Ontario, some students with special needs are formally identified as exceptional by an Identification Placement and Review Committee (IPRC), which is made up of at least three people, one of whom must be a principal or superintendent.
Special education has evolved a great deal in the Ontario education system and is fully integrated in all schools. The identification, placement, and review processes can involve parents, teachers, and principles in considerable debate, paperwork and, at times, litigation. It is important that all educators have a broad understanding of the rights of learners with exceptionalities, special education law in Ontario, and the administrative processes involved.
One of your students is partially blind - name one educational (tech or physical) tool that you could use in your classroom.
Online Searches Permitted!
Large print calendar, sight enhanced scientific calculator, Sceneeye 500 (camera that connects to computer to magnify image 50X), braille compass, Ovation (tech that can read and translate text), etc,.

Who is responsible for ensuring accommodations for students with exceptionalities/IEPs are met?

The School Board
*unless it can argued that it creates undue hardship for the board
List all 5 Categories of Exceptionalities

Behaviour, Communication, Intellectual, Physical and Multiple
In Ontario it is made explicit in the Education Act that every person who qualifies has the right to attend a school free of charge section 32(1) - including students with exceptionalities
The educational needs of students who are 'exceptional' however were often neglected prior to the 1980s
Even today in an era with Special Education programs and placements that exist across Ontario the education of students with exceptionalities remains an issue of contention in schools and in the courts
Maria is a student with AD/HD. Maria's grandmother believes she would be more successful in a fully self-contained classroom.
Using your Professional Judgement is this 'good' or 'problematic' assumption. Why?

Problematic: Inclusion has become the norm in Ontario since the Supreme Court ruled in the case of Eden versus Brant county Board of Education 1997. While advocates for learners with exceptionalities were disappointed that the court rejected the parents' insistence that their child be placed in a regular classroom rather than a special class they were pleased by the courts affirmation that consideration must first be given to placements in regular classroom with appropriate budget education supports. In response two public debate concerning this issue the Ontario Ministry of Education strengthened is resolved to favor inclusion as is evidenced by the special education transformation report. This report clearly states that in cases in which special education classes are the only option, these placements would be duration specific, intervention focus, and subject to regular reviews.
State one responsibility of the School Principal in terms of Special Education

The school principal:
* carries out duties as outlined in the Education Act, regulations, and policy documents, including policy/program memoranda and board policies;
* ensures that appropriately qualified staff are assigned to teach special education classes;
* communicates ministry and board policies and procedures about special education to staff, students, and parents;
* ensures that the identification and placement of exceptional pupils, through an IPRC, is done according to the procedures outlined in the Education Act, regulations, and board policies;
Name TWO AQ (additional qualifying) courses that you can take upon graduation to help support your understanding of Special Education/IEPs and Students with Exceptionalities/Disabilities

Special Education Part 1
Special Education Part 2
Teaching Students with Communication Needs
Special Education Specialist
The parent of one of your students does not agree that their child should be assessed for an IEP - can they put a hold on an assessment meeting? Why or why not?
No - while parents may clarify the student's personal history they are not entitled to be part of the final decision-making
Name TWO Resources that are available to you if you would like to better understand Special Education in Ontario
Just one example:
Ontario Ministry of Education. (2001). Special education: A guide for educators. Toronto: Author. Available at www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/general/elemsec/ speced/guide.html.
OR, 
Name one of two pieces of legislation that have played a critical role in ensuring that special education is provided to meet the needs of exceptional learners in Ontario

Two pieces of legislation have placed a critical role in ensuring that special education is provided for exceptional learners in Ontario;
The Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, and,
The Educational Amendment Act, generally known as Bill 82
The Charter guarantees every Canadian “the right to life, liberty, and security of the person." This right has been interpreted by courts to include the right to an education."
Provide 2 examples of Proactive Teaching in a Special Education Classroom:
Meaning, what are 2 things you can do to both plan ahead and support a student with an exceptionality?

Examples:
1) Set environmental conditions up for success/conditions that support student learning (turn off bright lights/move tables/etc.)
2) Create a profile of the student to better assess student needs
3) Seek academic support (AQ COURSES!)
What is the following document?
You as a teacher must fill this out alone.
True or False?

Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) for school-age students are written collaboratively, with input from an entire team. The team is composed of:
- the parents of the child;
- at least one regular education teacher of the child (if the child is or may be participating in the regular education environment);
- at least one special education teacher;
- a school district representative who is knowledgeable about the general education curriculum and the availability of resources and who is responsible for ensuring that the IEP, when finalized, is carried out as planned
- someone who can interpret evaluation results contained within the Evaluation Report; and
- others with knowledge about the child as requested by the parent or district, for example, speech therapists or behavioral consultants.