What is the following slide showing?
Cochlea
What is the name for the structure that splits the cerebrum into equal halves?
Longitudinal fissure

A child is complaining because they have a stomach ache. Provide two descriptive terms for the receptors picking up the stimuli in this situation.
Interoceptors and nociceptors
What structure provides a substance that traps chemicals for cilia to sense?
For an extra 100 points: what substance does it secrete?
Olfactory glands (secretes mucus)
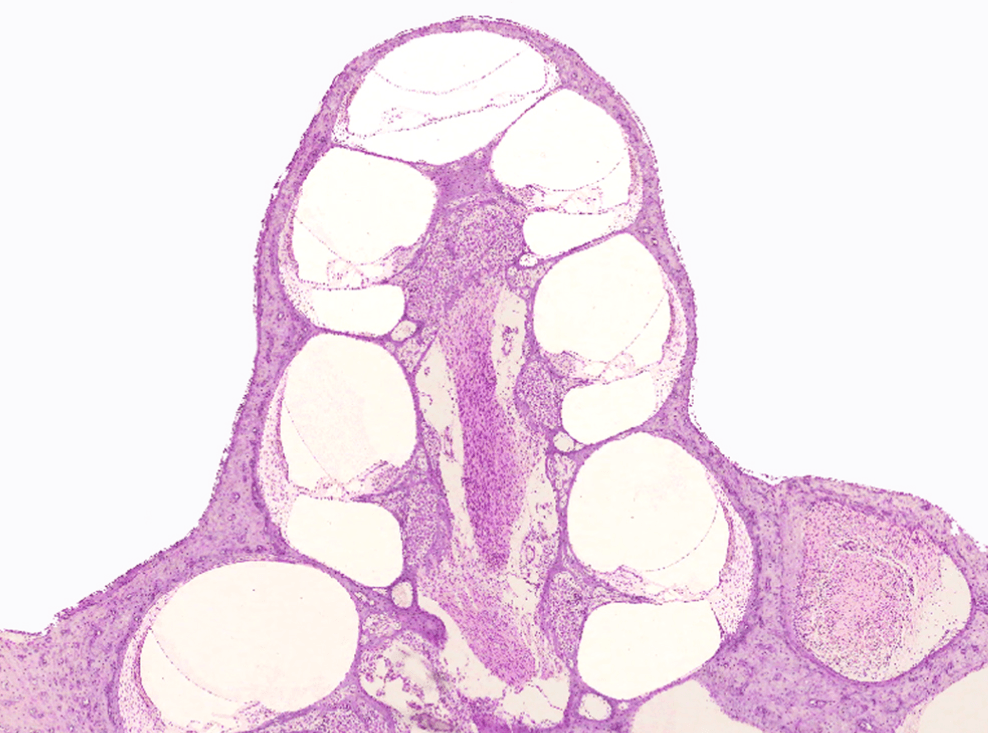
What kind of receptors are specific to the senses of smell and taste?
For an extra 100 points each: Name the receptor type for the other 3 special senses.
Chemoreceptors (photoreceptors for vision and mechanoreceptors for balance and hearing)
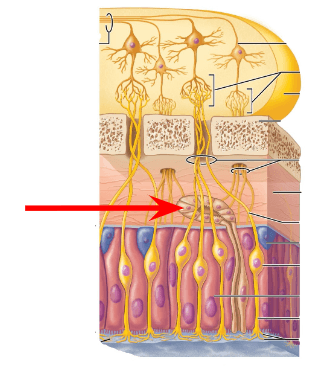
What is this? (inner area)
For an extra 100 points: what liquid nourishes this structure?
Aqueous humor
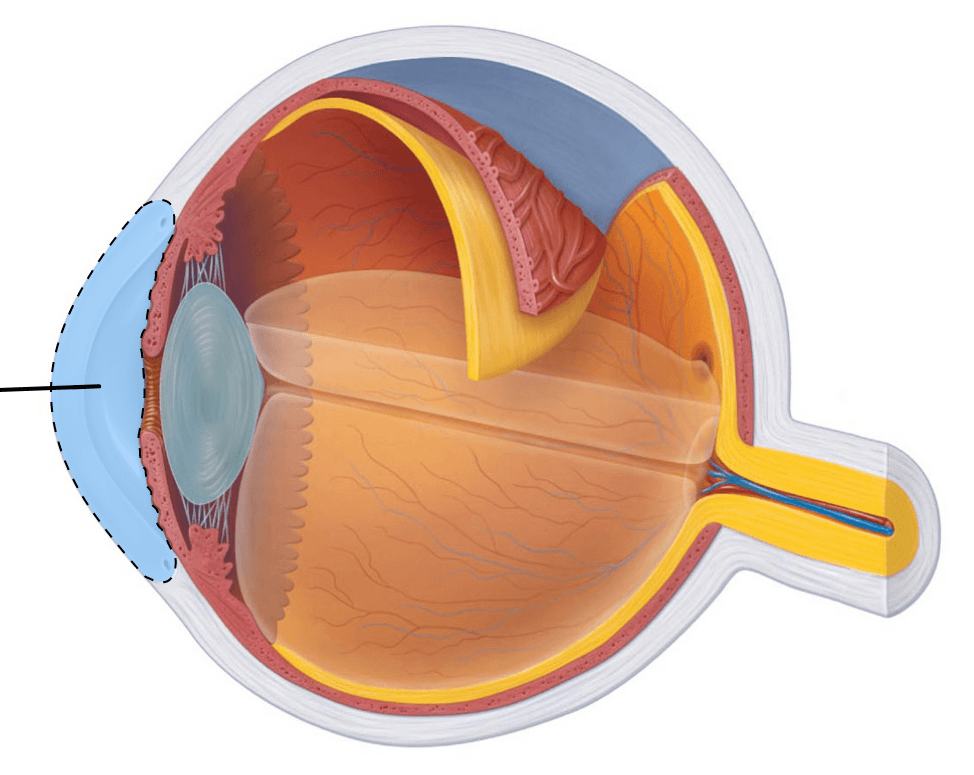
What is this?
For an extra 100 points: what lobe of the cerebrum is gustation processed?
Papillae (processed in the insula)
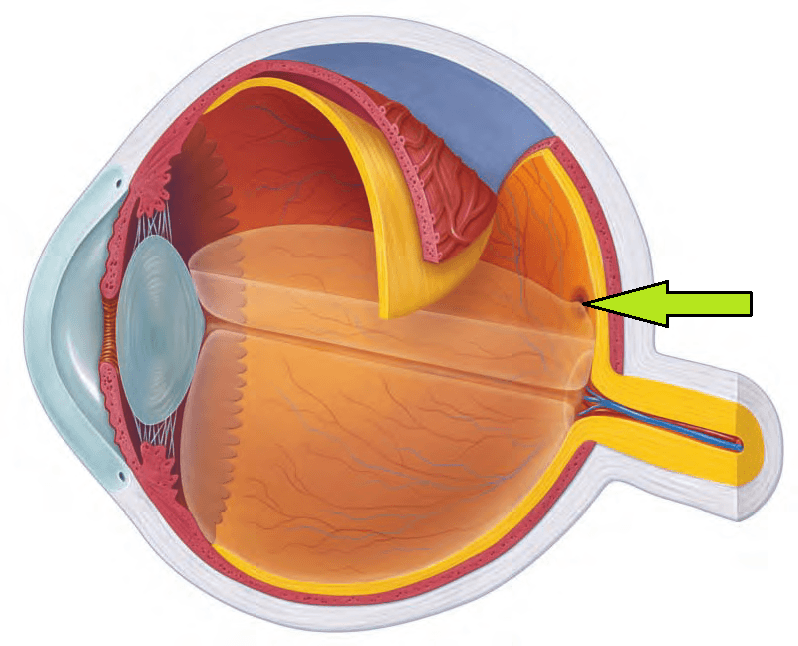
What structure is the arrow pointing to?
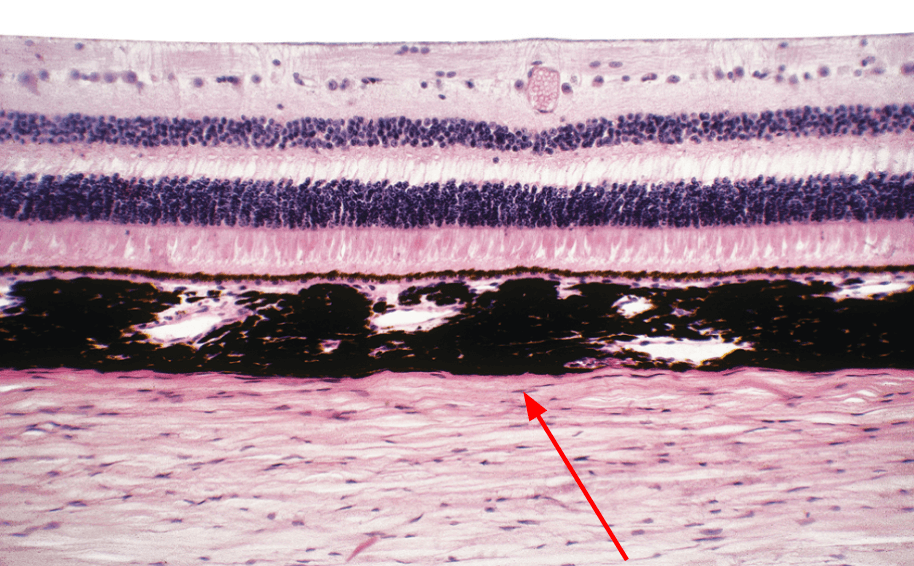
For an extra 100 points: What is the main function of this structure?
Choroid (main function is providing nourishment for the eye layers)
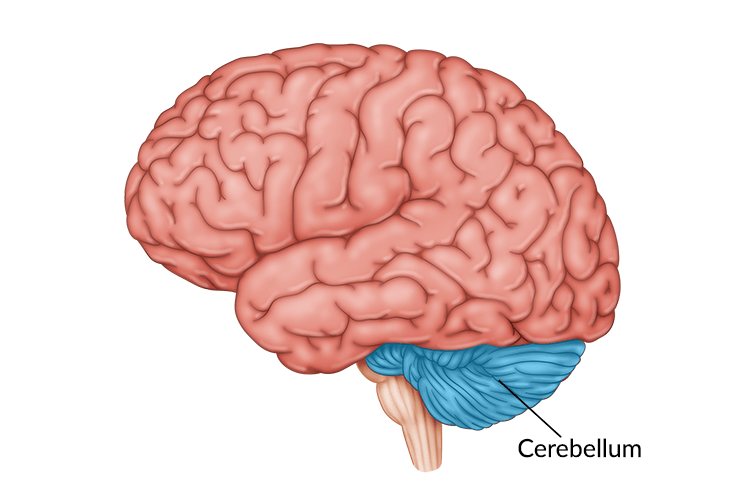
What CNS structure would be majorly responsible for processing balance?
Cerebellum
Dual innervation (also dynamic antagonism in this case)
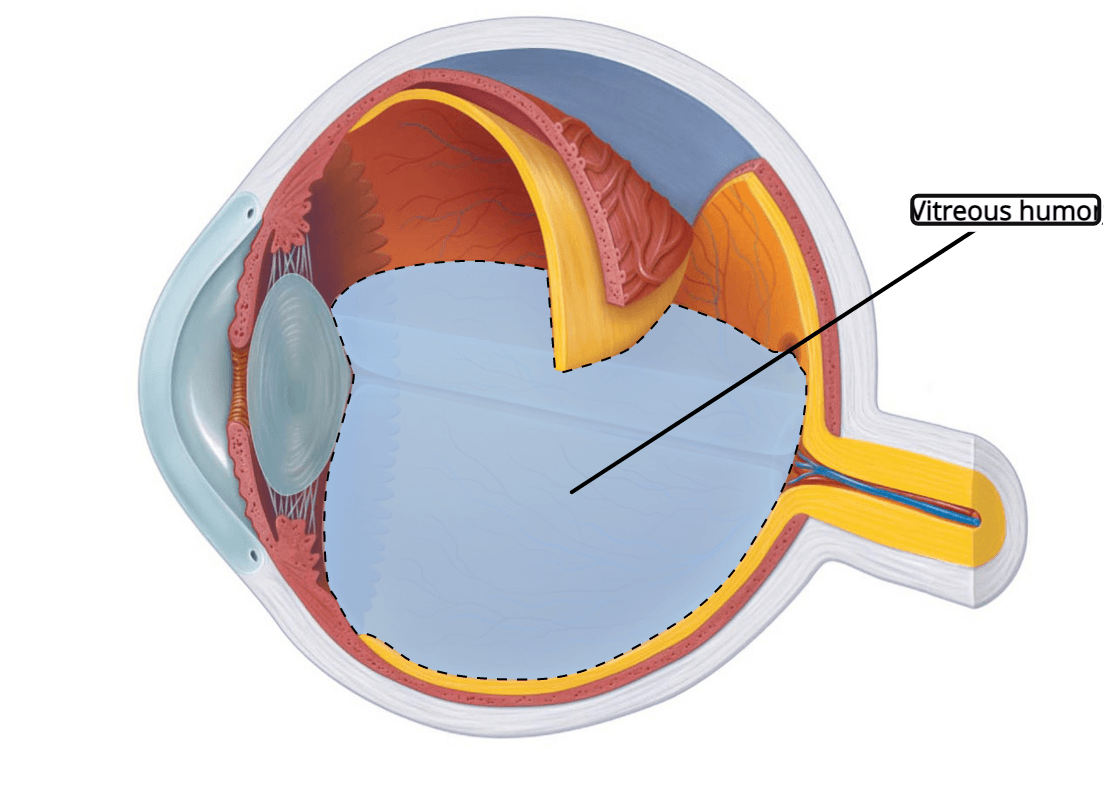
What is the name of the liquid that fills the retinal space?
For an extra 100 points: what is a function of this liquid?
Vitreous Humor (maintain infraorbital pressure and allow light to pass through the retina)
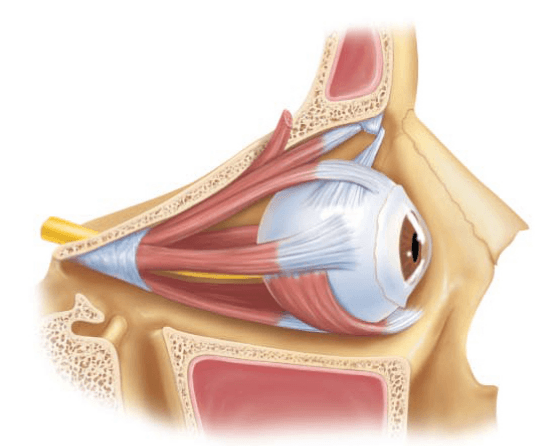
What structures allow movement of the eyes?
For an extra 100 points: how many is there?
For an extra 100 points: what cranial nerve(s) innervate these structures?
Extrinsic Eye Muscles (there is 6 and CNs are Oculomotor, Trochlear, and Abducens)
What is the name of the structure highlighted?
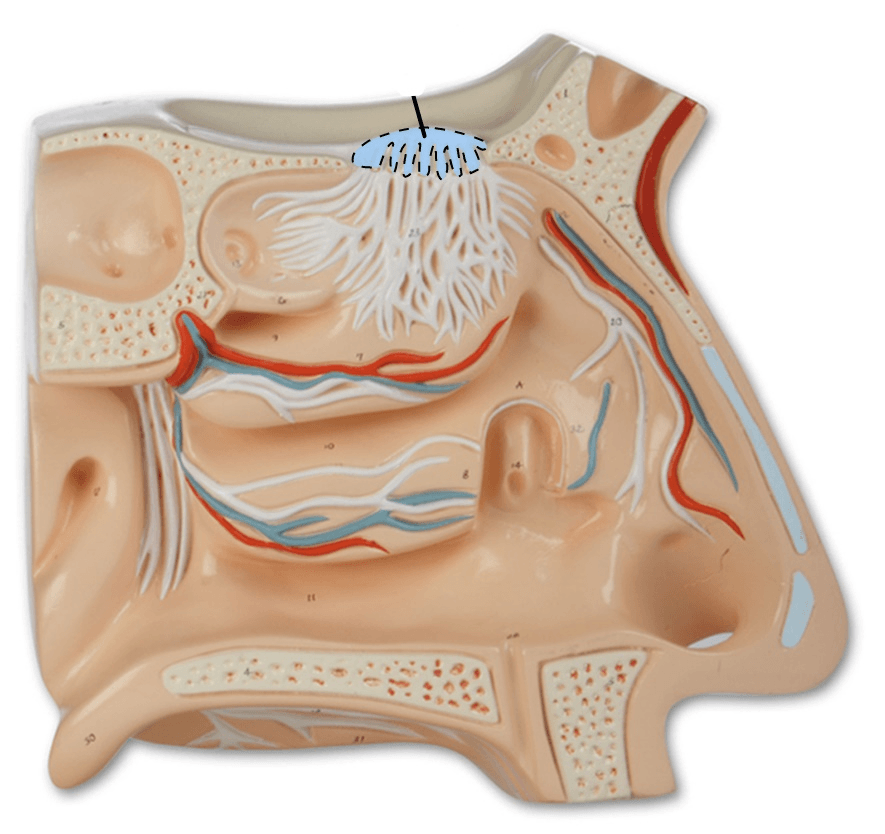
For an extra 100 points: What specific cells are found in this structure?
Olfactory Bulb (has mitral cells in it!)
What is the name of this area?
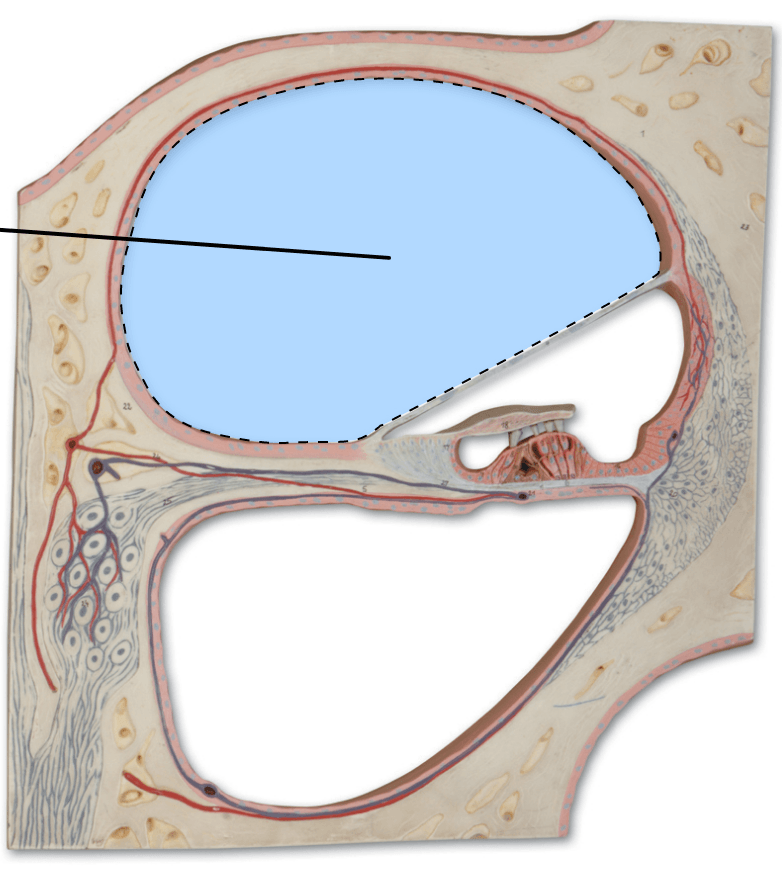
Scala Vestibuli
The following slide is showing a structure for what special sense?
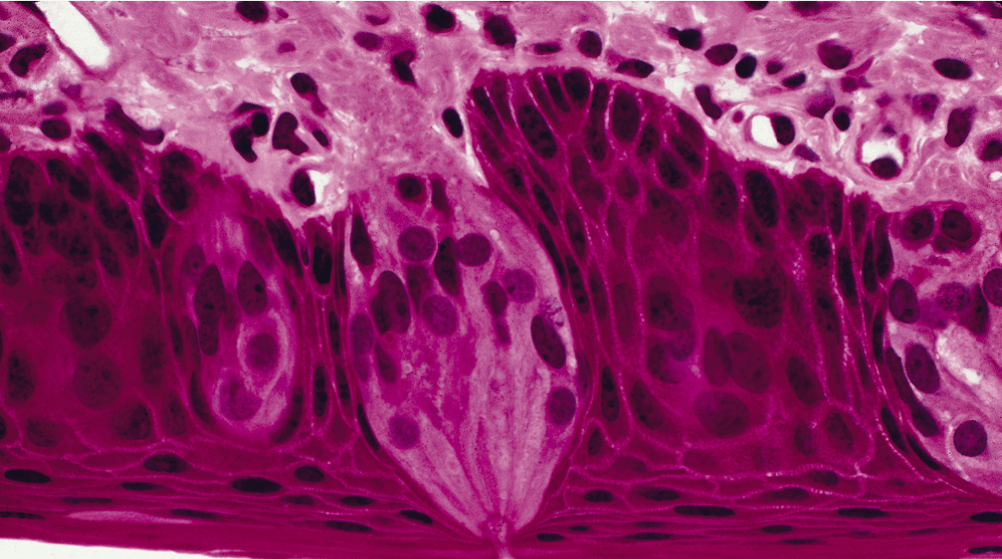
Gustation (showing the tongue!)
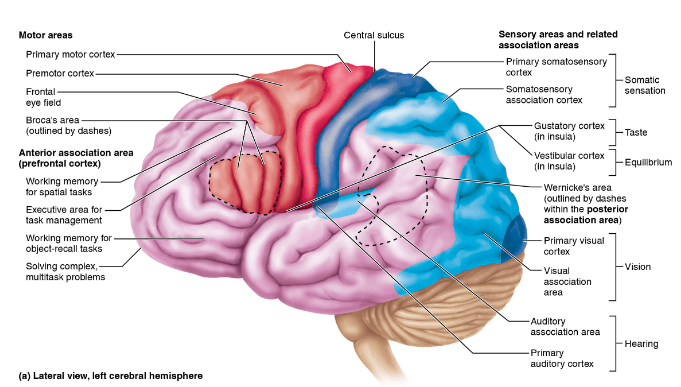
The outside layer of gray matter seen in the cerebrum give rise to what specialized structure(s)?
Functional areas
The sweat reflex is what type of reflex?
For an extra 100 points: If a person's sweat glands decrease their activity, what division(s) of the nervous system would cause this?
Autonomic reflex (any activity of the sweat glands is controlled by the by the sympathetic nervous system)
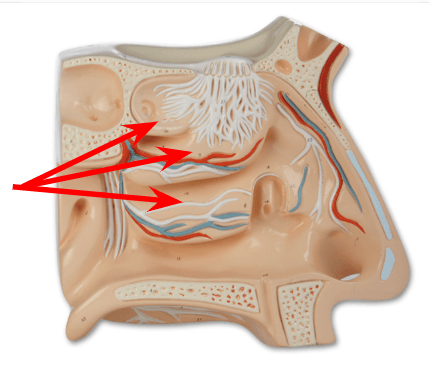
What structure increases the nasal mucosa area and works to warm/filter the air we breath in?
Nasal conchae
If ionized chemicals bonded to gustatory hairs, what basic taste would the person perceive?
Salty
What is this? (them together)
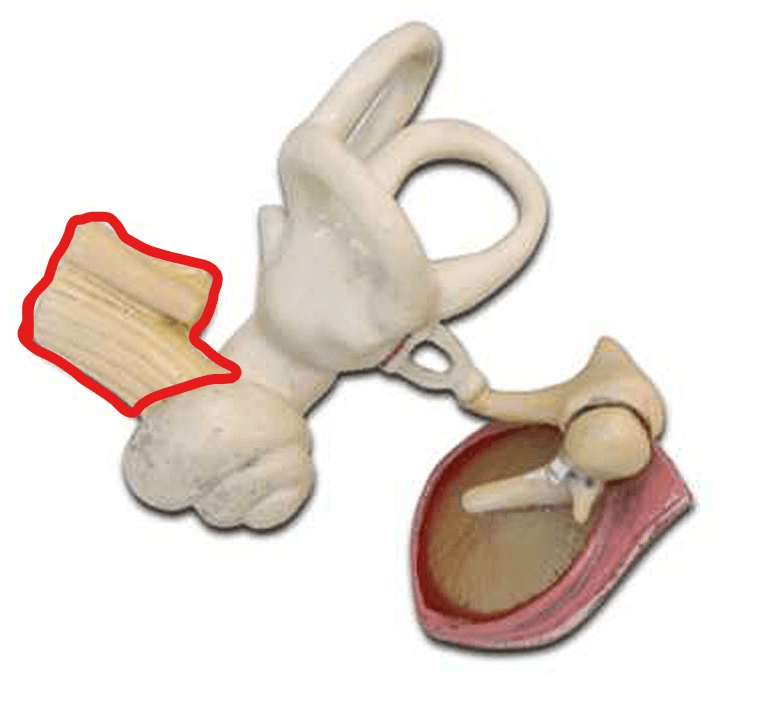
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
The highlighted structure is a portion of what?
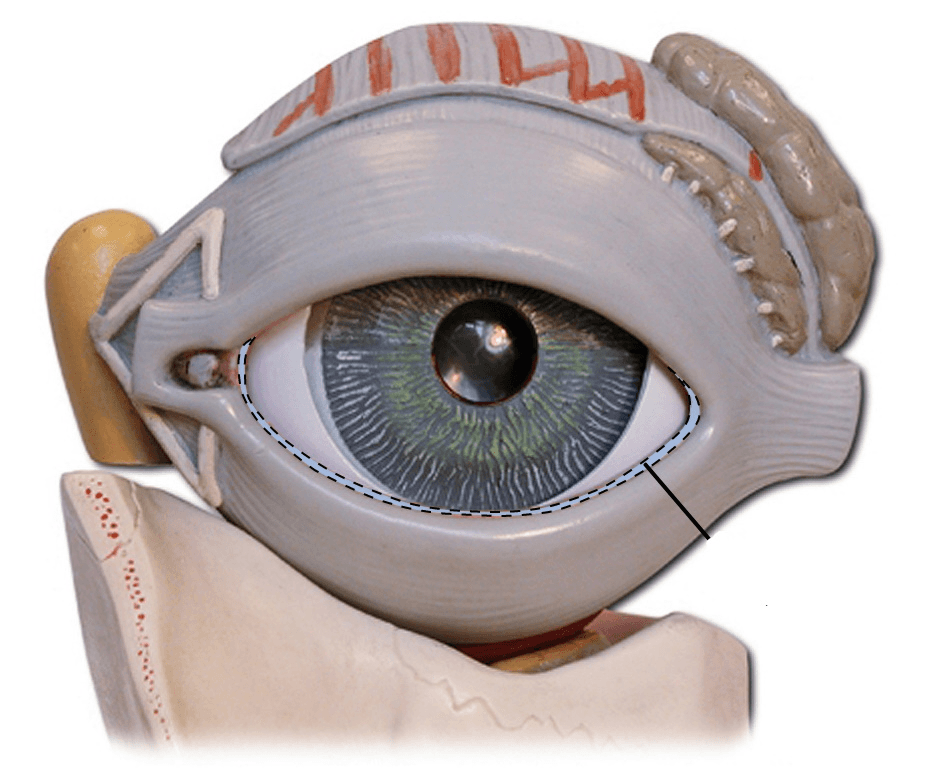
Conjunctiva
What structure is the arrow pointing to?
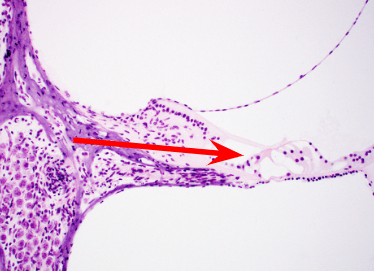
Organ of Corti
Varicosities are an example of the sympathetic version of what?
Axon terminals

Based on this chart, what area would have the smallest amount of sensory receptors?

Calf or shoulder (greater the line = greater the distance to tell its two different points = lesser amount of sensory receptors)
Describe the pathway of sound, saying each of the structures that play into it.
(From start to where sound transduction would occur)
Pinna → Auditory canal → Tympanic membrane → malleus → incus → stapes → oval window → vestibule → cochlea → organ of corti → hair cells
What is the name of the small, string-like structures that extend off of the ciliary body/muscle?
For an extra 100 points: They run through the equator of what structure?
Zonular fibers (run through the lens)
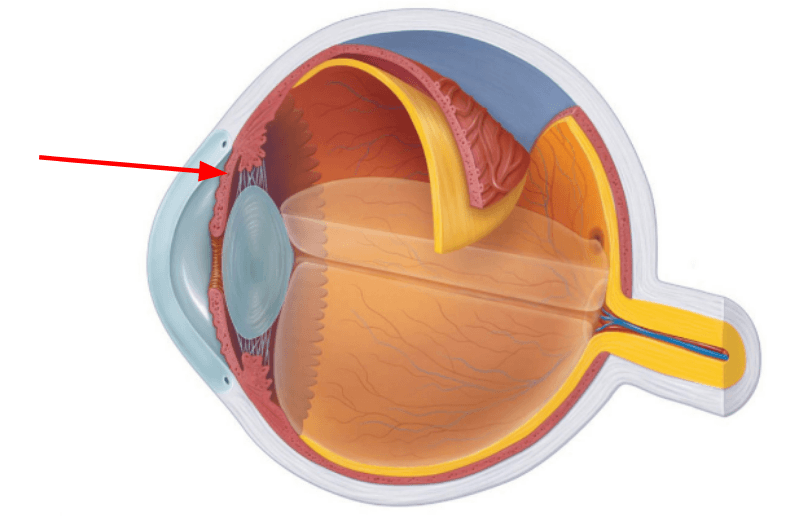
What is this?
For an extra 100 points: this area only has a certain type of receptor in it. What specific receptors are found here?
Fovea (contains only cones!)
What is this?
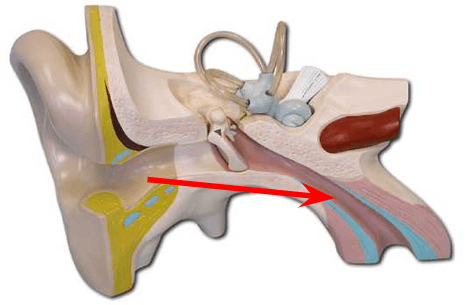
Eustachian Tube
What structure is the arrow pointing to?
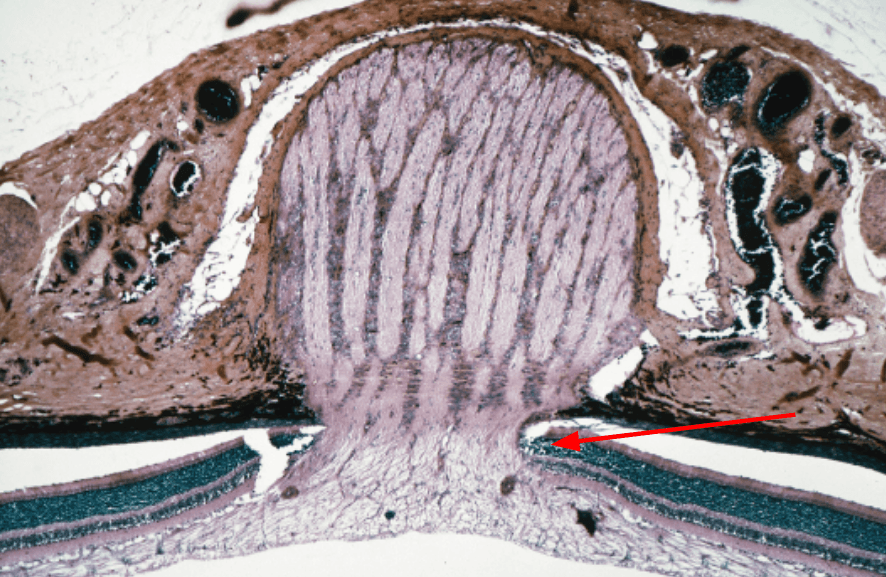
For an extra 100 points: What cranial nerve is this structure closely associated with and why?
For an extra 100 points: This indicated area is lacking what type of cells?
Optic disc (associated with optic nerve and it lacks photoreceptors (rods and cones))
A person has a spinal injury, specifically impacting their 22nd spinal nerve. What section of spinal nerves has been damaged in this instance?
Lumbar spinal nerve (C1-8, T1-12, L1-L5)

What is the only type of receptor that has no influence on special sense transduction?
For an extra 100 points: name an example of one of these receptors.
Thermoreceptors (free nerve endings)
What is the name of the transducer cell for the sense of balance?
For an extra 100 points each: Name of the transducer cells for the other 4 special senses.
Cristae of ampullares (vision - cones and rods, hearing - hair cells, taste - gustatory receptor cells, and smell - olfactory receptor cells)
What structural type of neurons are found in the olfactory epithelium and the retina?
For an extra 200 points each: What are the names of those neurons in those structures?
Bipolar neurons (olfactory receptor cells and bipolar cells)
What is this?
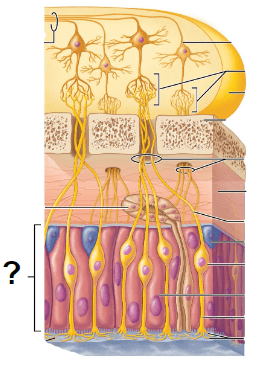
Olfactory epithelium
What is this section called?
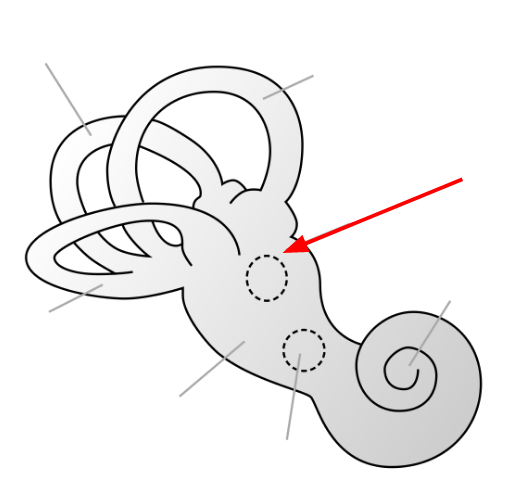
For an extra 100 points: this section connects to a group of structures called the what?
Utricle (connects with semicircular ducts/canals)