Name the four sub systems involved in the communication process
What are velopharyngeal, pharyngeal oral, laryngeal, respiratory
Anatomy is..
Physiology is..
Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism
Physiology is the study of the function of the living organism and its parts, as well as the chemical process
The position with the body erect with the arms at the sides and the palms forward is referred to as the ______________ position
Anatomical position: Upright, palms forward, eyes directly ahead, feet together 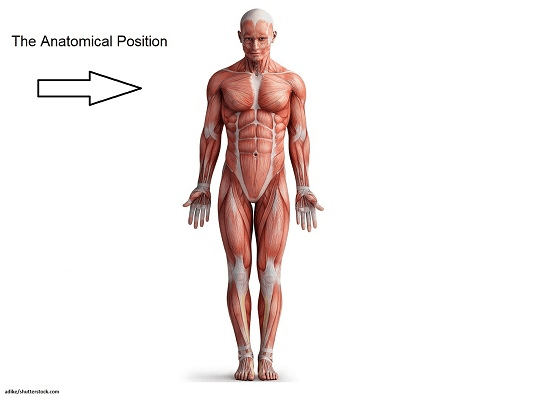
list and define the skeletal framework of the larynx
What are the cricoid cartilages, arytenoid cartilages, thyroid cartilage, hyoid bone, and epiglottis
List the four primary types of tissue.
epithelial
connective
muscle
neural
The three phases of swallowing
What is oral, pharyngeal and esophageal
How is Respiratory involved in the communication process?
The respiratory system (involving the lungs) provides the “energy source” for speech
Adduction is
Abduction is
vocal cords coming together toward the midline
Vocal cors moving away from the midline
What is the difference between midsagittal and sagittal planes?
Sagittal Section- Left and right portion but not equal
Midsagittal plane – divides the body into equal halves (right and left halves) at the medial plane
Sagittal plane – divides the body into right and left parts that are unequal.
The space between the vocal folds
What is the glottis
Describe the purpose of connective tissue.
Connective tissues bind structures together, form a framework and support for organs and the body as a whole, store fat, transport substances, protect against disease, and help repair tissue damage. They occur throughout the body. Connective tissues are characterized by an abundance of intercellular matrix with relatively few cells.
Connective tissue cells are able to reproduce but not as rapidly as epithelial cells. Most
connective tissues have a good blood supply but some do not.
The four lobes of the brain
What are Occipital, temporal, parietal, frontal
How is the articulatory/resonatory system involved in the communication process?
The articulatory/resonatory system modifies the acoustic source provided by voicing (or other gestures) to produce the sounds we acknowledge as speech
Responsible for the movement of structures to produce speech sounds Add nasal (air flowing into nasal cavity) – oral (airflow through the mouth (differenate between phonemes)
Descriptive Anatomy is..
Descriptive anatomy (systemic anatomy) – the part of anatomy involved in the description of individual parts of the body and the relations to functional systems, but not of their disease conditions. For example, the study of the anatomical parts of the larynx and their relation to phonation.
5. ______ near the tail or hind parts; posterior
6. ______ relating to the skull or cranium
5. Caudal is near the tail or hind parts; posterior
6. Cranial is relating to the skull or cranium
The main variables that influence laryngeal structure and function
What are age and gender
Name the 3 longitudinal pharyngeal muscles and define their purpose
What are the salpingopharyngeus, palatopharyngeus, stylopharyngeus
shorten the pharynx
a collection of blood that forms between the dura mater (the outer layer of the brain's protective membranes) and the brain itself.
What is a subdural hematoma
Name the four hearing subsystems
What are outer ear, middle ear and inner ear
Gross Anatomy is..
Gross (macroscopic anatomy) - The study of the organs, parts, and structures of a body that are visible to the naked eye.
7. ______of, at, toward, or from the side or sides. A side part of something
8. ______furthest away from the center of the body or from the point of attachment
7. Lateral: toward the side of the body
8. Distal: Further from the trunk or thorax; further from the attached end
The rate at which the vocal folds vibrae
What is fundamental frequency
These are muscles that fill the outer portion of the rib spaces. they expand the thoracic cage by elevating and extending the sternum.
What are the external intercostal muscles
the structures of neurons, which conduct electrical impulses toward the cell body of the nerve cell.
What are dendrites
Name and define the stages of spoken communication
Microscopic anatomy is..
Microscopic anatomy – the study of body structures through the use of microscopy.
9. ______ (frontal plane) is any vertical plane that divides the body into ventral and dorsal (belly and back) sections
10. ______ nearer to the center of the body or the point of attachment
9: Coronal plane: Any vertical plane that divides the body into ventral and dorsal sections.
10. Proximal: Closer to the trunk or thorax; nearer to the attached end
A form of sudden explosive bursts, usually involving a glottal stop plosive
What are transient utterances
Name the pharyngeal constrictors. Define their purpose
What superior, medial, inferior
constrict the pharynx
The Meningeal layers
What are the
•Dura mater
•Arachnoid mater
•Pia mater
–
Name and define the respiratory subsystems and its divisions
What are pulmonary apparatus (lungs and airways)
Chest wall (rib cage, diaphragm, abdominal wall)
Surface Anatomy is..
The study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin surface e.g. the clavicle and ribs can be viewed in part by observing the skin surface.
Another term for posterior is ____________________________ and anterior is
__________________.
Posterior- AKA -Dorsal: Pertaining to the back of the body or the posterior surface
Anterior AKA -Ventral: Pertaining to the belly or anterior surface
Laryngeal function is concerned mainly with protecting what?
What are pulmonary airways, containment of pulmonary air supply, and sound generation
These muscles lie in the inner portion of the rib interspaces.
they enable forced expiration by depressing the ribs, thus shrinking the diameter of the thoracic cavity and pushing the air out of the lungs.
What are the internal intercostal muscles
The cranial nerves for speech and swallowing
What are Cranial nerves 5, 7, 9 and 12