Natural food sources, such as fruits and honey, as well as industrially processed foods such as candy and sugary sodas contain a lot of this monosaccharide...
Fructose
For this reason, a carbohydrate mouth-rinse would likely not be useful to a marathon runner.....
Need to ingest the carbohydrates in order to get the metabolic benefits
Free fatty acids are transported in the bloodstream via this protein.....
Albumin
This is the sphincter that controls the rate of gastric emptying....
Pyloric sphincter
Your friend is going keto and has lost several pounds in just the first few days of the diet. This is the most likely explanation....
Glycogen depletion and associate water loss
Short chain fatty acids have this many carbons or less.....
6 or less
How much carbohydrate should a trained runner competing in a 5K run (3.1 miles) consume during the race?
None!
In trained individuals who are not on a long-term low-carbohydrate diet, the peak rate of fat oxidation occurs around __________% VO2max.
62-63%
Contraction of this sphincter prevents the reflux of food and fluids, which would result in "heartburn" if not functioning appropriately...
Esophageal Sphincter
These are two specific examples where short-term adoption of a low-carbohydrate diet could be useful in competitive athletics..
Quickly making weight (MMA/wrestling/boxing/weight lifting competitions etc.)
Enhancing fat oxidation in early season conditioning (low intensity, higher volume, fat dependent conditioning)
This mineral is important in the diet because it is a constituent of hemoglobin...
Iron
Modern recommendations for total daily carbohydrate intake for athletes and exercisers are given relative to these factors...
Body weight and training volume
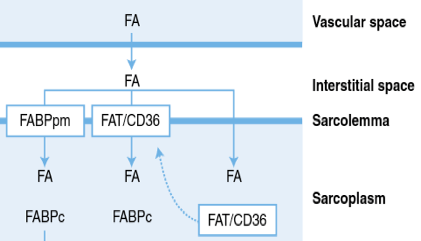
You could call this sarcoplasmic fatty acid transporter the "GLUT-4" of fat transport...
Sodium bicarbonate released from the pancreas into the small intestine serves this purpose...
Neutralize hydroclhoric acid from the stomach
A combination of endurance training and long-term adaptation to a low-carb diet could push the peak rate of fat oxidation to ______% of your VO2max...
70%
In trained and well-fed runners, there is enough glycogen stored in muscle to fuel roughly this many minutes of running at marathon pace...
90 minutes
These are four different reasons using a classical glycogen supercompensation approach can cause problems for athletes...
1) Hypoglycemia during low-carb period
Increased risk of injury, mood disturbances during low carb period
2) Practical issues preparing extreme diets
3) Gastrointestinal issues
Low-carb period à adjust to eating more fats/proteins to maintain energy requirements
High-carb period à adjusting to eating more carbs than normal
4) Mental tenseness due to not training
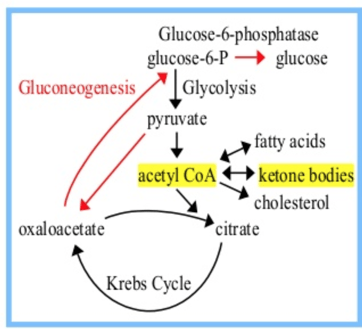
When liver glycogen stores are depleted, the depletion of this "Krebs cycle intermediate" impedes the entry of Acetyl CoA, and promotes the formation of ketone bodies......
These are the best types of training sessions to practice "gut-training" during....
High-intensity (above or at threshold) and race simulation efforts...
Based on the studies observed in lecture, this is the one type of sporting performance that wouldn't be negatively impacted by short-term adoption of a low-carb diet...
Olympic lifting/power-lifting (one short maximal burst effort)
These types of muscle fibers have the greatest citrate synthase activity....
Type I
In order for an individual to engaged in the "classical" method of glycogen supercompensation in the week leading up to an important event, they would need to do all of these things.....
1) Deplete muscle glycogen via exhaustive
training session
2) 3 days of low carbohydrate (25% of
energy intake) diet
3) Perform another exhaustive training
bout on day 4
4) Cease training and consume high
carbohydrate diet (70% of energy
intake) for 3 days prior to comp
Based on current research, what muscle level adaptations occur in skeletal muscle that allow trained individuals oxidize more fat during exercise...
•Increased mitochondrial density and oxidative enzyme activity
•Increased capillary density
•Increased FABPpm concentrations
•Increase CPT concentrations
•Increased concentration of IMTGs and movement of IMTGs closer to mitochondria
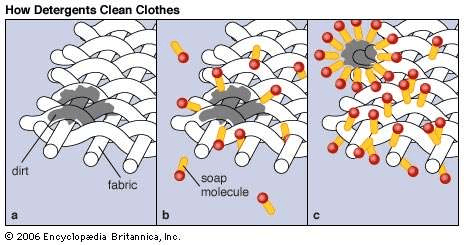 If we were to use this diagram as an analogy for the digestion of fats, what would be the "soap molecules" and what would be the "container" of detergent?
If we were to use this diagram as an analogy for the digestion of fats, what would be the "soap molecules" and what would be the "container" of detergent?
Soap molecules = Bile
Container = Gall bladder
Why isn't the "container" the liver?
Chronic glycogen depletion is the primary drawback for most athletes if adopting a low-carb diet due to the importance of glycogen as a fuel source. Name five other potential drawbacks...
Low energy availability if dietary choices are restricted
• Dehydration due to glycogen depletion as well as potential beverage restrictions
• Increased breakdown of protein and amino acids
• % of energy from protein will increase
• Lethargy and fatigue
• Long period of adaptation during exercise