What are the three macronutrients & what is one role each plays?
Protein- Rebuild muscle!
Carbs- Energy tank!
Fat- General health, processing, and immune
It's best to go into a workout without eating because it helps you feel "lighter" (T/F)
False! Training with low fuel can reduce performance and increase injury risk.
What macronutrient is the primary fuel during high-intensity ski intervals? What's the primary fuel at low-intensities?
Mainly Carbs / Creatine / ATP at high
Mainly Fats at low
What is a supplement? And what's one way to make sure it's safe?
A supplement is a product that is intended to add to or enhance the diet. It typically contains nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, herbs, amino acids, or enzymes. Supplements can be taken in various forms, including tablets, capsules, powders, or liquids.
NSF for Sport or Informed Sport testing
Signs of dehydration?
What are dry mouth, fatigue, thirty, low weight, dark urine, and dizziness?
Do bagels or toast have more carbs? How many grams of carbs do each have? (2pt question)
Bagel: ~60g
Toast: ~30g
What are carbohydrate dense foods?
Pasta, potatoes, rice, quinoa, bread, bagels, bars, gels, sugar, starchy veggies
Green supplements like AG1 are more effective than most fruits and veggies (T/F)
False! Whole fruits and veggies provide fiber and phytonutrients missing from many supplements.
How many hours before training should you eat your main pre-training meal? Why? What happens if it's outside that window?
(2–4 hours)
Too close? Nausea, bloating, GI distress
Too far out? Not going into training with a full gas tank
Is processed sugar bad? And why?
No—not always. Natural and added sugars around workouts can be helpful for energy.
Is coffee/caffeine dehydrating?
No, the fluid in coffee, tea, or an energy drink generally offsets the mild diuretic effect of caffeine in moderation. High doses will have a net negative effect.
Which is higher in iron - beef or pork? Why is it important to eat high iron foods as a winter sport athlete?
Beef! Iron helps to transport oxygen in your body. Your body has to work harder as an athlete and as one who spends significant time at altitude.
What is too much protein (y/n)? Is there such a thing - if so, what is it? (2pt question)
What is more than 2.2g/kg or 2.5g/kg (in injury) of body weight per day—your body won’t use as effectively, and it can displace carbs needed for energy.
A high calorie diet is one of the best ways your support your body as an athlete (T/F)
True! Calories is what ultimately give your body the resources to rebuild, recover, and repair! (muscles, fatigue, and immune)
What’s one sign that an athlete is under-fueled?
Low energy, poor recovery, irritability, frequent illness, poor sleep, low motivation, injury
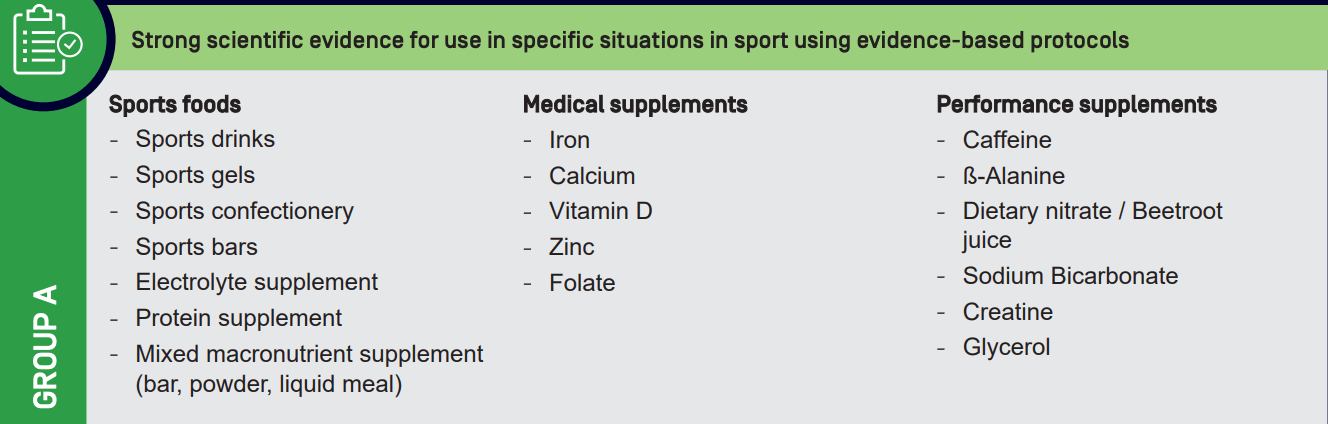
Name 3 of the most backed performance-related supplements? Excluding medical/health supplements.
What circumstances make dehydration more likely?
High altitude, travel, intense training, cold weather, not drinking enough fluids, and wearing lots of layers?
What vitamin comes from the sun & why are winter athletes commonly low?
Vitamin D! Winter athletes experience reduced sun exposure, leading to decreased vitamin D levels. Additionally, stress on the body from high-intensity activities can further lower vitamin D.
This type of fat from fish supports brain function and reduces inflammation.
Omega-3
Creatine makes you gain weight (T/F). Bonus - how is creatine effective for athletes?
What is partially true—it can increase water in muscles, not fat, and can improve power performance. But only 1kg (2-3lb) max. It's your bodies prefered fuel source at 90%+ intensity. Naturally through diet you can get your storage in your body ~80% full.
What should travel nutrition look like?
Balanced meals/snacks packed ahead (trail mix, wraps, protein bars), hydration, and not skipping meals. One reason digestion might be more difficult after long travel days - dehydration, poor sleep, disrupted GI from different foods, or altered meal timing
Are seed (canola/soybean) oils bad?
No—moderate intake of oils like canola and soybean can be part of a healthy, balanced diet.
Electrolytes help replace fluid when I don't drink enough. (T/F)
False — they help replace sodium, potassium, and fluids lost in sweat, not the fluid. Regulating fluid balance within the body, ensuring water is efficiently absorbed and retained by cells
Which has the most protein? 4 eggs, 4oz of a ribeye, 1 cup of Greek yogurt, or 1 cup of edamame?
4oz Ribeye: ~28-30g
4 eggs: ~24g (~6g/egg)
1 cup edamame: ~17g
1 cup of Greek yogurt: 15-20g
This fruit has more potassium than a banana.
An avocado
The leaner you are, the better you'll perform (T/F)
False! Performance depends on strength, energy, and recovery—not just leanness. Too lean can mean under-fueled.
How much body weight loss (%) from dehydration can impair performance?
(2%)
Blood volume decreases → your heart has to work harder to pump blood.
Core temperature rises faster → you overheat more easily, especially in ski suits or layers.
Muscle endurance drops → you fatigue earlier in both long aerobic sessions (XC skiing) and short explosive events (slopestyle, GS).
Cognitive performance declines → slower reaction times, reduced focus, worse decision-making (critical on course).
Drinking lemon water in the morning detoxes your body. (T/F)
False — your liver (toxins) & kidneys (waste) handle detox 24/7.
While lemon water contains vitamin C and antioxidants, these don’t “flush” toxins.
Do all electrolyte drinks have carbs in them? If so, is it good? If not, should they? (3pt question)
Not all do—those with carbs (like sports drinks) help fuel during long training; zero-carb options help hydrate without extra carbs outside of training.
What's a better pre-training snack - a protein shake or a piece of toast w/ jam?
Toast + jam!