Higher incidence in African American population
Obesity, physical inactivity, excessive sodium intake and smoking are some of the risk factors
What are risk factors for hypertension?
First steps in management of this disorder are managing hyperlipidemia, cessation of smoking, exercise and reduction in stress
What does DASH diet include?
What is lifestyle modification?
More fruits, vegetables, fish and leaner cuts of meats
Heart failure, cardiogenic shock and EKG changes are complication of ___________
What are complications of MI?
1.Arteries in the legs are clogged
2. List three lifestyle modifications recommended for a Diabetic patient with hypertension
1. What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?
2. What is DASH diet?
Decreased sodium, moderation of alcohol intake & increased physical activity.
1. Pulsatile abdominal mass approximately 5cm diameter in your thin 81 y/o male (usually by the belly button)
2. Rupture and Bleeding
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm?
What are complications of AAA?
Smoking, alcohol, high cholesterol, sedentary lifestyle, obesity and high blood pressure
Morphine Oxygen Nitro and Aspirin
What are risk factors for coronary artery disease?
What is Mona?
Chest pain that goes away with rest or taking medication (nitro)
What is stable angina ( acute coronary syndrome)?
Dyspnea, fatigue and edema are clinical manifestations of _____
What are the cardinal symptoms of heart failure?

What is the risk factor for AAA?
What is Aortic Aneurysm?
What is HTN?
What is endocarditis?
Rheumatic heart disease, IV drug abuse, structural cardiac abnormalities, implantable devices, prosthetic heart valves and immunosuppression are some of the risk factors for this cardiac disorder
What specific heart sound is heard in a patient with pericarditis?
What are risk factors for infective endocarditis?
What is a loud grating sound: friction rub?
Untreated strep is a risk factor for this disorder
What is Rheumatic Heart Disease?
1. Pink frothy sputum, Orthopnea and Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
2. Dilates blood vessels and improves blood flow while decreasing high blood pressure, vascular muscle spasm and workload of heart.
1. What are clinical manifestation of left sided heart failure?
2. What is the effect of Ace Inhibitors?
1. Hepatomegaly, Splenomegaly, ascites and Jugular vein distention
2. MONA?
3. Digoxin, Furosemide and Ace Inhibitor?
1. What are clinical manifestation of right sided heart failure?
2. What is the treatment for MI?
3. What is the treatment for HF?
Intermittent pain (intermittent claudication), poor wound healing, numbness or tingling and edema.
What are symptoms of peripheral vascular disease?
The sound of blood flowing/passing through an abnormal/diseased heart valve
Stenosis or regurgitation of valves will cause this _____
What is murmur?
what is Dyspnea, fatigue and risk for thrombus
Inflammation of the outermost layer of the heart
What is pericarditis?
What actions should the nurse take first>
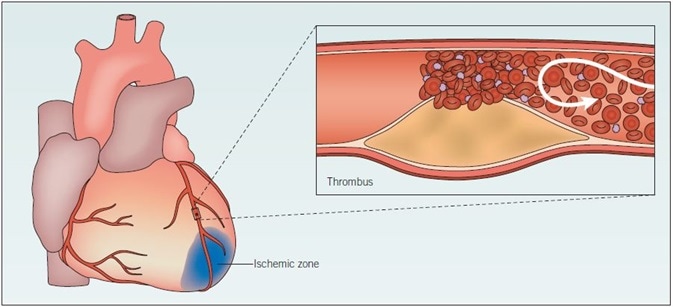
What is MI?
What is oxygenation?
Cardiac electrical activity is generated, spreads through the heart, and creates electrical waves.
What is Electrocardiogram?

Nursing management for blood transfusion
Insert 18 gauge IV
Transfuse PRBCs within 4 hours
Check the patient's ID and All documentation on PRBC bag with a 2nd RN.
Check patient's VS prior to transfusion
Stop transfusion if there are any changes in patient's status (VS, Rash, dyspnea, chills and restlessness etc)
Send the tubing along with PRBC to lab
Notify MD
Document the incident
These cardiac drugs are contraindicated in vasospastic angina, Asthma and DM
These drugs are antiplatelets.
What are beta blockers?
What is Aspirin & Plavix?
Crushing chest pain
Dyspnea
Nausea, heart burn, burping and vomiting
What are clinical manifestations for MI?
1. Most likely diagnosis for a patient with no angina but three day history of dyspnea, fatigue and 10 lbs weight gain.
2. These foods are high in folic acid
1. What is heart failure?
2. What are green leafy vegetables, beans, legumes and lentils?
Disorganized electrical activity of the heart in which the atrium depolarizes too quickly and sends erratic impulses to the ventricles. The presence of a pulse deficit between the apical and radial pulses is an indication of ________.
What is atrial fibrillation?
Therapeutic effects of Furosemide
Therapeutic effects of Ace Inhibitors
Therapeutic effects of Nitro
What is decreased weight and increased urine output?
What is decreased BP?
What is resolution of angina?