The reason Earth has seasons
Tilt
Name for the oval shape that describes a planet's path around the Sun.
Ellipse
The original stage all stars begin as, and what determines their future path.
Cloud of dust and gas
The current scientific model for how the universe started.
Even in a galaxy full of stars, this number lets each atom stand out in the element-ary school yearbook
Number of protons
This term describes the two times of the year when nighttime and daytime are the came length.
Equinox
The position in a planet's orbit when it is farthest from the Sun.
Aphelion
When a star is stable in size, its because these two forces are balanced.
Fusion & gravity
This observed phenomenon how we know the universe is expanding.
Redshift
This cosmic unit helps us measure distances between stars — because ‘a bazillion kilometers’ isn’t scientific enough.
Light years
Kepler's 2nd Law or "Equal Areas in Equal Times"
At the end of its life, our Sun (a main sequence star) will be in this stage.
Black dwarf
They’re dense, rocky, and keep things down to Earth — unlike those giant gasbags hanging out past the asteroid belt.
Terrestrial planets or Inner planets
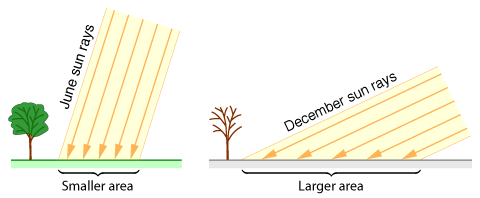
You would find this angle of sunlight happening during the winter in Iowa
Low angle
The Kepler's Law that says planets farther from the Sun take longer to orbit.
Kepler's 3rd Law or p2 = a3
The powerful explosion that ends a high-mass star’s life and can create any element on the periodic table
Supernova
If stars had dating profiles, this trait would tell you who’s cool, who’s hot, and who’s just a red giant pretending they still got it.
Color
The two places during stellar evolution where the whole process can start over from the beginning
Planetary nebula & supernova
What happens to the speed of a star/galaxy as it gets farther away
Speeds up
This spectral stretching doesn’t involve yoga — but it does tell us when galaxies are moving away and taking their light with them.
Redshift