The amount of energy or biomass that is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
What is the 10% rule?
A group of tissues working together for a specific function.
What is an organ?
The types of organisms that perform photosynthesis.
What are producers (plants/autotrophs)?
The shape of DNA.
The shape of RNA.
What is a double helix?
What is a single helix?
The central dogma of life.
What is DNA-> RNA -> Ribosome -> Protein?
The original source of energy in all ecosystems.
What is sunlight?
A group of organs working together for a specific function.
What is an organ system?
The products (outputs) of photosynthesis.
What are oxygen and glucose?
The backbone of DNA.
The "rungs" of the ladder.
What are the sugar and phosphate groups?
What are the nitrogen bases?
Using the letter "B" what would the genotype be for the following:
Heterozygous, homozygous recessive, homozygous dominant
Heterozygous: Bb
Homozygous R: bb
Homozygous D: BB
If your producer has 13000 kcals of energy, the amount available to your tertiary consumer.
What is 13 kcals?
The level of organization being shown here.
What is a tissue?
The reactants (inputs) for photosynthesis.
What are carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight?
The complementary base pairs for RNA
Adenine - Uracil
Thymine - Adenine
Guanine - Cytosine
The location of transcription in a cell.
The location of translation in the cell.
What is the nucleus?
What is the ribosome?
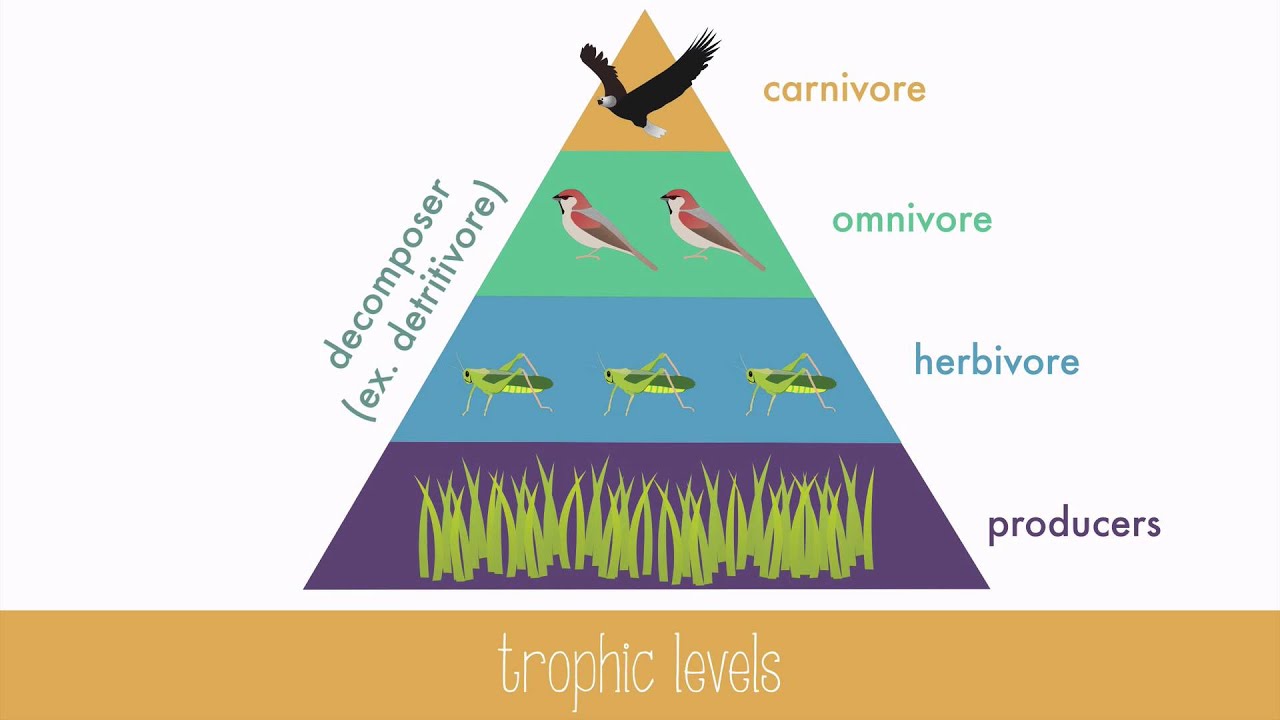
The grasshopper has 101 kg of biomass. Fill in the rest of the pyramid (top to bottom).
Grass (producer): 1010 kg
Grasshopper (pc): 101 kg
Bird (sc): 10.1 kg
Eagle (tc): 1.01 kg
Two or more atoms bonded together.
What is a molecule?
The organelle that photosynthesis occurs in.
What is the chloroplast?
The complementary base pairs for DNA.
Adenine - Thymine ; Guanine - Cytosine
Straight hair is dominant over curly hair. Use the letter "h" to represent the alleles.
Draw a punnett square; cross a homozygous recessive mom with a heterozygous dad.
What are the possible genotypes along with what phenotype that genotype would show.
h h
H Hh Hh
h hh hh
Genotypes: Hh - straight hair or hh - curly hair
Percentages: Hh - 50% hh - 50%
Your secondary consumer has 45 kcals of energy available to them. Fill in the rest of the levels from producer to quaternary consumer.
Producer: 4500 kcals
Primary Consumer: 450 kcals
Secondary Consumer: 45 kcals
Tertiary Consumer: 4.5 kcals
Quaternary Consumer: 0.45 kcals

Based on the definitions of the different levels of organization, the level that is being shown here.
What is a cell?
Things that will increase the rate of photosynthesis?
What is temperature, or increasing the amount of reactants?
Difference between pyrimidines and purines & which bases are which.
Pyrimidines are smaller with only 1 carbon ring (cytosine and thymine)
Purines are larger with 2 carbon rings (adenine and guanine)
Transcribe the following DNA code into mRNA, then translate it into protein using the codon chart:
TAC GTA ATG CCC AAG ATC
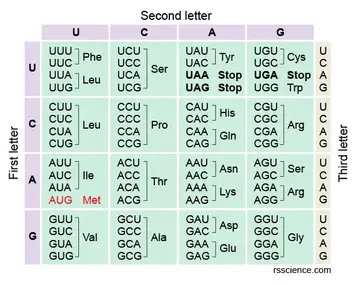
mRNA: AUG CAU UAC GGG UUC UAG
protein: Met - His - Tyr - Gly - Phe - Stop
