Why are greenhouse gases harmful?
Gases like CO₂ trap heat in Earth’s atmosphere, causing global warming.

What is a circuit?
A loop that lets electricity flow through to power devices.

What does “IR” stand for?
Infrared
What is the main purpose of a security system?
To protect people and property by detecting and alerting danger.
What is created around a wire when electricity flows through it?
A magnetic field.

What are the three essential parts of any simple circuit?
Source, Path, Load.
Name two renewable energy sources.
Solar, wind, hydropower, bio, and geothermal energy.

What’s the difference between open and closed circuits?
Closed = electricity flows (like a light on)
Open = electricity stops (like a light off).

What is the main difference between active and passive IR sensors?
Active IR sends out a beam and detects reflection; Passive IR senses heat radiation.

What does a tilt switch do?
It detects if something is tipped or moved from level position.
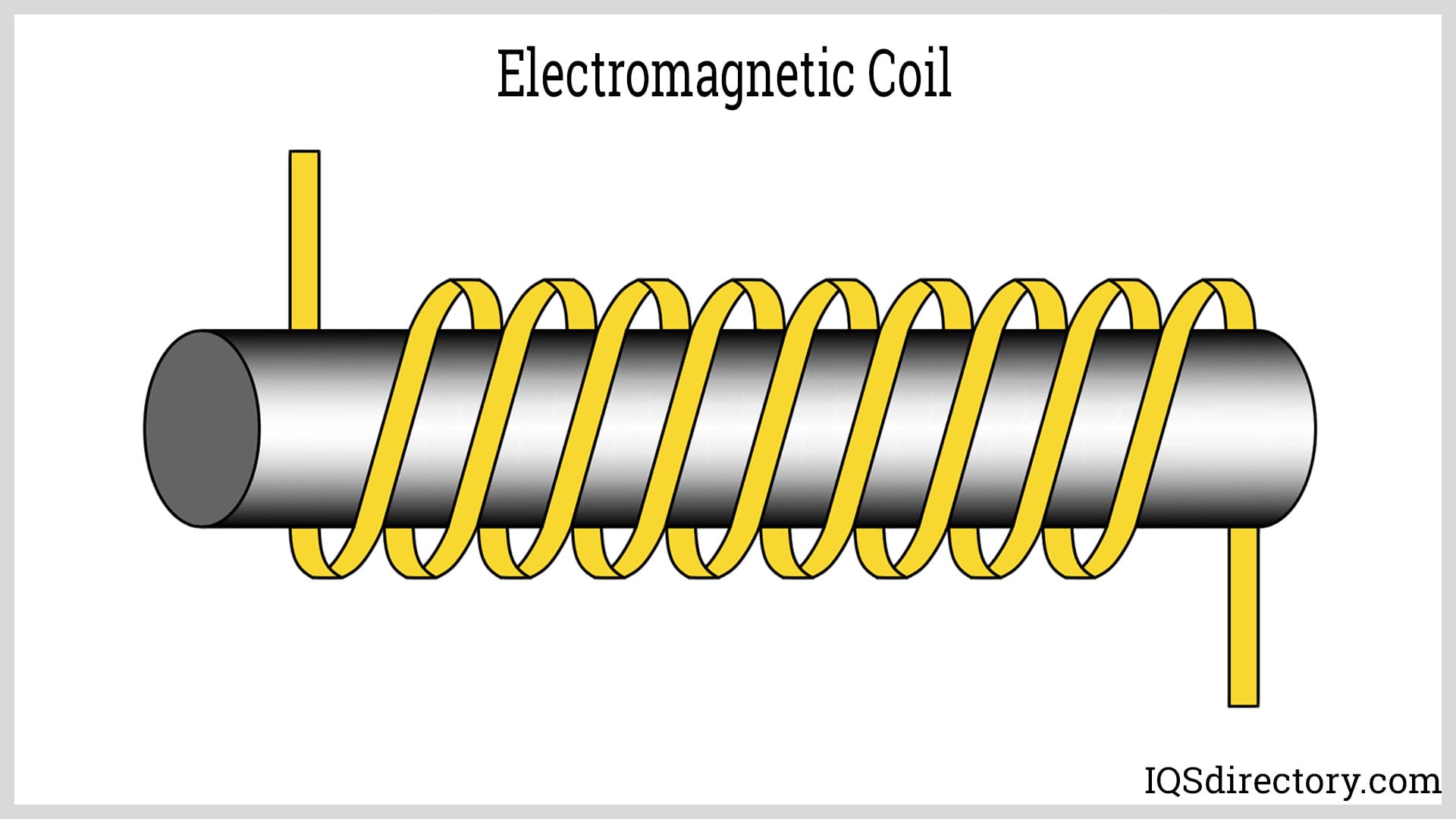
What is an electromagnet?
A magnet powered by electric current that can be turned on and off.
AC vs. DC: Which one comes from wall outlets, and which one comes from batteries?
AC = wall outlets; DC = batteries.

How do solar panels create electricity?
They collect sunlight in solar cells that convert light into direct current (DC).

What is a parallel circuit
A parallel circuit is an electrical circuit where multiple components are connected across separate branches, allowing current to split and flow through each path simultaneously
Name a device that uses an IR sensor.
TV remote, automatic door, or security light.
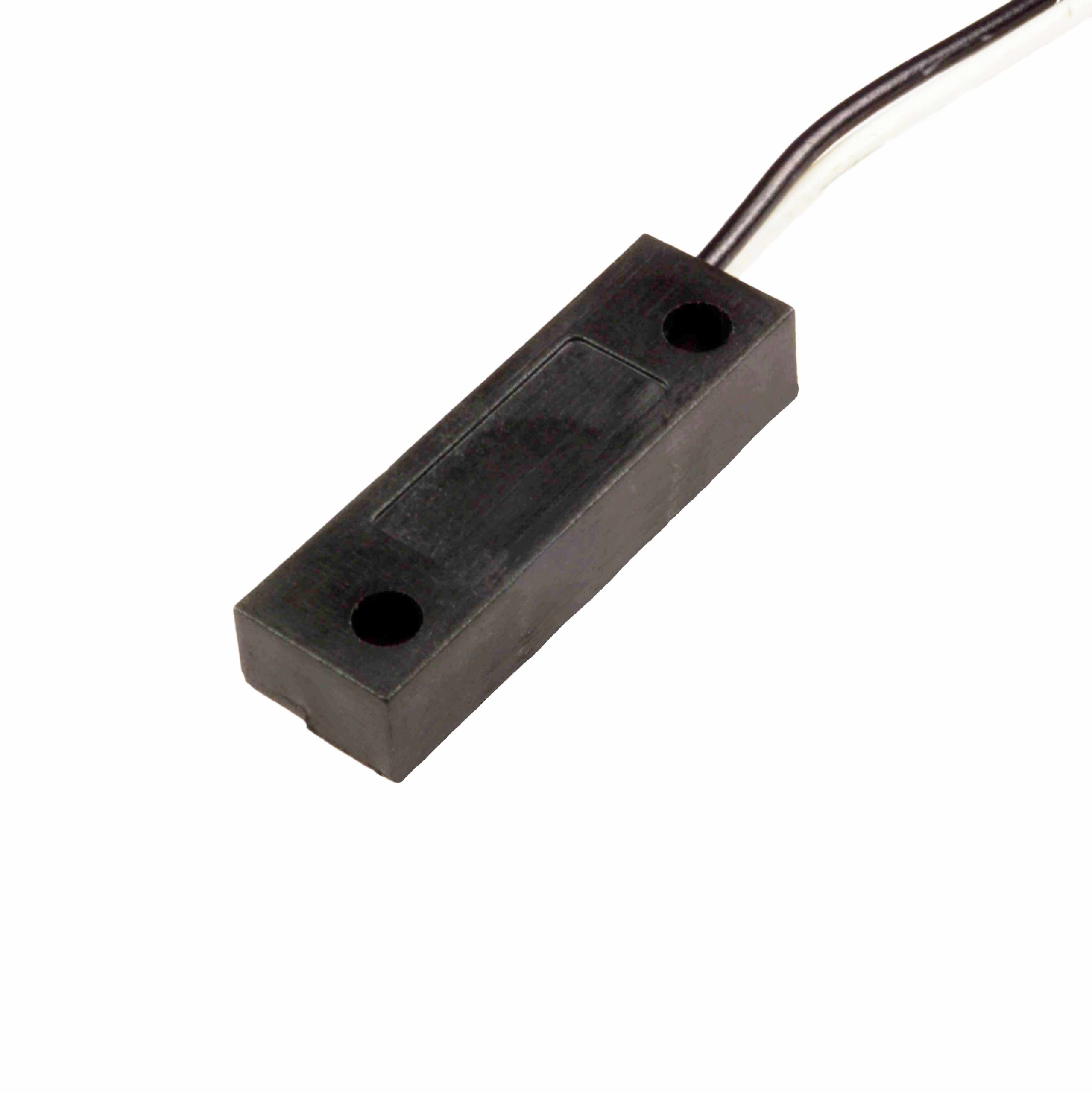
How does a magnetic reed sensor work?
It uses a magnet to close a circuit when doors or boxes are shut.

How can you make an electromagnet stronger?
Add more wire coils or increase the current.
What’s the difference between static electricity and current electricity?
Static stays in one place; current flows through a path/loop.
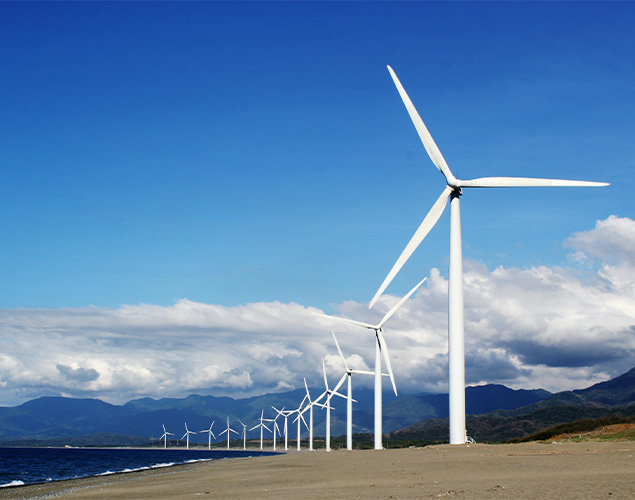
What machine does wind power use to generate electricity?
A wind turbine spins a generator to produce electricity.

Name one reason why we hide circuits inside devices.
For safety, protection, and design —to keep them clean and safe to touch.
Why might IR sensors not work well in sunlight?
Bright light interferes with infrared signals and confuses the sensor.
Name one real-world object that uses a tilt switch.
Pinball machine, car alarm, or treasure box alarm.

How do motors use magnetism to move?
They turn electric energy into motion by spinning a magnetic coil.
On a breadboard, what are the long edge strips called, and what do we usually connect to them?
They are power rails
connect + (red) – (blue/black) from the battery.

Why are renewable energies important for AI data centers?
They reduce pollution while meeting the growing electric demand from AI servers.

Why is polarity important when building a circuit?
Electricity must flow in the right direction (+ to –) or parts won’t work.

What is a JK Flip Flop used for in an IR circuit?
It stores on/off memory so a signal can toggle a light or motor.

How are VEX IQ and Scratch similar in coding?
Both use block-based logic with loops, events, and if/then blocks to control outputs.
What’s the difference between a permanent magnet and an electromagnet?
Permanent magnets always stick; electromagnets only work with electricity flowing.
In a series circuit with two LEDs, why do they get dimmer than in parallel?
In series they share the same current/voltage drop across more parts; in parallel each branch gets full supply voltage.