BUT you got this!
The process that transports rocks, soil and sediments to a different location is called _________.
A. Crystallization
B. Deposition
C. Erosion
D. Weathering
C. Erosion
Acid rain is an example of:
A. Physical Weathering
B. Chemical Weathering
B. Chemical Weathering
Which number represents the O - Horizon
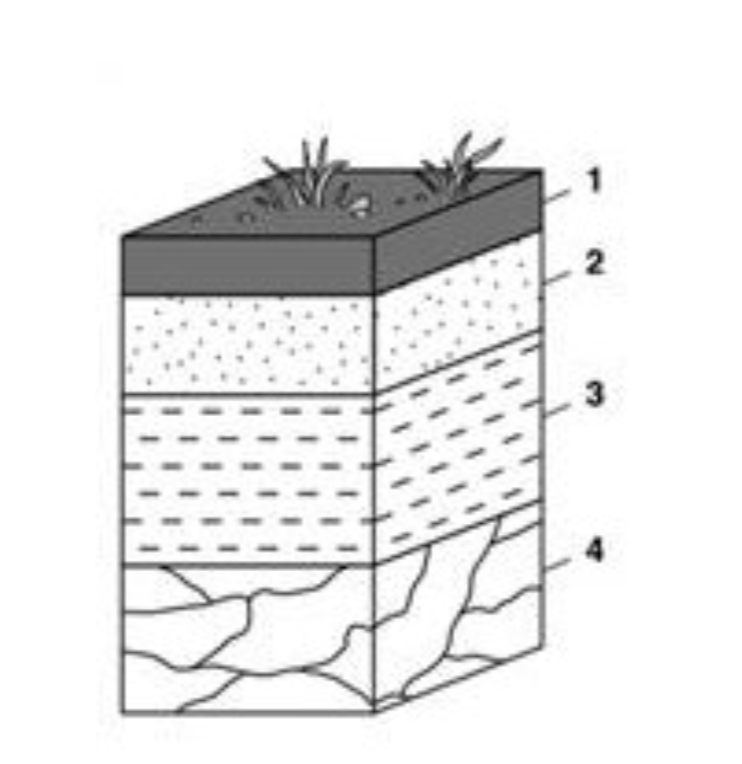
1
Fertility of soil relates to:
A. how the soil was formed over time
B. the amount of nutrients that allow plants to growth
C. the amount of water found in the soil
D. the amount of bacterias found in the soil
B. the amount of nutrients that allow plants to growth
The chart that allows you to determine what types of soil you have.
What is a Soil Triangle
Type of chemical weathering that turns rocks red because the minerals are reacting with the oxygen in the air.
What is Oxidation?
Which layer of the soil profile would be affected the most by weathering and erosion?
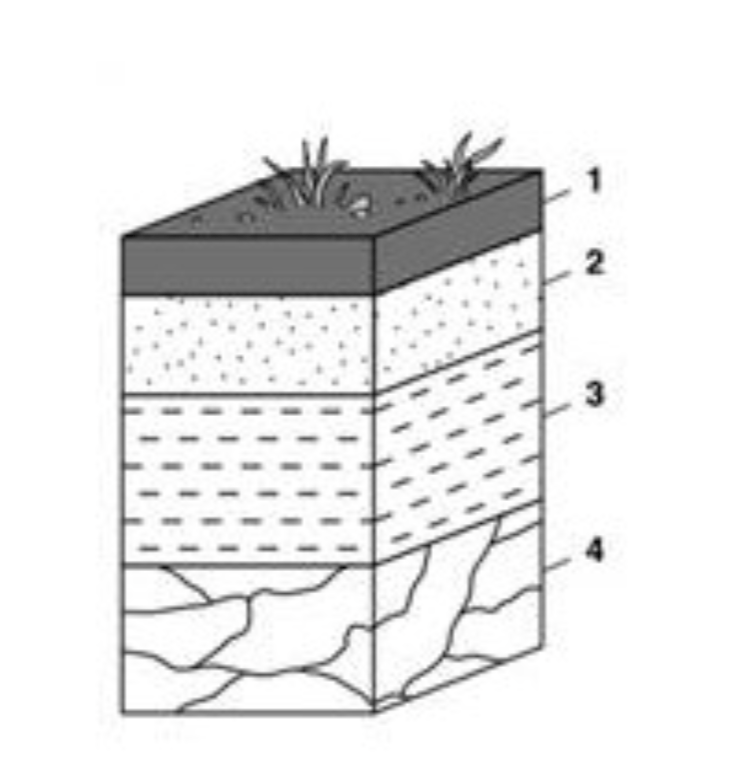
1
Ice expansion is an example of:
A. Physical Weathering
B. Chemical Weathering
A. Physical Weathering
Which of the following best describes how most soil forms?
A- through the growth of trees
B- through the build up of snow
C- through the weathering of rock
D - through the cooling of lava
C- through the weathering of rock
Soil color is a clue to the types and amounts of _________ and organic matter in the soil.
A. minerals
B. decomposers
C. air
D. water
A. minerals
Another name for a "Layer" of soil.
What is a Soil Horizon?
What type of acid forms when water combines with carbonates underground?
What is Carbonic Acid?
Flood waters moving soil from one location to another is an example of:
A. Crystallization
B. Deposition
C. Erosion
D. Weathering
C. Erosion
Which type of weathering is illustrated:

Chemical
Biological
Chemical and Biological
A ______ is a living thing that breaks down dead material, turning it into soil.
A. herbivore
B. decomposer
C. predator
D. carnivore
B. decomposer
The measure of how fast the water enters the soils is called:
A. infiltration
B. filtration
C. moisture
D. temperature
D.
A. infiltration
A picture or description of all of the layers of soil.
What is a Soil Profile?
Another name for the "A" horizon in soils.
What is Topsoil?
The process of breaking down rocks is called _______.
A. Crystallization
B. Deposition
C. Erosion
D. Weathering
D. Weathering
When the roots of a plant growth over a rock breaking it down is an example of:
A. Physical Weathering
B. Chemical Weathering
C. Biological Weathering and Physical Weathering
D. Biological Weathering and Chemical Weathering.
C. Biological Weathering and Physical Weathering
The layers of the soil are called:
A. Levels
B. Columns
C. Horizons
D. Spheres
C. Horizons
Choose the letter that better represents the blocky structure.
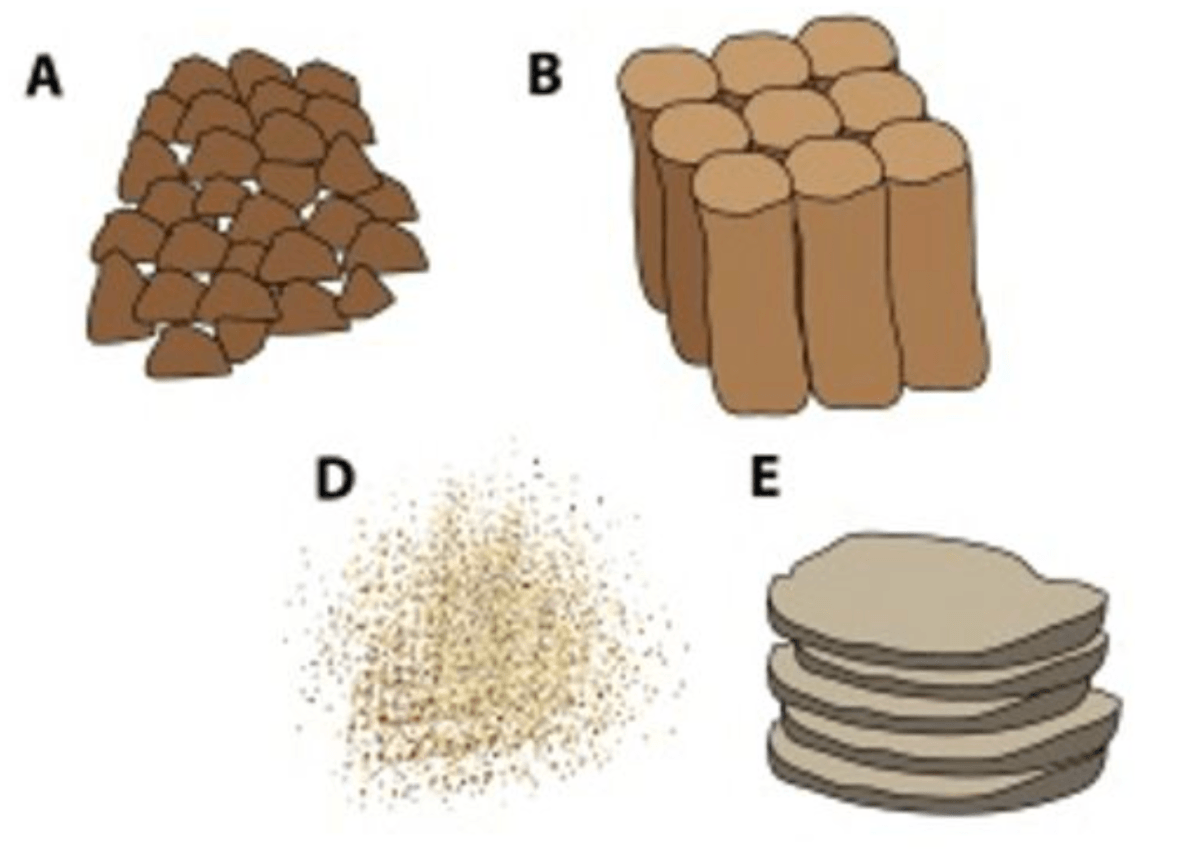
A
This forms when a soil containing Carbonates is reacted with Hydrochloric Acid?
What are Bubbles?
This type of mass movement leaves a crescent or "U" shaped scar on the land.
What is a slump?
Which of the following aids in the weathering and erosion of rocks?
A. rain
B. water
C. wind
D. all are correct
D. all are correct
Plants roots that secretes acids that gradually breaks down rocks is an example of:
A. Physical Weathering
B. Chemical Weathering
C. Biological Weathering and Physical Weathering
D. Biological Weathering and Chemical Weathering.
D. Biological Weathering and Chemical Weathering.
Decayed plants and animals in the soil create:
A. Humus
B. Bedrock
C. Weathered rocks
D. Subsoil
A. Humus
Choose the soil property illustrated:
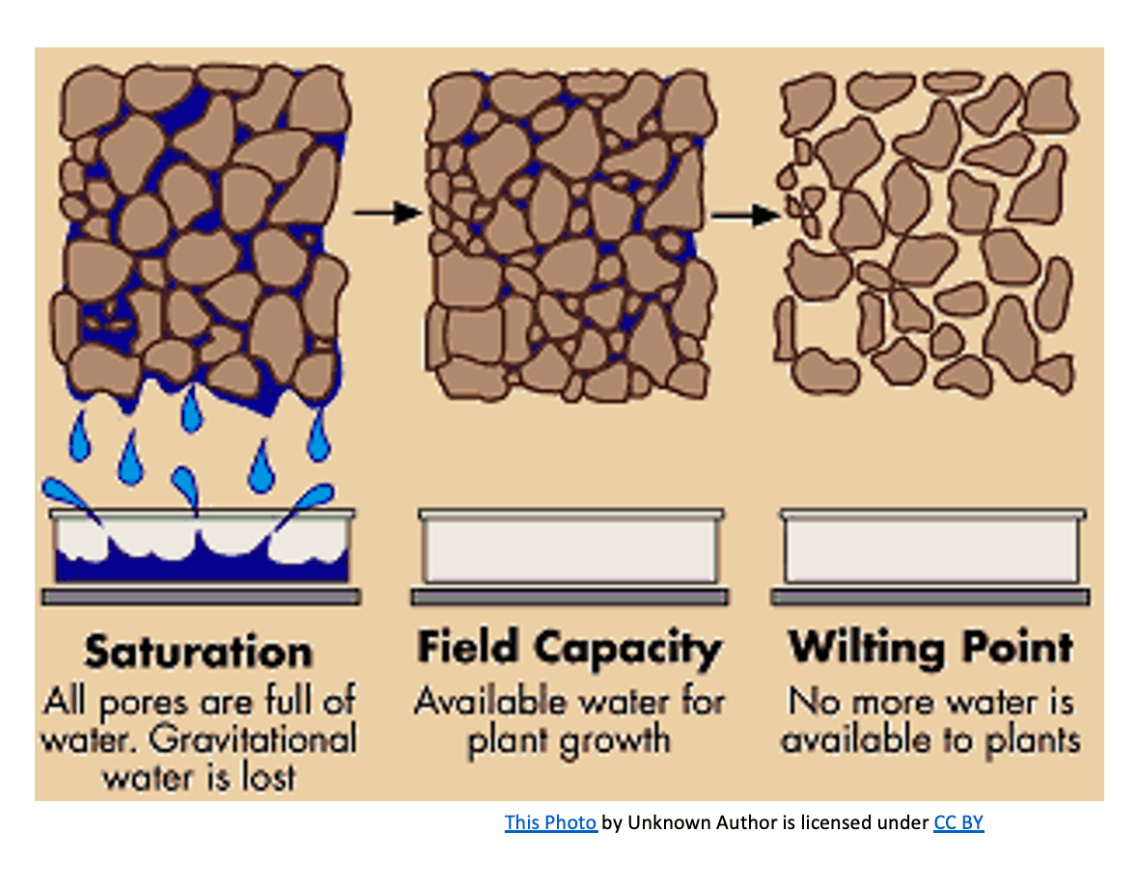
A. Soil consistency
B. Soil moisture
C. Soil Temperature
D. Soil pH
B. Soil moisture
This term describes the soil that is "mature" and has living and non-living components?
What is Organic?
True or False
Erosion and weathering works together to change the Earth's surface.
What is True
Erosion and weathering contribute to the development of different types of:
A. Faults
B. Landforms
C. Tectonic boundaries
D. Stress
B. Landforms
Which type of weathering is illustrated:

Physical
The solid layer of rock at the bottom of the soil profile is called:
A. Topsoil
B. Subsoil
C. Humus
D. Bedrock
D. Bedrock
Gardeners and farmers are sometimes concerned about soil being to acidic. Which pH reading could be found in a soils that is slightly acidic?
A. 3.1
B. 5.5
C. 7.1
D. 9.7
B. 5.5
Which 2 earth systems are involved in the following statement: Plants grow in Soil.
A- Biosphere
B. Atmosphere
C. Hydrosphere
D. Geosphere
A- Biosphere
D. Geosphere
Which is the largest soil particle?
A. clay
B. sand
C. silt
What is Sand