& Spectra
What is a constellation?
A constellation is a group of stars in the (night) sky that often make a shape.

What is the electromagnetic system?

It is the full range of all types of radiation. It includes magnetic and electric fields that travel in waves. It's organized by frequency/wavelength.
Definition of the effect?
An increase or decrease in light/sound frequency (the source) due to the observer's distance (moving relative to the source)
What are the most common star colors?
Red, orange, yellow, white, blue
What is the diagram?
It shows the relationship between a star's temperature and luminosity.
How many constellations are there?
88
How is spectra applied to astronomy?
Spectra shows the intensity of light being emitted over a range of energies; a common example of it is rainbows. In astronomy it helps understand how black holes, galaxies, and neutron stars produce light.

Red vs. Blue Shift?
Red- object moving away
Blue- object moving towards
Why does the viewer see the stars as the same despite their distance?
The apparent magnitude of star A makes it appear the same brightness as B because it's closer. B is the brighter star but the distance makes it look dimmer and the same as star A.
What are the main 4 groups of the diagram?
Super Giants, Giants, Main Sequence, and White Dwarfs

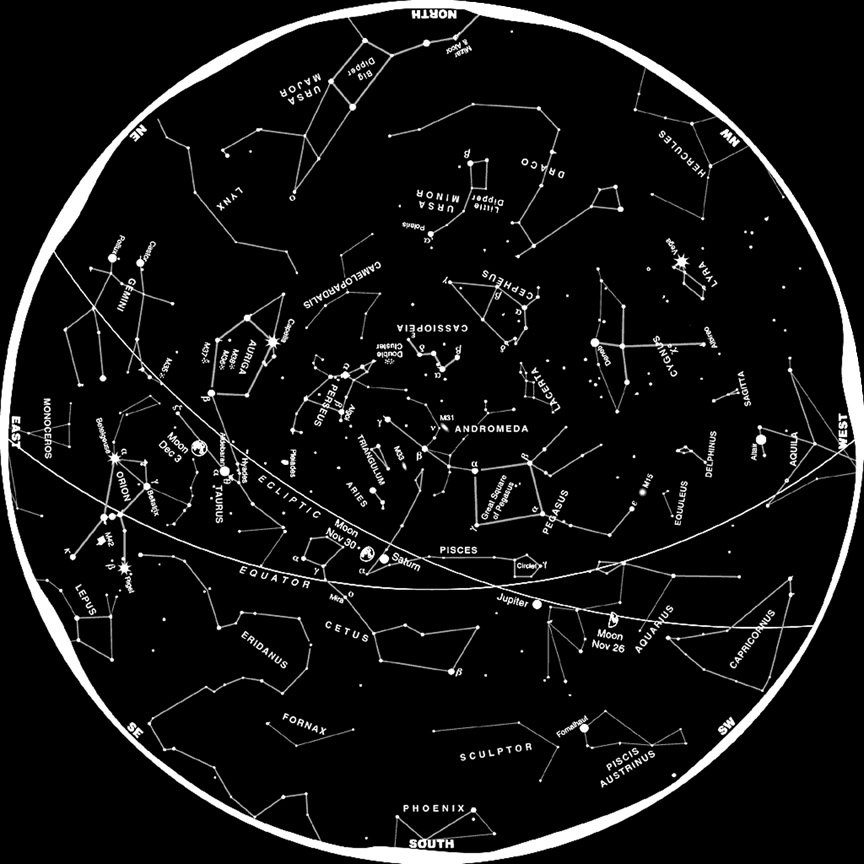
 What constellation is this?
What constellation is this?
Ursa Major-
Known as the Great Bear, it is the largest constellation in the Northern Sky. The brightest star in the constellation is Alioth.
What are the 7 electromagnetic waves?
Radio, microwaves, infrared light, visible light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, and gamma rays
What do the wavelengths mean? 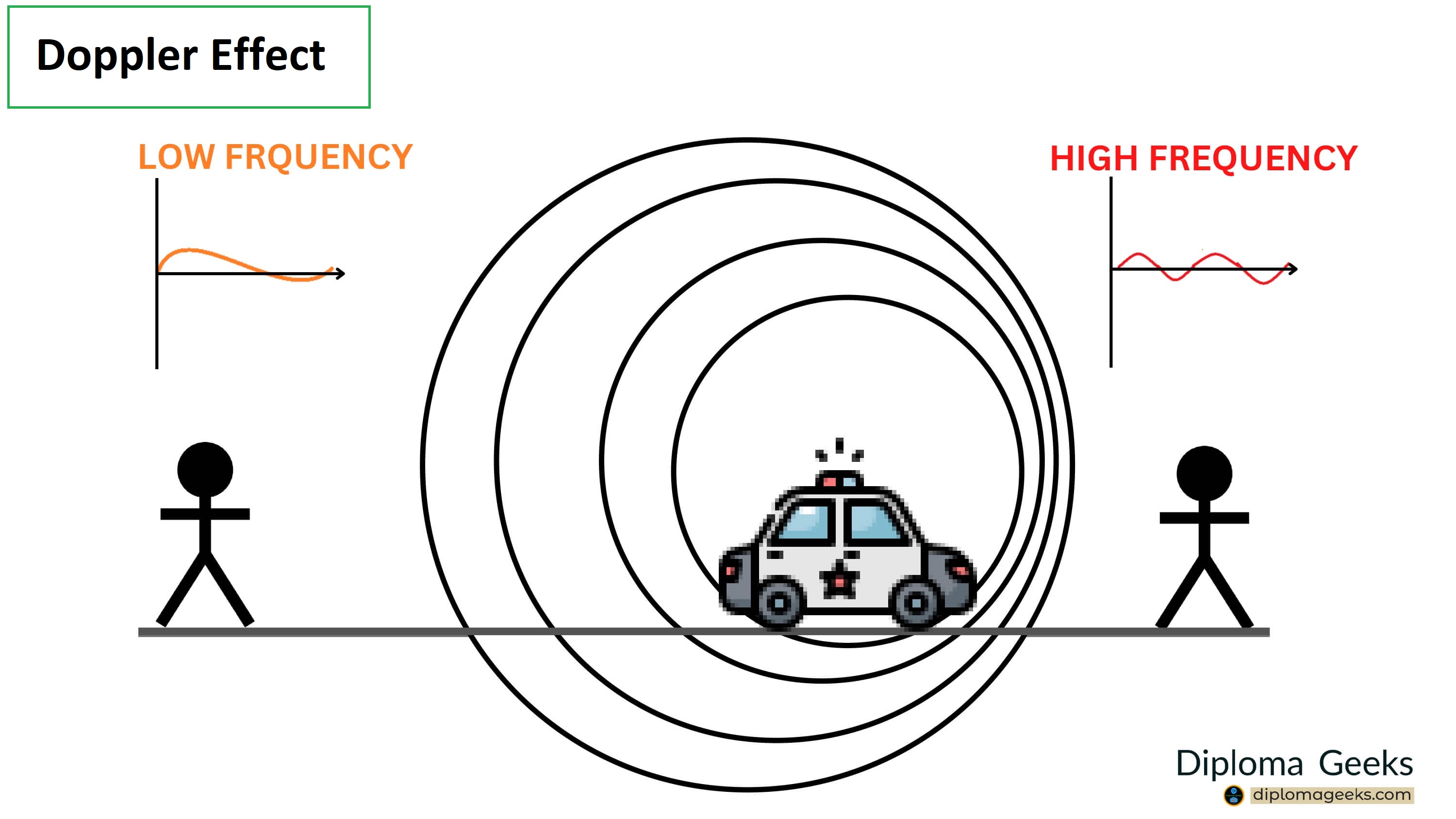
Low frequency is going to experience a red shift as the wavelengths are becoming longer and more spread out.
High frequency is going to experience a blue shift as the car is approaching them making the wavelengths shorter and more compact together.
How are these concepts related?
They are related because they both involve the color of stars, and what information we can discover about them.
What group are the majority of stars in?
Main sequence
What constellation is this?

Orion-
Visible during winter in the Northern hemisphere. Rigel and Betelgeuse are the brightest stars.
What has more energy: red or purple wavelengths?
Purple- it has a high frequency because the wavelengths are shorter
Red- it has a lower frequency due to the longer wavelengths

What would someone in the middle hear?
They would hear an average/regular siren as they are directly at the source. They are not shifting towards or away from it.
What do star colors indicate about their temperature and age?
The color indicates the surface temperature being emitted (blue-hottest red-lowest heat)
Due to running out of hydrogen to burn when stars age, they emit less energy. So younger stars can be bluer compared to older ones who are red.
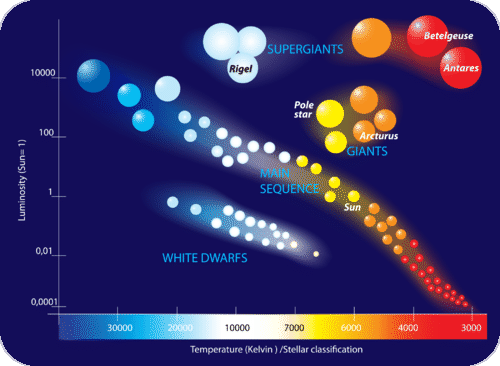
Supergiants- size, temperature, and luminosity
What two languages are used for naming the constellations?
Greek and Latin
How does the electromagnetic spectrum relate to astronomy?
It relates because astronomers use telescopes that have lenses that are special to specific parts of the electromagnetic system. This allows them to see different parts and focus on specific celestial bodies.
How is it applied in astronomy?
By observing and using the Doppler Effect it allows astronomers to see how fast something is coming towards Earth (blue Shift) or away from Earth (red shift). Or it can be used to see the general direction the object is going in space.
Absolute vs. Apparent Magnitude
Absolute: the actual brightness of the star
-Mnemonic: absolute
Apparent: the brightness of the star seen from Earth -Mnemonic: appears
What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity?

The Supergiants and Giants have low temperatures but high luminosities.
red-yellow colors