Asexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction
This is the portion of DNA that codes for a protein.
This is the type of reproduction associated with mitosis.
What is asexual reproduction?
This is the type of reproduction associated with meiosis.
What is sexual reproduction?
This occurs when individuals within a single species are unable to mate (or reproduce), therefore 2 new species are formed.
What is speciation?
This is the model used to predict the possible phenotypes and genotypes of offspring.
What is a Punnett Square?
What is the acronym for deoxyribonucleic acid.
What is DNA?
This is the correct order of the phases of mitosis.
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, & Telophase (PMAT)
What is the main difference between the chromosome number at the end of mitosis and chromosome number at the end of meiosis?
In mitosis, the chromosome number is the same as the parent, whereas in meiosis, the chromosome number is cut in half.
These are the types of structures that are studied to determine evolutionary relationships.
What are homologous and analogous structures?
What are the two factors that influence the growth of organisms?
What are environmental and genetic factors?
This is the form DNA takes when traits are being passed from one generation to the next.
What is a chromosome?
True or False:
Organisms that use asexual reproduction produce offspring genetically identical to themselves.
True
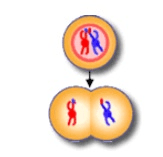 This event occurs during Metaphase I of meiosis and leads to genetic information switching chromosomes.
This event occurs during Metaphase I of meiosis and leads to genetic information switching chromosomes.
What is crossing-over?
This scientist is credited with developing the Theory of Evolution (Natural Selection).
Who is Charles Darwin?
This is the type of plants that Mendel was studying when he discovered the laws of genetics.
What are pea plants?
This is where chromosomes found within a cell.
What is the nucleus?
This is the number of cells and type of cells produced from a cell undergoing mitosis.
What are 2 identical diploid cells?
This is the number of cells and type of cells produced from a cell undergoing meiosis.
What are 4 unique haploid cells?
This type of selection is considered to be man-made. Examples include selective breeding and bioengineering.
What is artificial selection?
This scientist is known as the Father of Genetics.
Who is Gregor Mendel?
This is the correct order in the relationship between DNA, protein, gene, and chromosome.
What is DNA, genes, protein, and chromosome?
What is 36 chromosomes?
At the beginning of meiosis, a parent cell has 36 chromosomes. How many will each of the 4 daughter cells have?
What is 18?
This theory states that organisms the process by which organisms change over time due to the development of inheritable physical or behavioral traits which makes them likely to survive.
What is the Theory of Natural Selection?
In a cross between 2 heterozygous parents (Hh), what would possible genotypic percentages?
What is:
HH -25%
Hh - 50%
hh -25%