Plant and animal cells are both examples of what type of cell?
What are eukaryotes?
In this food chain:
grass → grasshopper → frog
Name the producer.
What is the grass?
A group of organs working together (like the digestive group) is called this.
What is an organ system?
Which is abiotic: fungus, sunlight, leaves, bacteria.
What is sunlight?
Lion hunting zebra—name the interaction.
What is predation?
What is this organelle?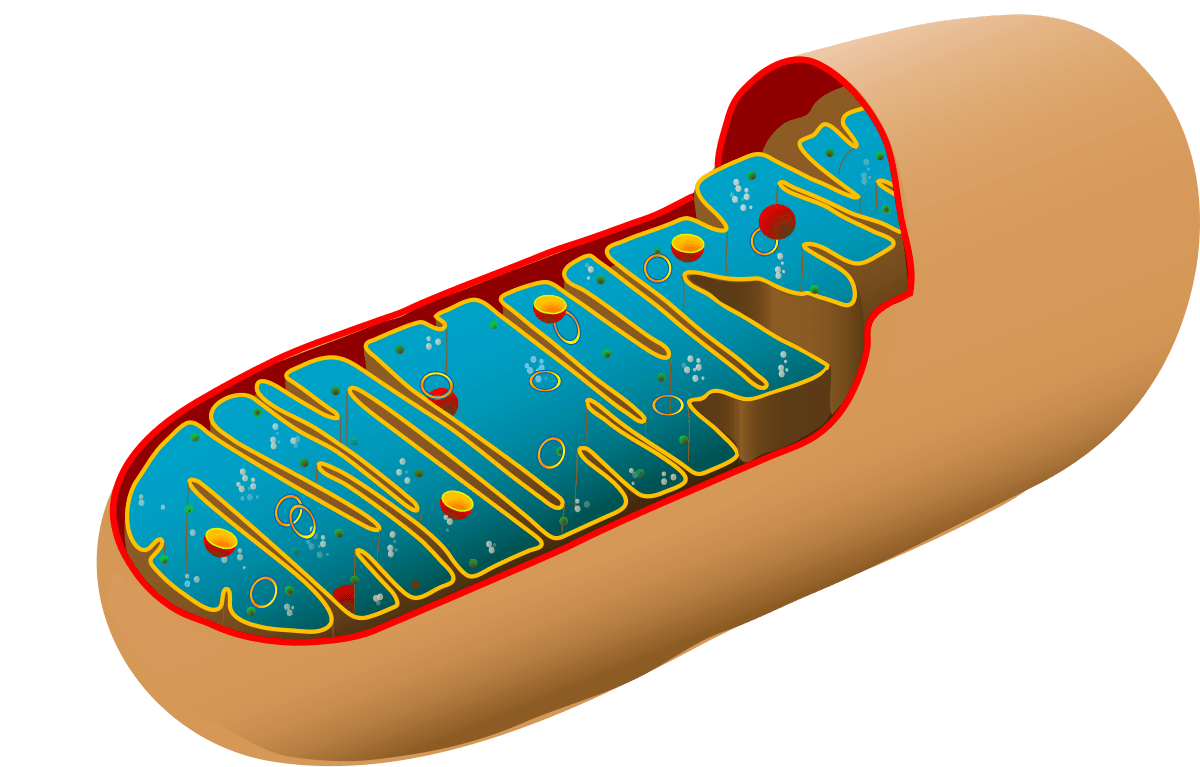
What is mitochondria?
Organisms that break down dead material and recycle nutrients.
What are decomposers?
Put these in order (small→big): organ systems, tissues, organism, organs, cells.
What is cells→tissues→ organs→ organ systems→ organism?
Name one example of a natural disaster?
What is a wildfire, hurricane, tornado, earthquake, flood, etc.
Answers will vary.
Two oak seedlings growing side-by-side both need sunlight and water. Name the interaction.
What is competition?
What is this organelle?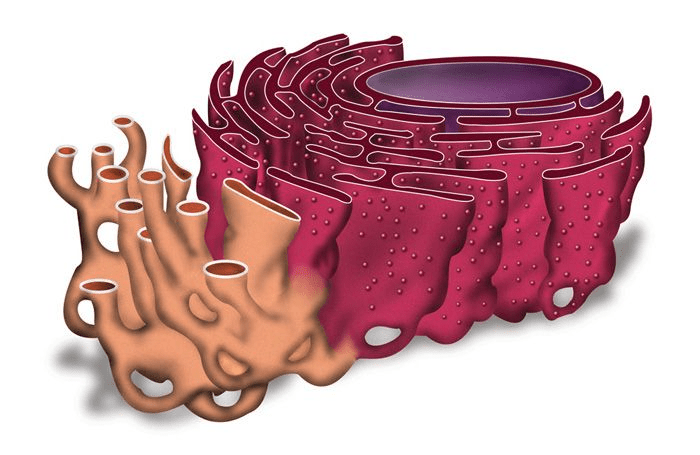
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The arrows in a food web show the transfer of this.
What is energy?
What are all individuals of the same species in the same area?
What is a population?
A pond’s water level drops for weeks. Predict what happens to the fish population and name the limiting factor.
Fish decrease; limiting factor = water (or oxygen)
Tick on a dog—one benefits, one is harmed. Name the interaction and the roles.
What is parasitism? (tick = parasite, dog = host)
What are the three organelles that are found in plant cells but not animal cells?
What is cell wall, chloroplast, and central vacuole?
In an energy pyramid:
- which level has the most energy?
- why do higher levels usually have less energy?
Producers (the bottom of the pyramid) have the most energy.
Higher levels have less energy because they do not get their energy from a direct source (like the sun). Consumers have to get their energy from other organisms.
What is the level that includes multiple populations interacting with one another?
What is a community?
Clue: Identify the level in each case.
A) “All ducks in City Park Pond” → ________
B) “Ducks, fish, insects, and plants in City Park Pond” → ________
C) “City Park Pond + water, rocks, air, and sunlight” → ________
D) “Desert areas around the world” → ________
A) Population B) Community C) Ecosystem D) Biome
Cleaner shrimp removing parasites from a moray eel—both benefit. Name the symbiosis type.
What is mutualism?
What are the three statements of the cell theory?
What are
1. All living things are made of cells.
2. All cells come from pre-existing cells.
3. Cells are the basic unit of life.
In a meadow food web:
grass → rabbit → hawk AND
grass → grasshopper → frog → hawk
If the hawk population drops, what is one population likely to increase and one likely to decrease? Explain briefly using the food web.
Increase: rabbits or frogs/grasshoppers (fewer predators).
Decrease: grass (more rabbits/grasshoppers eating it).
Order these (small→big): biosphere, ecosystem, organisms/species, community, biome, population.
What is organisms/species → population → community→ ecosystem→ biome→ biosphere?
After a flood, which limiting factor most immediately limits burrowing animals? (creatures that dig holes or tunnels in the ground to create homes for themselves)
What is shelter/space?
Remora riding on a shark to catch scraps; the shark isn’t helped or hurt. Name the symbiosis type.
What is commensalism?