Name the three cells of the mucosa of the stomach.
Parietal cells, Chief cells, and Enteroendocrine cells.
Breaks down the bolus into.
Chyme 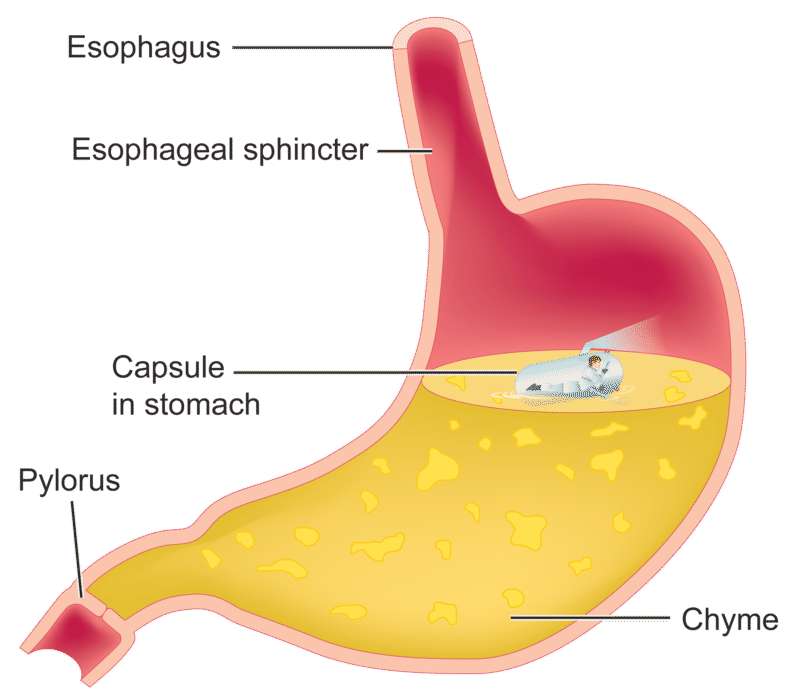
The stomach is connected to what organ?
The small intestine at the duodenum.
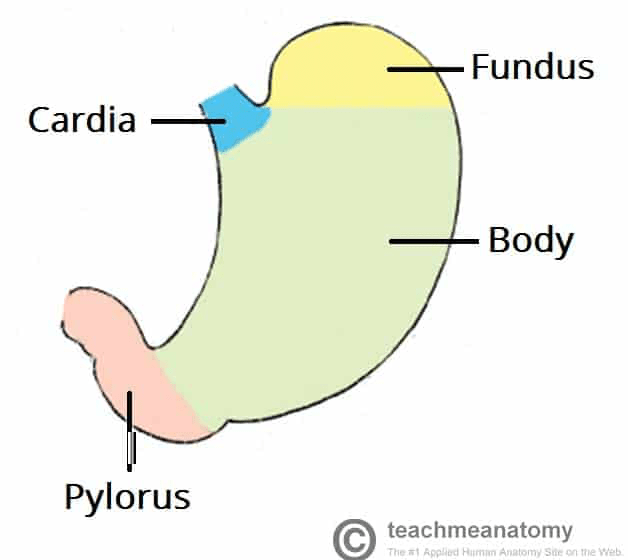
How many regions of the stomach are there?
4
How does the stomach break down food?
Through mechanical and chemical digestion.
Which cell is responsible for the secretion of pepsin?
Chief Cells
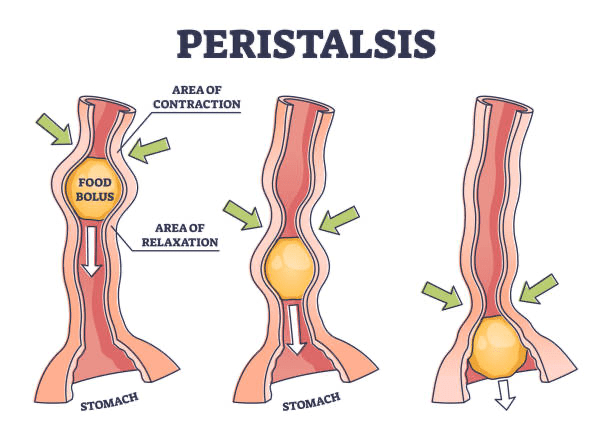
The movement of the breaking down of the bolus.
Peristalsis
Name the regions from superior to inferior.
Cardiac, Fundic, Body, Pyloric
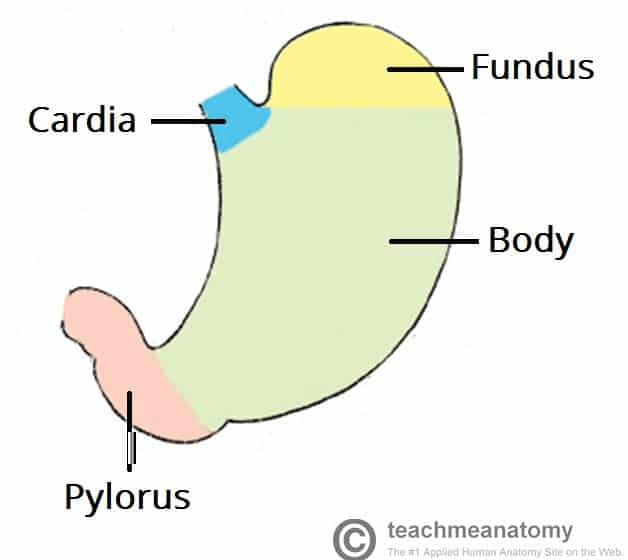
What is the most superior region?
Cardiac
Once your stomach receives food, it produces acids and enzymes for what?
Breaking down food
The gastric pit and gastric gland are found in what layer of the stomach wall?
Mucosa
What stage of digestion occurs in the stomach?
Gastric phase
The stomach begins and ends where?
Begins at the esophagus and ends at the duodenum.
What is the middle region of the stomach?
The body.
Bolus enters the stomach through what organ?
Esophagus
Name the three layers of the muscularis externa of the stomach.
Oblique layer, circular layer, and longitudinal layer.
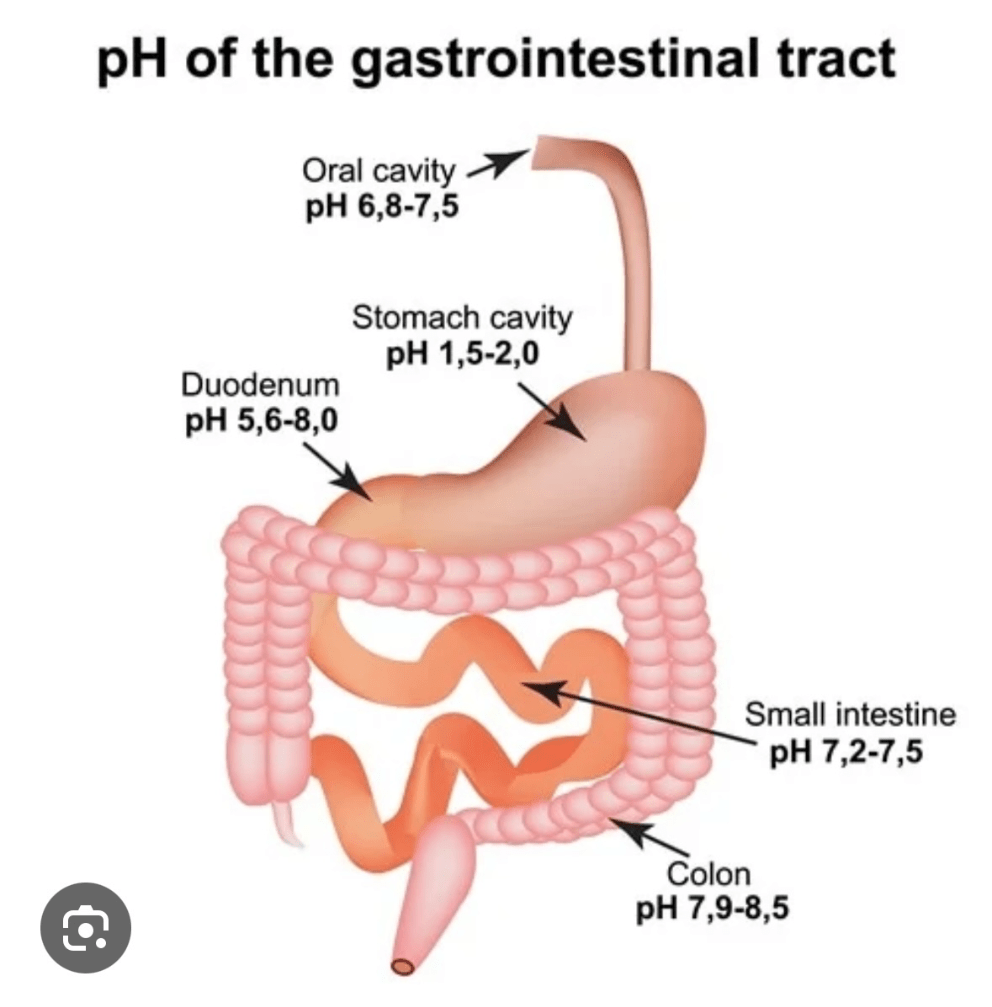
What is the pH of the chyme after peristalsis and the mixing of hydrochloric acid?
2
The mucosa layer is folded into what?
Rugae
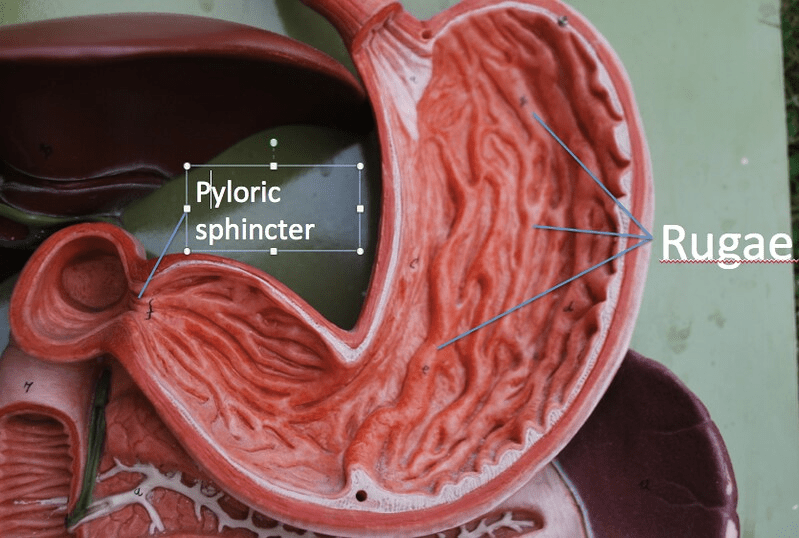
What does the pyloric region encase?
Pyloric Sphincter and Pyloric Orifice, right before entering the Duodenum.
What is the process of propulsion?
The stomach’s muscular walls churn and mix food with digestive juices, which breaks down food into smaller pieces.
What type of cells line the inner surface of the stomach?
Surface mucous cells or foveolar cells
What type of digestion mainly occurs in the stomach
Chemical digestion
What does the enteroendocrine cell do in the stomach?
Secretes gastrin, which stimulates secretion by parietal cells.
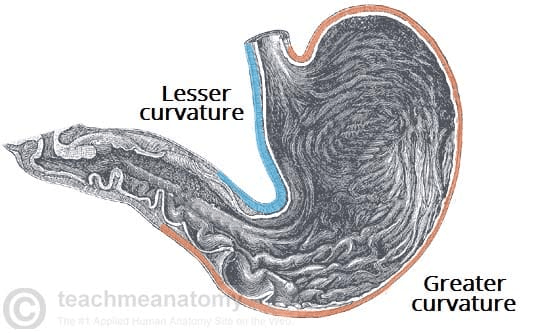
The convex lateral surface of the stomach is ____.
Greater curvature.
How does food move through the digestive system?
By wavelike muscle contractions.