Jill is the CEO of Note’s Etc, a stationary manufacturer. She decides to open up a retail store to sell her products directly to consumers instead of just selling to retailers. In order to do this, Jill will need to engage in ________, which is a corporate level, strategy.
Forward vertical integration
List and define the three types of diversification using the case of Disney or Amazon (it is not about levels of diversification or not corporate diversification!)
Product Diversification:
•Increase in variety of products / services.
•Active in several product markets.
Geographic Diversification:
•Increase in variety of markets / geographic regions.
•Regional, national, or international markets.
Product-Market Diversification:
•Product and geographic diversification.
What is the main reason that acquisitions fail?
Post-acquisition integration (lack of cultural fit)
This is my favorite fast-food chain. Give the name of the chain and cite one example of local adaptation viewed in class.
McDonalds - germany (mc brezel), brazil (pao de queijo/mc cafe/guarana), thailand (temples, eggs), japan (shrimp burger)
What is the role of a firm from a sustainable development/sustainability perspective?
They are fundamental actors within a community and have direct and indirect impact in many sustainability indicators
To create jobs
To promote social good - do good stuff
Contribute to environmental protection
This tool helps decision-makers visually map options and their potential outcomes, often assigning probabilities to branches to evaluate risks and benefits.
A decision tree
A vertical market failure happens
when transactions in the market are too risky or costly.
OR
when there are small number of buyers and suppliers, asset specificity, and frequent transactions
LVMH’s acquisition of luxury hotels and high-end skincare brands builds on its core strengths in luxury branding, design, and customer experience. This type of diversification, where some but not all competencies are shared, is called what?
related linked diversification
LVMH enters new industries (like hospitality or wellness) where some core capabilities—like luxury experience management—can still be leveraged. This is more flexible than “constrained” diversification, but still strategic.
DAILY DOUBLE
NoRu Inc. is a publicly traded firm that does not wish to be acquired by FRESHPoP Corporation, a much larger publicly traded firm, who is planning an acquisition of NoRu Inc. This is an example of a
Hostile Takeover
Name and define the elements of the framework we use in International Business to assess the similarities and/or differences between home and host countries when internationalizing?
Distance is the main cost and risk of expansion.
CAGE is an acronym for different types of distance:
•Cultural.
•Administrative and political.
•Geographic.
•Economic.
Guides multinational enterprise decisions on which countries to enter.
How to balance market and nonmarket strategies?
Understand community needs, firms' assets and capabilities as well as firms' performance and market strategy.
This type of cognitive bias occurs when individuals over-rely on the first piece of information encountered during decision-making, potentially distorting outcomes. What is this bias called?
anchoring bias
Name the two types of transaction costs firms experience when engaging in market transactions and give ONE example of each
External transaction costs:
•Searching for contractors.
•Negotiating, monitoring, and enforcing contracts.
Internal transaction costs:
•Recruiting and retaining employees.
•Setting up a shop floor.
Explain the relationship between diversification and the performance of a firm.
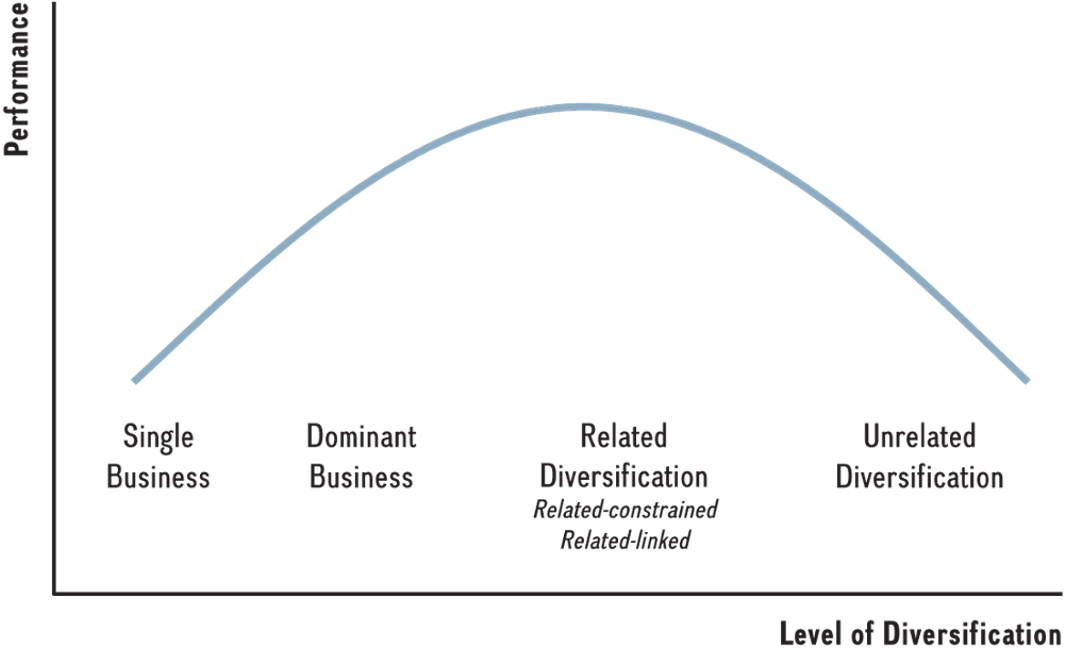
List four of the five reasons we discussed in class why firms enter into strategic alliances/M&AS
Strengthen competitive position.
Change industry structure, influence standards.
Enter new markets.
New products, service, or geographic market
Hedge against uncertainty.
Real options perspective (staggered investment)
Access critical complementary assets.
Marketing, manufacturing, after-sale service.
Learn new capabilities.
Co-opetition & learning races
Market Power
Transferring skills
Cost savings
Maintain competitive parity
Revenue enhancement
Explain what is the Global Standardization Strategy and give at least two examples of companies that implement this strategy.
Pursuing lower costs and economies of scale
Duracell, Caterpillar, Microsoft
List the three types of CPA tactics
Financial; informational; constituency building
Despite knowing the right actions to take, such as washing hands in hospitals or wearing seat belts, individuals often fail to follow through. What is this behavioral challenge called?
The knowing-doing gap
This luxury conglomerate uses backward integration not only to control raw material sourcing (e.g., vineyards, tanneries, and textile production) but also to protect craftsmanship and product quality across its portfolio of 75+ brands. This decision reflects which key benefit of vertical integration?
Facilitating investments in specialized assets —especially relevant in industries with high asset specificity and brand-driven value creation.
LVMH vertically integrates to directly own and manage parts of its supply chain that require high craftsmanship, quality, and brand protection. These are specialized assets—like leather tanneries or heritage vineyards—that are critical to the luxury value proposition. Because these assets are unique and not easily substituted, owning them allows LVMH to invest in them without risk of suppliers failing to meet standards or switching to competitors. This reduces coordination risks and ensures long-term brand integrity.
Companies' diversification across product categories and geographies supports performance by reducing exposure to demand shocks in any one segment or region. This benefit of diversification is known as what?
risk reduction through portfolio diversification
By spreading operations across brands and markets, LVMH buffers itself against sector-specific downturns (e.g., a drop in wine sales won’t collapse the group if fashion and cosmetics perform well). This improves long-term stability and investor appeal.
Instead of acquiring a local firm or building new operations from scratch, a company may choose to partner with a local player in exchange for equity to share market knowledge, distribution networks, and risk. This market entry strategy is known as what?
Equity Alliance
It allows firms to enter new or foreign markets by collaborating with local partners in exchange of investments/equity. This reduces cultural and operational risks, speeds up market access, and enables knowledge transfer—without requiring full ownership or investment. In the luxury sector, alliances may help with local distribution, licensing, or co-branding to test new markets before committing capital.
Name the mode of entry that (1) requires the least investment and yields the least control and (2) requires the most investment and yields the most control for the headquarters

Define "lobbying" and list two issues associated with this tactic
Lobbying is a form of corporate political activity in which firms engage with government officials, policymakers, or regulatory agencies to influence legislation, regulation, or public policy in ways that support their business interests. This can involve direct communication, participation in advisory committees, or hiring professional lobbyists to advocate on the company’s behalf.
Two key issues associated with lobbying:
Unequal Influence:
Large corporations often have greater financial and organizational resources to engage in lobbying, which can lead to disproportionate influence over public policy compared to smaller firms or civil society. This raises concerns about fairness and democratic accountability.Public Perception and Legitimacy Risks:
Lobbying efforts—especially when done behind closed doors or perceived as self-serving—can lead to reputational damage and accusations of regulatory capture or corruption. This may erode public trust in both the company and the policymaking process.
Give ONE example of firms successfully using blue ocean strategy discussed in class and explain what drives their success
cirque du soleil, trader joes
When LVMH chooses to integrate forward into retail—owning its boutiques instead of relying on third-party retailers—it avoids diluted customer experience and maintains full control of pricing, merchandising, and service. This strategic choice most directly addresses what concept covered in vertical integration theory?
Vertical market failure.
Vertical market failure happens when relying on external partners—like retailers—leads to poor coordination, inconsistent service, or misaligned incentives. For a luxury brand like LVMH, these risks are too high. If third-party retailers discount products, provide poor service, or misrepresent the brand, it damages the overall brand image. By owning the stores (forward integration), LVMH avoids these problems and maintains full control of how its products are sold and experienced.
DAILY DOUBLE
When LVMH acquires established luxury brands—like Tiffany & Co. or Bulgari—instead of developing competing products internally, it is choosing which entry mode in the Build–Borrow–Buy (OR Make-Buy-Ally) framework, and what does this suggest about its diversification priorities?
Buy—to quickly acquire brand equity and strategic assets that would be costly or slow to build organically
LVMH often chooses “Buy” in the Build–Borrow–Buy framework to enter new product segments or reinforce its dominance in luxury categories. This approach enables rapid diversification while capturing intangible assets like brand heritage, customer loyalty, and distribution networks—critical in luxury markets where reputation takes decades to build.
Explain using the Porter's Three Tests (attractiveness, cost of entry and better off test) why Microsoft's acquisition of Activision Blizzard can be deemed successful?
1. Industry Attractiveness Test
This test asks: Is the industry Activision operates in fundamentally attractive in terms of profitability and growth?
✔️ Yes. The global gaming industry is large, growing, and highly profitable, with strong long-term demand, especially in mobile and cloud gaming. Activision Blizzard owns top-tier franchises like Call of Duty, World of Warcraft, and Candy Crush, making it a leader in a very attractive segment of the digital entertainment market. The gaming industry also benefits from increasing digital distribution, user engagement, and subscription-based models—all aligned with Microsoft’s strategic goals.
2. Cost of Entry Test
This test asks: Is the cost of entering the industry through acquisition so high that it erodes future profits?
✔️ Partially. At $68.7 billion, the acquisition was expensive—the largest in Microsoft’s history—but Microsoft has the financial strength to absorb it. While the cost is high, the acquisition provides not just new revenue streams, but also valuable IP, a massive user base, and talent. Moreover, compared to building this portfolio from scratch, the acquisition accelerates Microsoft’s ambitions in gaming and the metaverse, potentially justifying the high price over time.
3. Better-Off Test
This test asks: Will the two companies create more value together than separately?
✔️ Yes. Microsoft can leverage its cloud infrastructure (Azure), subscription service (Game Pass), and device ecosystem (Xbox/PC) to scale Activision’s reach. The acquisition enhances Microsoft’s vertical integration in gaming by combining content creation (Activision) with distribution and platform ownership (Xbox, Game Pass, cloud). This synergy can improve margins, user retention, and competitive positioning—especially against rivals like Sony and emerging cloud gaming players.
Conclusion:
While the cost of entry is high, the acquisition appears to pass all three of Porter’s tests, especially the industry attractiveness and better-off tests. If executed well and if regulatory hurdles are managed effectively, the deal positions Microsoft as a dominant player in a fast-growing entertainment sector.
List and define the two facets or dimensions of globalization
•The globalization of markets refers to the merging of historically distinct and separate national markets into one huge global marketplace
•The globalization of production refers to the sourcing of goods and services from locations around the globe to take advantage of national differences in the cost and quality of factors of production (labor, energy, land, and capital)
What is the name of the sustainability agenda of the United Nations for 2030?
Sustainable Development Goals
DAILY DOUBLE
This cognitive bias occurs when a company chooses to ignore critical risks or warning signs—often because acknowledging them would require difficult choices or threaten existing incentives. Can you name it and provide an example in the context of your client?
TBD
Margaret Heffernan’s concept describes how people ignore obvious problems or avoid acknowledging them because resolution would disrupt the status quo.