Massive Dynamic Computers sources the components for its laptops from various suppliers on the market. The firm pays $100 for processors, $35 for disk drives, $50 for screens, $10 for memory, and $40 for graphics and wireless internet cards. Massive Dynamic has determined that it would cost $200 per unit to produce all of the necessary components in its in-house manufacturing facility. In this scenario, Massive Dynamic should make or buy?
Make (vertically integrate)
Backward Vertical Integration:
•Owning inputs of the value chain.
Forward Vertical Integration:
•Owning activities closer to the customer.
List and define the three types of diversification using the case of Disney
Product Diversification:
•Increase in variety of products / services.
•Active in several product markets.
Geographic Diversification:
•Increase in variety of markets / geographic regions.
•Regional, national, or international markets.
Product-Market Diversification:
•Product and geographic diversification.
DAILY DOUBLE
What is the main reason that acquisitions fail?
- Poor due diligenceUnforeseen liabilities, financial misrepresentations, and operational challenges can lead to losses, reputational damage, and legal headaches.
- Poor integrationPoor handling of change dynamics during post-merger integration can be a principal reason for failure.
- OverpayingOvervaluation of a target translates into higher premiums paid.
- Poor communicationWhen managers and employees fail to communicate or improve communication systems, things are more likely to fall apart.
- External factorsChanges in market conditions or other incalculable external factors are frequently cited as the main reasons for mergers and acquisitions falling short of expectations.
- Overestimating synergiesMergers and acquisitions assumed to be for creating synergies through increased revenue, reduced costs, and improvement in the investment intensity can lead to failure.
- Lack of cultural integrationEven companies with strong organizational cultures may develop into dysfunctional organizational cultures after a merger without actions to harmonize the two cultures.
Post-acquisition integration (lack of cultural fit)
List and explain two elements of the PESTEL framework that you think are the biggest threats for Netflix
TBD
List three of the five reasons of why firms need to grow?
To increase profits and shareholder returns.
Reinvest into the business
Higher wages and benefits (motivation)
*If not, there may be a hostile takeover (remember our Peloton discussion!)
To lower costs and achieve economies of scale.
To increase market power.
To reduce risk through diversification (especially if one SBU isn’t performing)
To motivate management.
What are some advantages of vertical integration? Cite ONE.
Vertical integration can help companies reduce costs, improve efficiency, and have more control over their supply chain. It can also help companies ensure access to raw materials and limit dependence on outside suppliers.
Amazon.com has decided to enter the college bookstore market. The goal of “Amazon Campus” is to offer co-branded university-specific web sites that offer textbooks and paraphernalia, such as logo sweaters and baseball hats. This development shows Amazon’s relentless pursuit of this corporate strategy
Product diversification
NoRu Inc. is a publicly traded firm that does not wish to be acquired by FRESHPoP Corporation, a much larger publicly traded firm, who is planning an acquisition of NoRu Inc. This is an example of a
Hostile Takeover
What are examples of diversification strategies implemented by Amazon?
Ecommerce, streaming, cloud etc
Name the two types of transaction costs and give an example of each
External transaction costs:
•Searching for contractors.
•Negotiating, monitoring, and enforcing contracts.
Internal transaction costs:
•Recruiting and retaining employees.
•Setting up a shop floor.
Jill is the CEO of Note’s Etc, a stationary manufacturer. She decides to open up a retail store to sell her products directly to consumers instead of just selling to retailers. In order to do this, Jill will need to engage in ________, which is a corporate level, strategy.
Forward vertical integration
Explain the relationship between diversification and performance
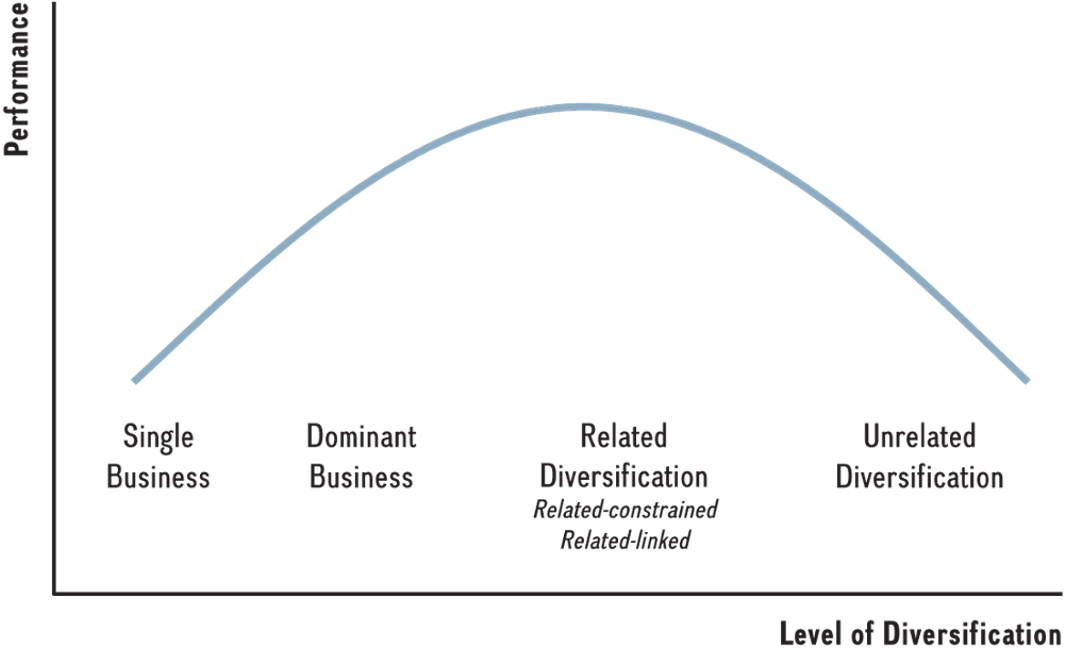
List four of the five reasons we discussed in class why firms enter into M&As
Market Power
Transferring skills
Cost savings
Maintain competitive parity
Revenue enhancement
A vertical market failure happens
when transactions in the market are too risky or costly.
when there are few buyers and suppliers, assets specificity and frequent transactions
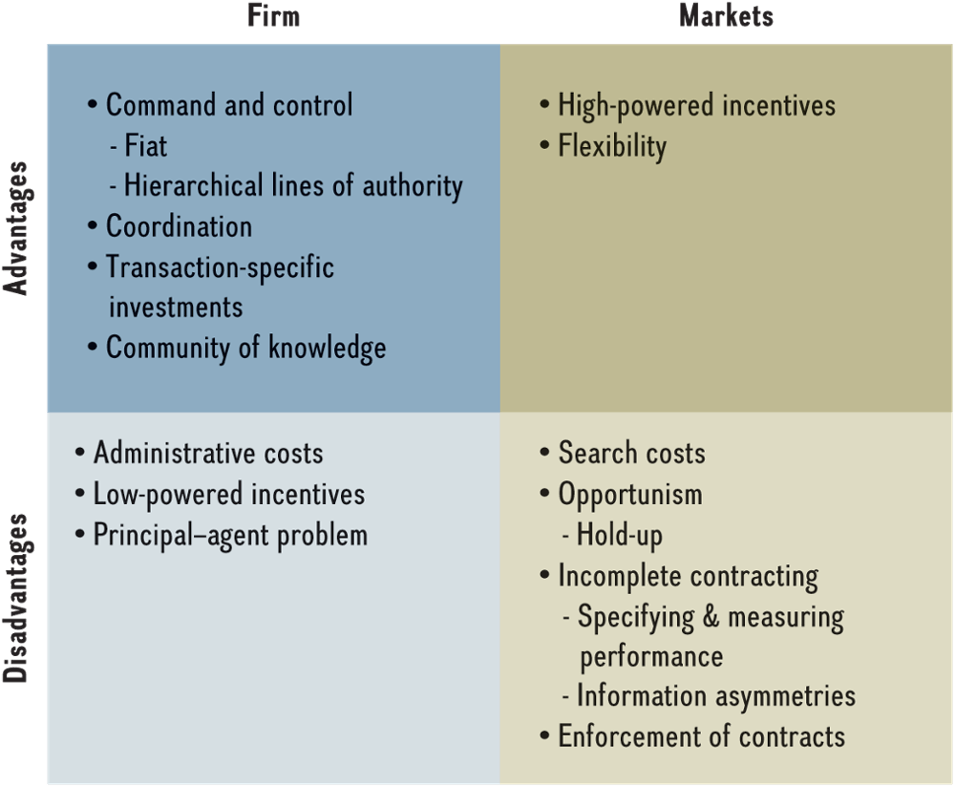
Give one advantage and disadvantage of (1) organizing economic activities within the firm and (2) within the market
List two risks of vertical integration and give an example (must be specific, but it can be invented)
Risks
Increasing costs.
Reducing quality.
Reducing flexibility.
Increasing the potential for legal repercussions.
The managers at Acme Corporation decided that their firm needed to diversify because of overall falling sales and lower performance in one sector. How does diversifying compensate for the declining performance in this sector?
by having higher performance in another sector
When Aviato Inc. wanted to sell its cars in the country of Yugoslakia, it lacked access to distribution channels and marketing expertise in the country. Thus, Aviato Autos had to enter into a strategic alliance with a local automobile company to get access to the foreign partner’s well-established distribution channels. This scenario illustrates a reason for entering into a strategic alliance, which is?
Accessing critical complementary assets
By acquiring suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers, LVMH has achieved a level of control that not only ensures quality but also creates barriers to entry for competitors. Critics, however, argue this strategy might stifle innovation. What are the long-term advantages and potential risks of LVMH’s vertical integration strategy in maintaining its competitive edge (1 advantage and 1 risk)?
LVMH’s vertical integration strategy is sustainable in the luxury market due to several key advantages:
- Control Over Quality: By owning suppliers, manufacturers, and distribution channels, LVMH ensures consistent quality, which is vital in the luxury sector.
- Exclusivity and Brand Integrity: Vertical integration allows LVMH to maintain control over brand perception and prevent unauthorized distribution or counterfeits.
- Cost Efficiency: While luxury products command premium prices, controlling the supply chain reduces dependency on third-party suppliers and external market fluctuations.
- Barrier to Entry: Competitors face significant challenges in replicating LVMH’s model due to the capital and expertise required.
Potential Risks:
- Reduced Flexibility: Over-reliance on internal processes may hinder the company’s ability to adapt to market shifts.
- Innovation Challenges: Owning every stage of production might limit exposure to external innovations that could enhance products or processes.
- Cost of Maintenance: Sustaining the integrated supply chain requires significant investment, which could strain profitability during economic downturns.
Overall, sustainability depends on LVMH’s ability to continuously optimize and innovate within its integrated structure to remain competitive.
The Umbrella Corporation (UC) recently acquired a smaller competitor, Packer and Associates, which specializes in issues not previously covered by UC, such as land use and intellectual property cases. Given the increase in the firm’s size and complexity, what is likely to happen?
It is likely that its internal transaction costs will increase
List and define the two alternative types of vertical integration (Or alternatives to pure vertical integration)
Taper integration and strategic outsourcing
List and define Porter's three tests to determine if diversification creates shareholder value
1)Attractiveness Test: diversification must be directed towards attractive industries (or have the potential to become attractive)
5 forces analysis of new industry
2)Cost of Entry Test: the cost of entry must not capitalize all future profits
3)Better-Off Test: either the new unit must gain competitive advantage from its link with the company, or vice-versa. (i.e. some form of “synergy” must be present).
Which corporate strategic choice for ALLIANCES results in the creation of third, separate company?
JV
While mergers and acquisitions can accelerate growth and expand market share, they often face challenges such as cultural clashes, regulatory hurdles, and integration issues. A prime example is the 2000 merger of two leading telecommunications companies, which resulted in significant losses and is often cited as a cautionary tale. What was this merger, and what were its main pitfalls?
What is the merger of AOL and Time Warner, and how did it fail due to overestimated synergies, cultural conflicts, and the bursting of the dot-com bubble