This term refers to the layers of sedimentary rock in Earth.
What is strata?
This term refers to the exact age.
What is absolute age?
Rock layers that are at the bottom are older than those above them
What is superpostion?
An igneous intrusion can tell us THIS about Earth's geological history.
What is volcanic activity?
This is where you would find the oldest fossils in the fossil record.
What is the bottom?
This term refers to the preserved remains of an organism, plant or animal.
What is a fossil?
This term refers to the age of a fossil or rock layer in comparison to other layers.
What is relative age?
Layers of sediment were deposited horizontally at first- any tilting or changes occurred afterwards
What is original horizontality?
In this picture, WHEN did the basaltic intrusion occur?
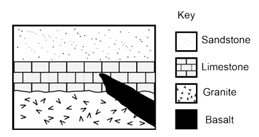
After the limestone layer formed
List the order in which these events occurred, from youngest to oldest.
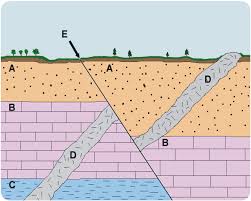
E, D, A, B, C
This term refers to magma that pushes up through layers of rock.
What is an intrusion?
The earth is 4.6 billion years.
What is absolute age?
We assume that layers that match up even after erosion were once a single layer
Lateral Continuity
When did the earthquake in this picture occur? (Which layer was last deposited?)
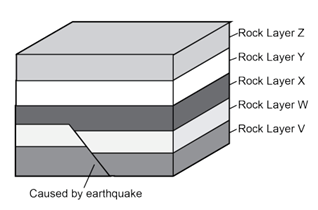
After Layer W was deposited.
At what point did the tilting occur in this diagram? After what layer?
What is D?
A line or break in rock layers where movement has occurred
What is a fault?
WHY are the oldest rock layers found at the bottom?
Because newer rocks and minerals pile on top of the older ones, creating visible layers.
A feature that cuts through a rock layer is younger than what it cuts through
What is the principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships?
Which numbers in this picture represents igneous intrusions? There are TWO.

What are 2 and 3?
Describe the order of events from youngest to oldest.
B, D, F, A, G, E, H, C
This term refers to the study of rock layers.
What is Stratigraphy?
Give an example of how rock strata can tell us how landforms are made.
Answers may vary. Example: Fault lines can show that earthquakes occurred and changed the shape of the landforms.
Events that happen today that shape the Earth also happened in the past.
Principle of uniformity or uniformitarianism?
Which letters in the diagram represent a FAULT? 
What are E and B?
 What does A represent in the image?
What does A represent in the image?
What is erosion?