78 y/o M with T2DM presents with sudden-onset word-finding difficulty and slurred speech at the ED with LKW of 1.5 hrs. Don't forget to ask the nurse for this important laboratory test before considering thrombolytic administration!
What is a bedside glucose?
Profound, fluctuating inattention, disorientation, and altered level of consciousness in hospitalized patients can be mistaken for acute ischemia, but point instead to this syndrome.
What is delirium?
A patient presents to a health fair where blood draws are being conducted. At the sight of the needle, he experiences palpitations, tunnel vision, and loses consciousness. Witnesses report that he exhibited involuntary movements. When he awakes, he is back to baseline, just a little embarrassed that he experienced this condition.
What is vasovagal syncope?
This post-seizure weakness can mimic an acute ischemic stroke.
What is Todd’s paralysis?
OPH calls you to consult a patient who has subacute vision loss with a remote history of left facial palsy. Classic. The patient has the following findings on MRI, and you already know you have to admit them because they have this stroke mimicker.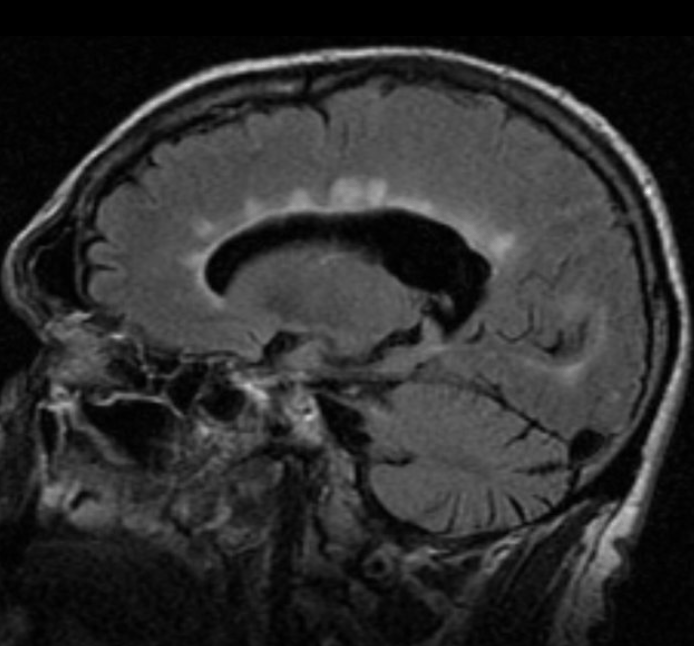
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
Paramedic brings 65 y/o F with alcohol abuse disorder to the ED as she was found with incoherent speech and bizarre behavior. On physical examination, she presents with nystagmus, bilateral lateral rectus palsy, dysmetria, and a wide-based gait. It seems like this is missing from her system.
What is thiamine?
29 y/o F with Hx of GAD and MDD presents with acute-onset incoordination, loss of balance, and difficulty with ambulation. A physical examination with suggestibility, distractability, and variability is most consistent with this disorder.
What is a functional neurological disorder?
A patient presents with episodic room-spinning sensation that is worse when she turns in her bed and subsides after several seconds. She denies hearing loss, tinnitus, and ear fullness. Dra. Deliz asks you to conduct the following procedure to confirm the diagnosis.
What is the Dix-Hallpike maneuver?
Shortly after developing left-sided weakness, a patient develops a severe headache with nausea, vomiting, and photophobia/phonophobia. All symptoms resolved spontaneously within 24 hours, suggesting a diagnosis of this disorder.
What is hemiplegic migraine?
*ring, ring* "Hi, it's Trauma. We want to consult a patient who was 'williando' at the Martinez Nadal and fell. We ordered an MRI and are concerned about a stroke." After seeing the image, you tell the resident that the imaging pattern is most consistent with this disease. 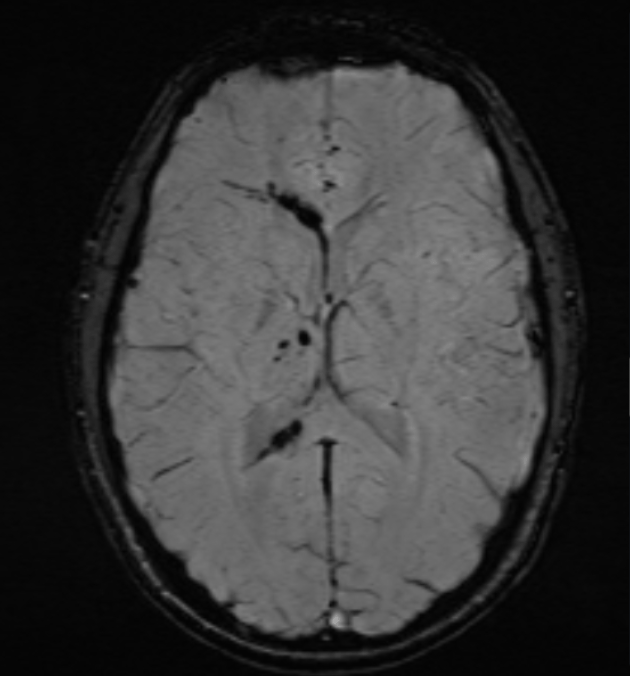
What is diffuse axonal injury?
This environmental toxin can cause headache, nausea, vomiting, confusion, focal neurological findings, and the following appearance on neuroimaging.
What is carbon monoxide?
A functional weakness where downward pressure strengthens the “weak” leg is detected with this sign.
What is Hoover’s sign?
50 y/o F presents with acute unidirectional horizontal nystagmus, nausea, vomiting, gait instability, and unilateral hearing loss. She has a positive head impulse test. No other cerebellar signs nor craniopathies are observed on physical examination. A viral syndrome might have preceded this presentation.
What is labyrinthitis?
A patient develops sudden drooping of one side of the face. The forehead is also involved, making it sound like a stroke, but this is more consistent with this peripheral condition.
What is Bell’s palsy?
78 y/o F with history of HTN, asthma, and breast cancer s/p resection and radiotherapy presents with AMS, dysarthria, nausea, and vomiting. The following image suggests that the patient may have this pathology.
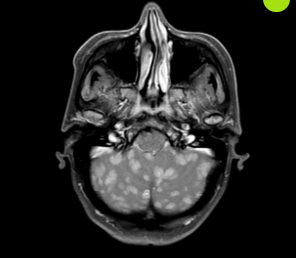
What is malignancy with metastasis to the brain?
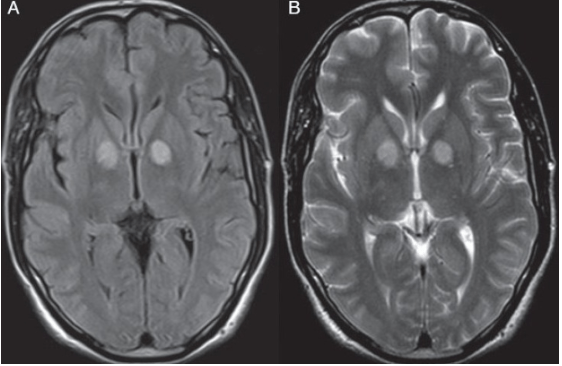
21 y/o M with Type I DM presents with abdominal pain, dehydration, and hyperventilation. DXT=450. After aggressive administration of insulin and fluids, the patient develops altered mental status and seizures. The following MRI is obtained, confirming your suspicion of this syndrome.
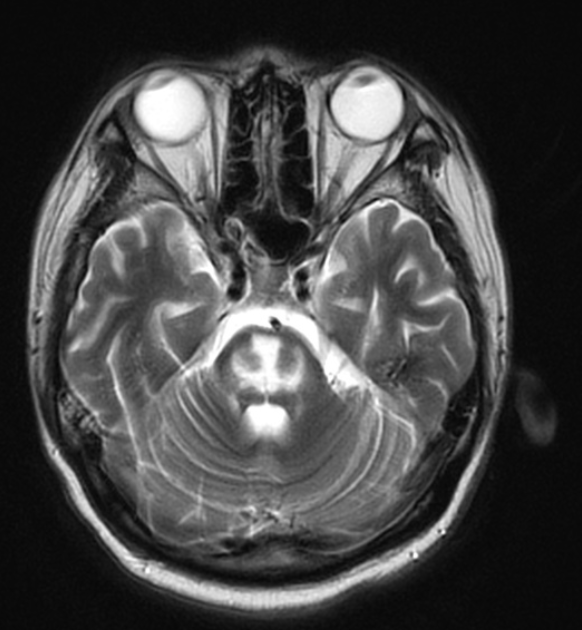
What is Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome (previously Central Pontine Myelinolysis)?
This psychiatric condition can present with mutism, immobility, or bizarre posturing, sometimes mistaken for stroke.
What is catatonia?
A patient presents to the ER with a severe headache with N/V, photophobia, and phonophobia. The event was preceded by slurred speech, double vision, incoordination, and vertigo. This has happened in the past, usually with complete resolution of symptoms in a day. Don't forget this pathology as part of the differential.
What is migraine with brainstem aura?
55 y/o M with no PMHX presents with acute-onset confusion. He is constantly repeating himself with prominent disorientation. He is unable to recall events of the day, but does recall remote events. His speech is fluid, and neurological examination is intact. After 12 hours, he is back to baseline, suggesting this pathology.
What is transient global amnesia?
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!
Following an organ transplantation, an immunosuppressed patient develops headaches, confusion, and cortical blindness. The following Head CT leads you to believe that the patient may be presenting with this syndrome. 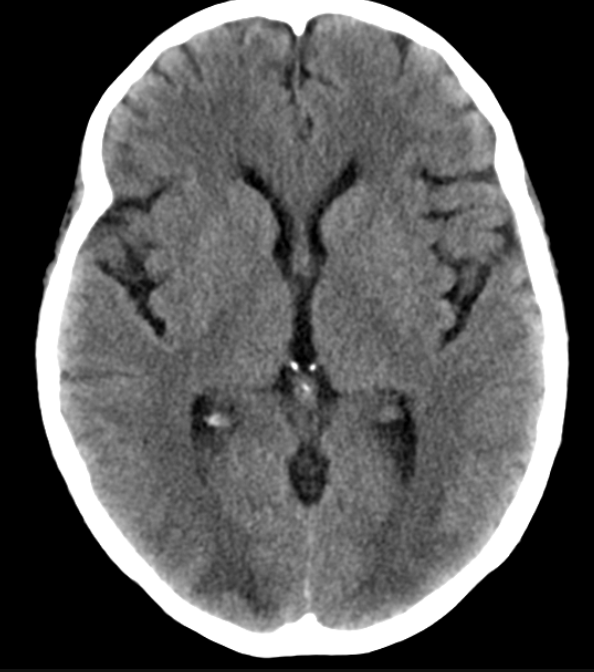
What is posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) or reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome?
It's Christmas, and your grandfather takes out his famous "pitorro de coco" that has been marinating for the last 10 years. After one too many shots, he starts to present with an acute headache, nausea, and visual changes. His Brain MRI shows the following findings. Looks like grandpa's pitorro gave him this disease.
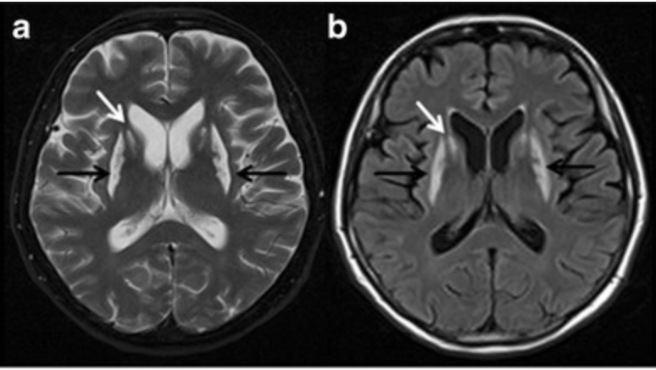
What is methanol poisoning?
The cops brought a patient to the ED after a physical altercation that required backup. BP 160/100mmHg and HR 130 bpm. On PE, he has agitation, bizarre behaviour, ataxia, rotatory nystagmus, and decreased pain sensation.
What is Phencyclidine (PCP) intoxication?
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!
An immunocompromised patient presents with Gram-negative bacteremia and is treated with Cefepime and Tobramycin. He later presents with vertigo, ataxia, tinnitus, and hearing loss. You tell the consulting team that this is the most likely cause of the patient's symptoms.
What is aminoglycoside toxicity?
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!
A patient with sudden headache, focal weakness, and aphasia may sound like a stroke, but the presence of fever, seizures, temporal lobe findings, and the following dermatologic manifestations point instead to an infectious process. What would be a likely finding on an EEG?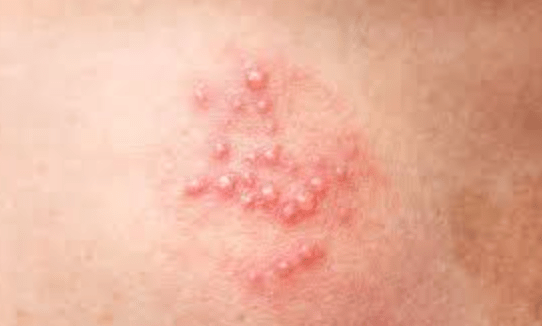
What are periodic lateralized discharges?
The patient is brought by EMT after being found with confusion, incoordination, and inattentiveness. On review of history, the patient refers to inhaling a substance, but is to droswy to recall the name. On PE he has UMN and ataxia. The following imaging is obtained.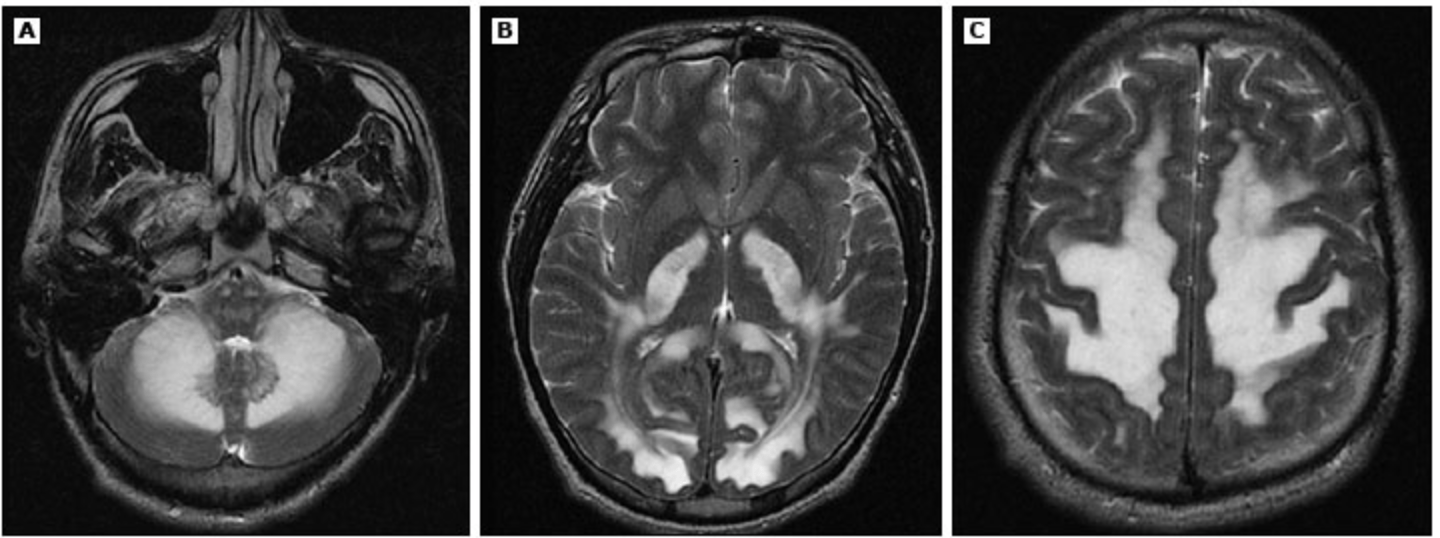
What is Heroin Leukoencephalopathy?