This imaging modality is commonly used first in stroke evaluation to rule out hemorrhage.
What is a CT scan?
A 58-year-old man with a history of hypertension and smoking presents with a sudden onset of difficulty seeing and confusion. He reports that he can't see out of the right side of his vision and has trouble recognizing objects on the left side of his environment.
Contralateral hemianopia with macular sparing is characteristic of a stroke in this artery.
What is the posterior cerebral artery (PCA)?)
Poorly managed hypertension can lead to small, deep strokes called these.
What are lacunar infarcts?
ACA strokes are often identified by changes in this brain region on imaging.
What is the medial and anterior part of the cortex?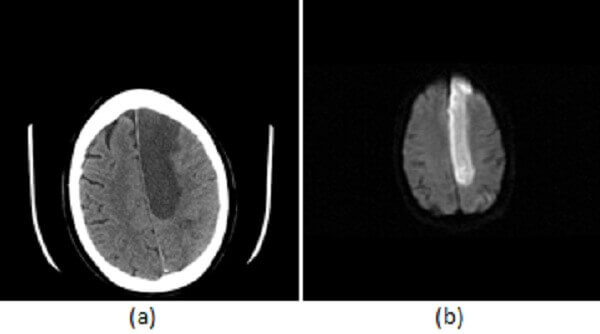
A 62-year-old man with a history of hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of weakness on the right side of his body. On examination, he has: 3/5 strength in the right upper and lower extremities, as well as in the lower half of the right face. Normal sensation to light touch, temperature, and proprioception. Intact speech and language with no evidence of aphasia. No visual field deficits or neglect.
Pure motor strokes with no cortical signs are often due to infarcts in this artery.
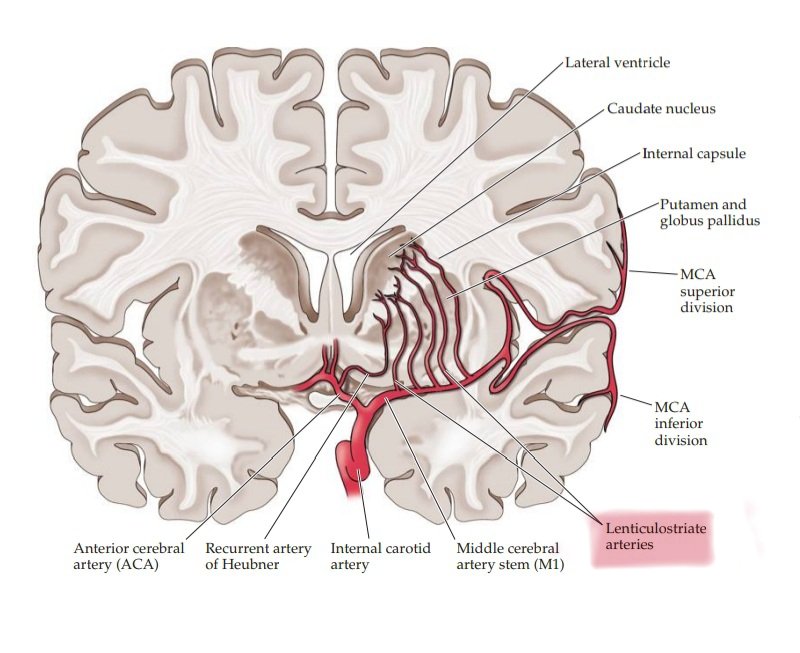
What is the lenticulostriate artery?
The basilar artery supplies this region, vital for consciousness and basic life functions.
What is the brainstem?
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/basilar-artery/vDxlc7TFZnyVk31jPnLu8A_vqWUjmbzINeRFn7HWFmoBw_A._basilaris_01.png)
Lenticulostriate artery strokes frequently affect this subcortical structure.
What is the internal capsule?
A 70-year-old woman with a history of atrial fibrillation presents with sudden onset of weakness in her right leg.On examination: She has 3/5 strength in the right lower extremity, while her right arm and face are unaffected. She struggles with initiating movements and appears apathetic, showing a flat affect. Her sensation is intact, but she reports difficulty with bladder control since the onset of symptoms. Contralateral paralysis and sensory loss in the lower limbs is characteristic of this artery's infarction.
What is the anterior cerebral artery (ACA)?
PCA strokes can result in this condition, where patients lose the ability to read but retain the ability to write.
What is alexia without agraphia?
PCA strokes cause infarction in this lobe, often leading to visual deficits.
What is the occipital lobe?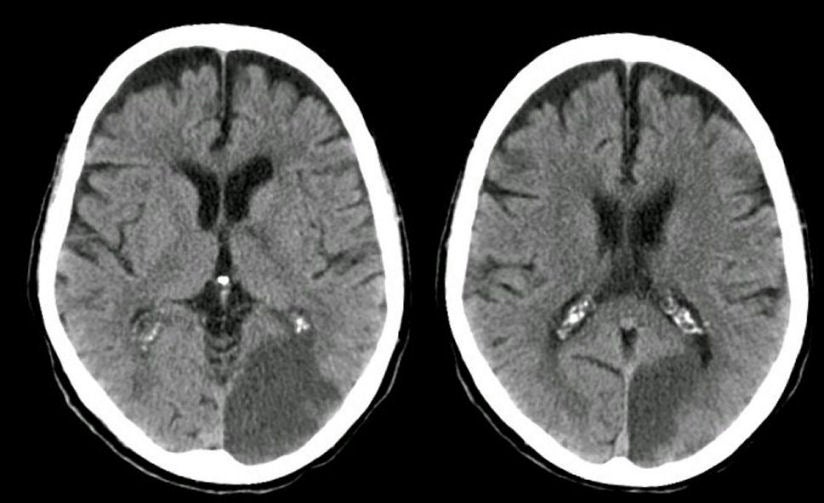
This rare visual disorder, characterized by the inability to recognize faces, can result from PCA strokes.
What is prosopagnosia?
The ACA supplies this specific portion of the brain responsible for motor control of the lower limbs.
What is the medial cortex?
Basilar artery strokes often show infarction in these brainstem structures, crucial for motor and sensory pathways.
What are the pons and medulla?)
This condition, caused by a basilar artery stroke, presents with quadriplegia, preserved consciousness, and the inability to speak, with communication possible only through vertical eye movements or blinking.
What is locked-in syndrome?
This artery supplies perforating branches to the internal capsule, making it a common site for hypertensive strokes.
What is the lenticulostriate artery?