True or False.
The atoms in a water molecule form polar covalent bonds because oxygen is more electronegative compared to hydrogen which results in unequal sharing of electrons between the two.
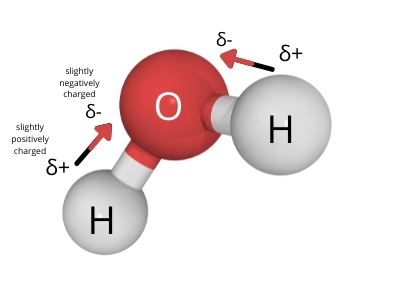
True
Based from the table, which element is the most necessary in the structure of all macromolecules?
Carbon
What do you call the chemical subunits used to create polymers?
Monomers
Polysaccharides are also referred to as complex carbohydrates. Organisms get their energy from these macromolecules.
Give an example of a polysaccharide.
Starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
What TYPE OF BOND forms between water molecules and other charged charged molecules?
Hydrogen bond

Pictured above is a phospholipid containing the elements of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and phosphorus. Phospholipids are structural components of what part of the cell?
Cell membranes
What type of bond connects monomers to form polymers?
Covalent bond
What do you call the the primary structure of proteins, consists of different amino acids in different orders as pictured below?
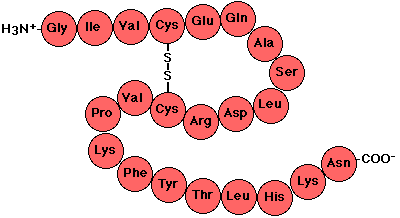

Polypeptide
What two properties allow water to be transported to from the roots of tall trees to the leaves?
Cohesion and adhesion
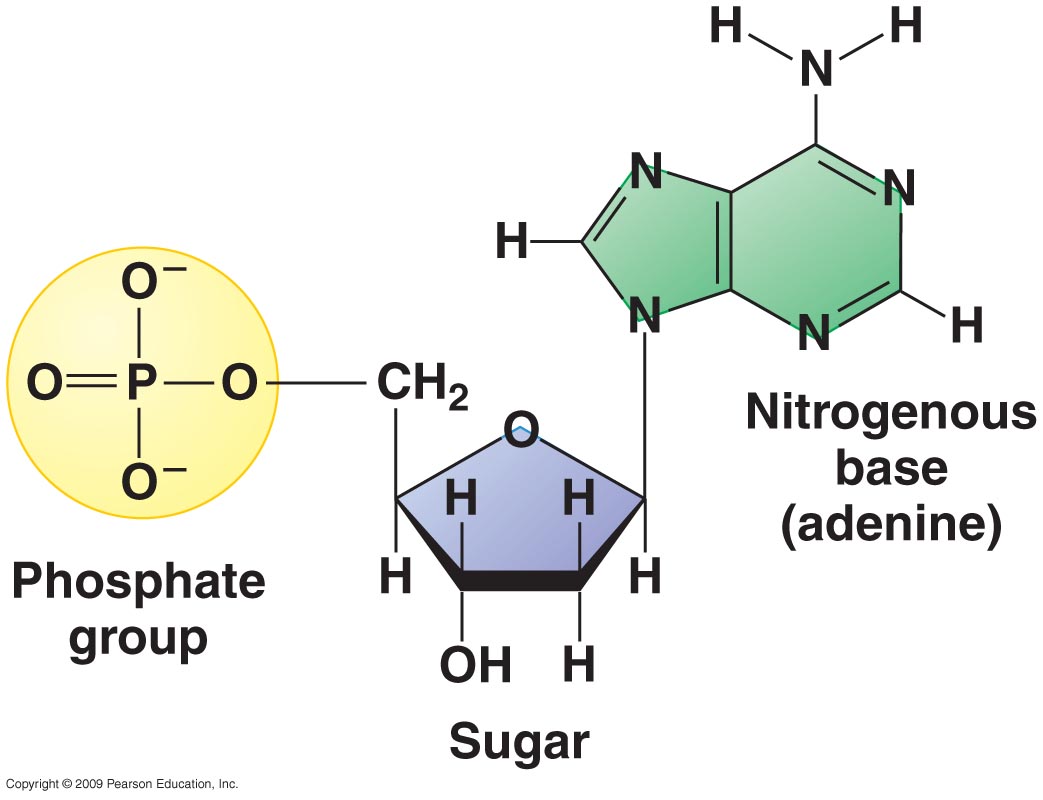
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and phosphorus are all present in the molecule above.
This molecule is the monomer or subunit of what major macromolecule and is responsible for what function?
Nucleic acids; Carrying genetic information.
Dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis are two important chemical reactions that make or break macromolecules.
Differentiate these two types of reactions.
Dehydration synthesis - polymers are MADE from interacting monomers; Water is PRODUCED as by-product.
Hydrolysis - polymers are BROKEN down into their smaller subunits; Water is USED in the process.
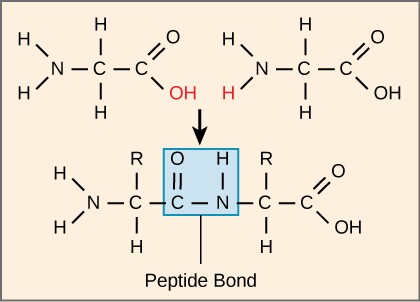
Identify the BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULE, the MONOMERS, and the TYPE OF REACTION pictured above.
Protein, Amino Acids, Dehydration Synthesis
Breaking the hydrogen bonds between water molecules require high amounts of energy which makes it resistant to sudden changes in temperature.
What property of water is described above?
High Heat Capacity

Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are all present in the molecule above.
This molecule is the monomer or subunit of what major macromolecule and is responsible for what function?
Carbohydrate; Source of energy
Lipids, unlike water, are non-polar, meaning that the charge distribution between atoms is evenly distributed, and the molecules do not have positive and negatively charged ends.
What does this say about how these two molecules may interact with each other?
Lipids will not mix with water and water will not be able to dissolve lipids.

Identify the BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULE, the MONOMERS, and the TYPE OF REACTION pictured above.
Carbohydrate, Monosaccharides, Hydrolysis
Explain how some insects can walk on water.
Mention the PROPERTY OF WATER and the TYPE OF BOND that make this possible.
SURFACE TENSION - increased HYDROGEN BONDING forces between water molecules at the surface allows some insects to walk on water.

Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are all present in the molecule above.
This molecule is the monomer or subunit of what major macromolecule and is responsible for what function?
Phospholipids are specialized lipids with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails that determine their interactions with other molecules.
Describe the interaction between the hydrophobic tail of a phospholipid and an amino acid with a hydrophobic side chain found in a membrane protein.
The hydrophobic regions of phospholipids and proteins can interact with each other but NOT the water environment.
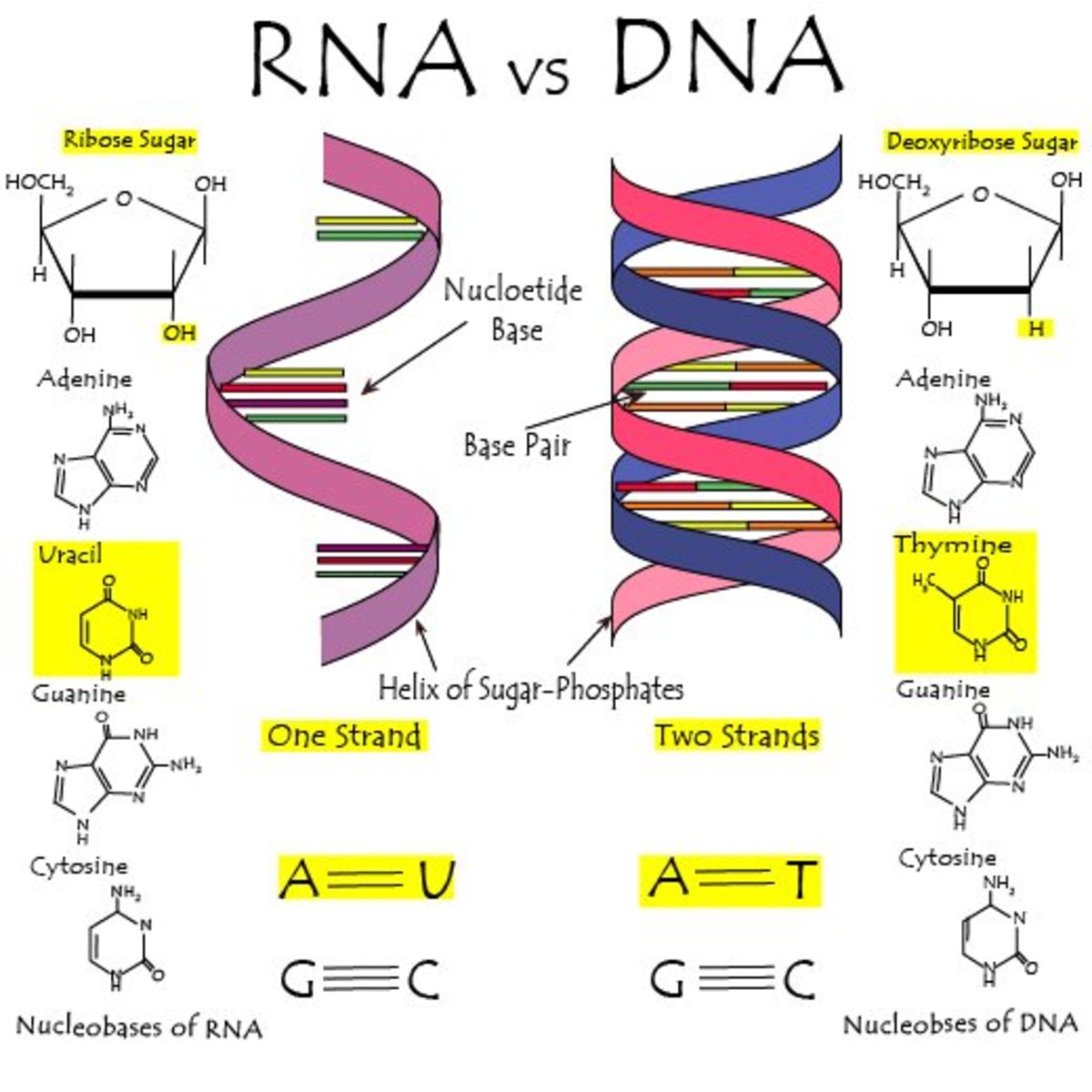
DNA and RNA have different functions because of the differences in their structures.
Mention at least two (2) differences between DNA and RNA.
Number of strands, nitrogenous bases (uracil in RNA, and pentose sugar (oxygen in RNA)