For the patient with symptomatic bradycardia, treatment consists of giving this
What is IV atropine (anticholinergic drug)?
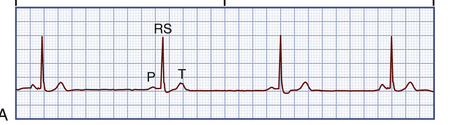 this is.
this is.
What is Sinus Bradycardia?
a graphic tracing of the electrical impulses produced in the heart. The waveforms on the ECG represent electrical activity produced by the movement of ions across the membranes of heart cells, representing depolarization and repolarization
What is The electrocardiogram (ECG)?
Ability to initiate an impulse spontaneously and continuously
What is Automaticity?
Stimulation of this causes a decreased rate of firing of the SA node and slowed impulse conduction of the AV node
What is the vagus nerve? (Valslva manuver)
The primary goal in treatment of atrial flutter is to slow the ventricular response by increasing AV block. Drugs used to control ventricular rate include
What is calcium channel blockers and β-blockers?
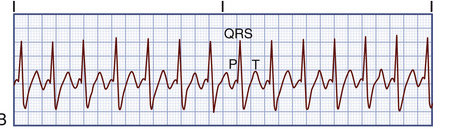 This is.
This is.
What is Sinus Tachycardia?
Clinical Associations.
Sinus tachycardia is associated with physiologic and psychologic stressors such as exercise, fever, pain, hypotension, hypovolemia, anemia, hypoxia, hypoglycemia, myocardial ischemia, heart failure (HF), hyperthyroidism, anxiety, and fear. It can also be an effect of drugs such as epinephrine, norepinephrine (Levophed), atropine, caffeine, theophylline, or hydralazine. In addition, many over-the-counter cold remedies have active ingredients (e.g., pseudoephedrine [Sudafed]) that can cause tachycardia.
ECG Characteristics.
In sinus tachycardia, the HR is 101 to 200 beats/minute and rhythm is regular. The P wave is normal, precedes each QRS complex, and has a normal shape and duration. The PR interval is normal and the QRS complex has a normal shape and duration.
A normal impulse starts here
What is SA node?
Ability to transmit an impulse along a membrane in an orderly manner
What is Conductivity?
This is a contraction coming from an ectopic focus in the ventricles.
What is a PVC?
If a patient is in atrial fibrillation for longer than 48 hours this needs to be started.
What is anticoagulation therapy with warfarin is needed for 3 to 4 weeks before the cardioversion and for several weeks after successful cardioversion.
 This rhythm is
This rhythm is
What is artifact?
Each large square consists of 25 smaller squares (five horizontal and five vertical). Horizontally, each small square (1 mm) represents 0.04 second. This means that one large square equals
What is 0.20 seconds?
This is the observation of a patient's HR and rhythm at a site distant from the patient.
What is Telemetry Monitoring?
This during an emergency this depolarizes the cells of the myocardium allowing the SA node to be the pacemaker.
What is defibrillation?
In Afib, The most common antidysrhythmia drugs used for conversion to and maintenance of sinus rhythm include
What is amiodarone and ibutilide?
 The nurse should
The nurse should
What is check the patient & start compression?
This is the planned therapy of choice for the patient with ventricular tachydysrhythmias (e.g., VT with a pulse) or supraventricular tachydysrhythmias (e.g., atrial flutter with a rapid ventricular response).
What is Synchronized cardioversion?
Two consecutive PVCs are
What is a couplet?
This means every other beat is earlier than expected, has no P wave, and has a QRS complex with a wide and bizarre shape.
What is Ventricular Bigeminy?
When every other beat is a PVC, the rhythm is called ventricular bigeminy. When every third beat is a PVC, it is called ventricular trigeminy.
Treatment of Ventricular fibrillation consists of immediate initiation of CPR and advanced cardiovascular life support (ACLS) with the use of defibrillation and definitive drug therapy including.
What is epinephrine and vasopressin?
This is a situation in which organized electrical activity is seen on the ECG, but there is no mechanical heart activity and the patient has no pulse. It is the most common dysrhythmia seen after defibrillation.
What is Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)?
This is an important technology for patients who (1) have survived SCD, (2) have spontaneous sustained VT, (3) have syncope with inducible VT or VF during EPS, or (4) are at high risk for future life-threatening dysrhythmias (e.g., have cardiomyopathy).
What is an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD)?
This is an atrial tachydysrhythmia identified by recurring, regular, sawtooth-shaped flutter waves that originate from a single ectopic focus in the right atrium or, less commonly, the left atrium
What is Atrial flutter?
This is the treatment of choice to end VF and pulseless VT
What is Defibrillation?
Thisis the drug of choice to convert SVT to a normal sinus rhythm. This drug has a short half-life (10 seconds) and is well tolerated.
What is Adenosine?
• Injection site should be as close to the heart as possible (e.g., antecubital area).
• Give IV dose rapidly (over 1 to 2 sec) and follow with a rapid 20 mL normal saline flush.
• Monitor patient's ECG continuously. Brief period of asystole is common.
• Observe patient for flushing, dizziness, chest pain, or palpitations.
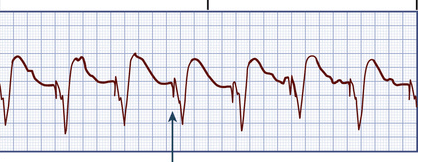 The arrow is indicating
The arrow is indicating
What is a pacer-spike?
The following are indications for this
Acquired AV block
• Second-degree AV block
• Third-degree AV block
• Atrial fibrillation with a slow ventricular response
• Bundle branch block
• Cardiomyopathy
• Dilated
• Hypertrophic
• Heart failure
• SA node dysfunction
• Tachydysrhythmias (e.g., ventricular tachycardia)
AV, Atrioventricular; SA, sinoatrial.
What is a permanent pacemaker?
This can detect heart rhythms and advise the user to deliver a shock using hands-free defibrillator pads.
What is an automatic external defibrillator (AED)?
This uses electrical energy to “burn” areas of the conduction system as definitive treatment of tachydysrhythmias
What is Radiofrequency catheter ablation therapy?
An electrode-tipped ablation catheter ablates accessory pathways or ectopic sites in the atria, AV node, and ventricles. Catheter ablation is considered the nonpharmacologic treatment of choice for atrial dysrhythmias resulting in rapid ventricular rates and AV nodal reentrant tachycardia refractory to drug therapy.