Deadly Laser
Immediate washing with this can remove up to 100% of poison ivy oil if performed right after exposure.
Soap and water
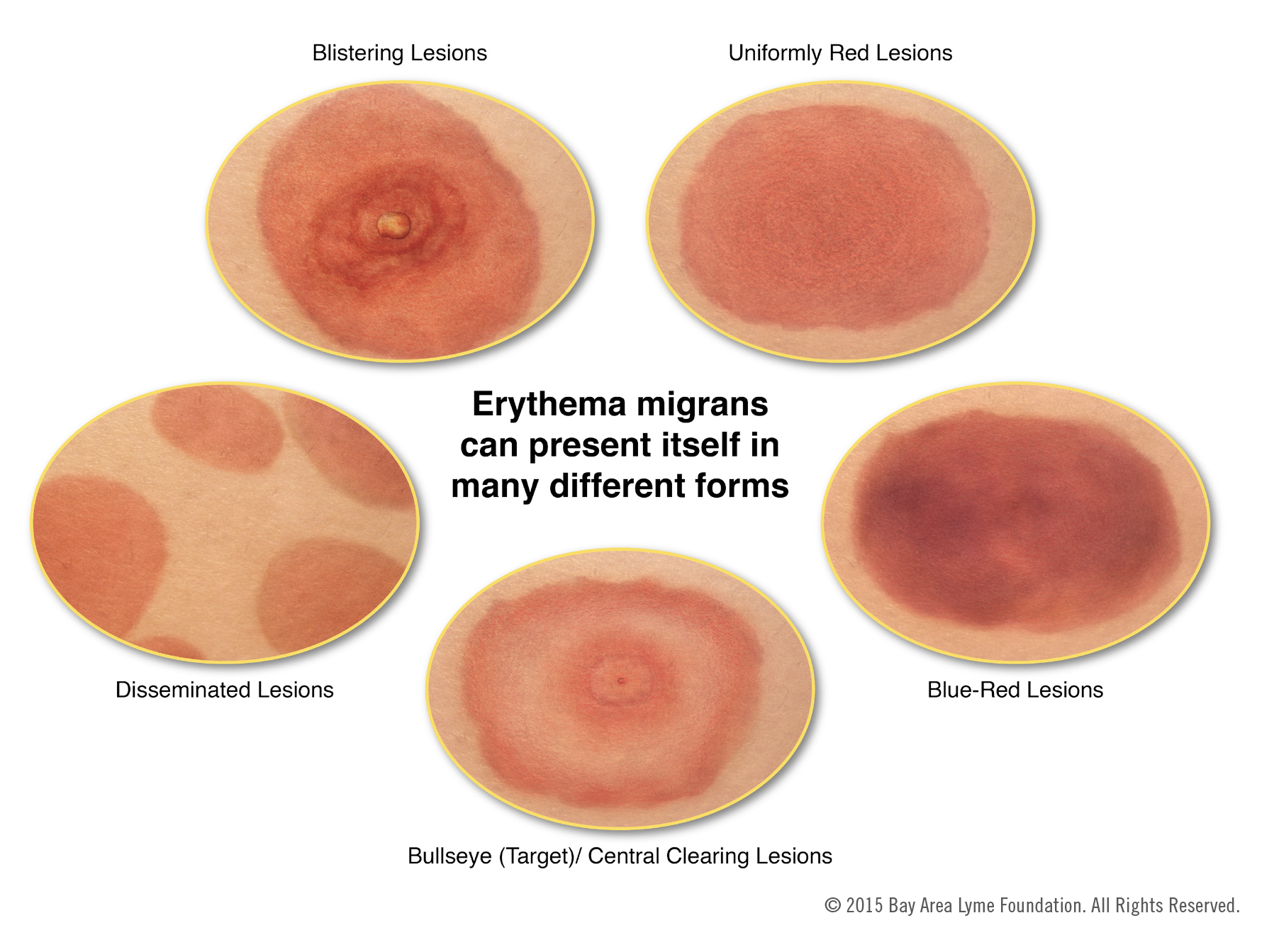
This expanding erythematous skin lesion, often at least 5 cm in diameter, is the hallmark of early Lyme disease.
Erythema migrans
This simple diet was historically recommended to patients with uncomplicated gastroenteritis, but is no longer promoted because it unnecessarily reduces caloric intake without clinical benefit.
BRAT diet (bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast)
PO hydration is the mainstay of treatment.
These two common topical agents have limited evidence, and are not routinely recommended for the treatment of sunburn pain.
Aloe vera and topical steroids
The pain from this rash can be managed with topical emolients and this PO therapy, which also helps to reduce erythema.
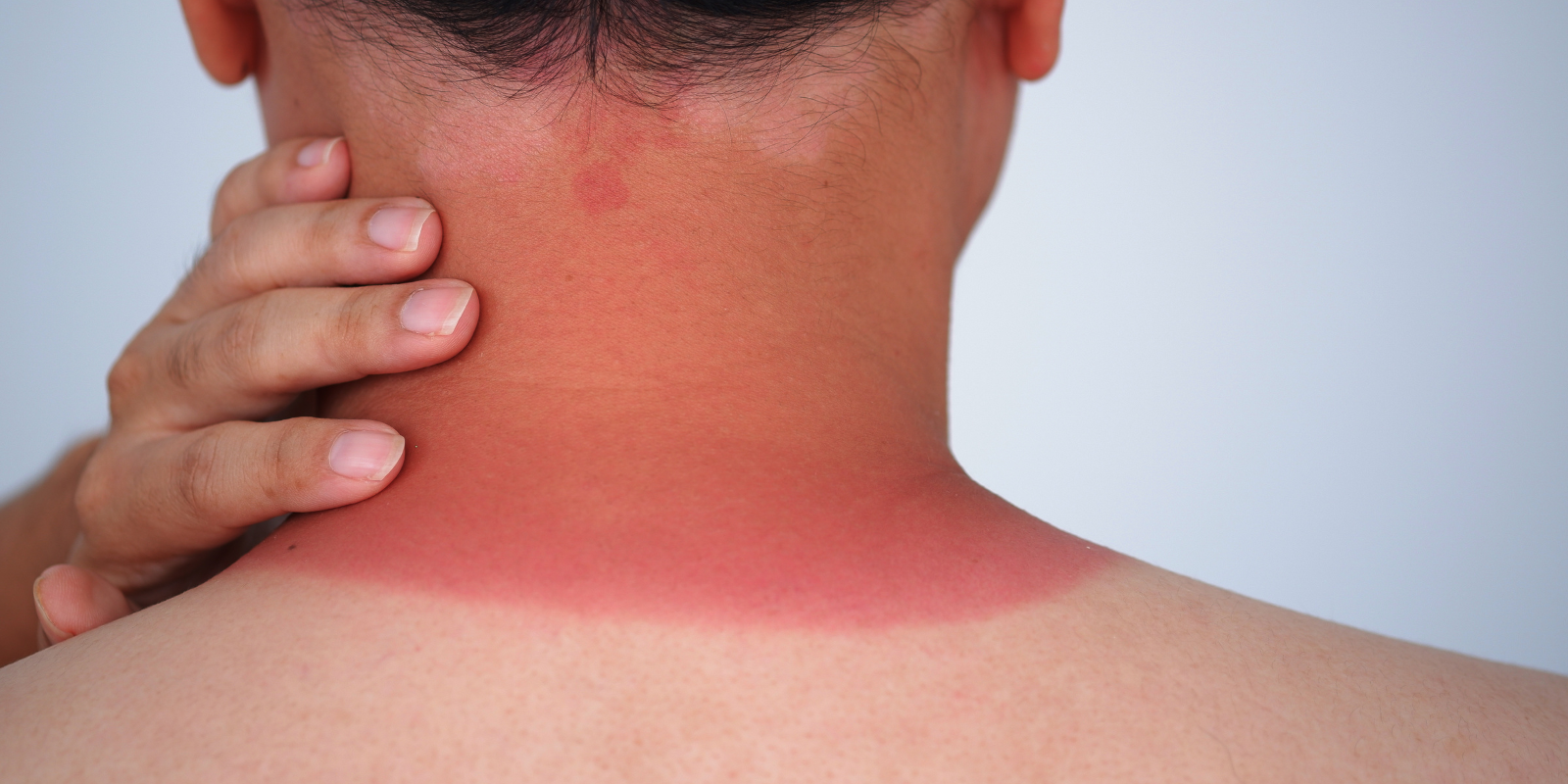

NSAIDs
This PO over-the-counter remedy is frequently used for symptomatic relief in poison ivy-induced pruritis, but lacks strong evidence for efficacy.
Oral antihistamines
This class of topical medication is recommended for reducing inflammation and pruritus in mosquito bite reactions; oral medicines of this other class can be used for larger local reactions.
Topical corticosteroids and PO second-generation antihistamines
Vomiting and diarrhea 1-6 hours after eating potato salad at a summer picnic is most likely this process, triggered by heat stable toxin from this pathogen.
Gastroenteritis secondary to S aureus
If your skin normally burns in 10 minutes, an SPF 30 sunscreen should allow you to stay in the sun this many minutes before burning?
300 minutes
The pictured itchy rash is best managed with this therapy (give diagnosis, medication name, strength, and duration)?

Poison ivy rash
Treat with clobetasol 0.05% cream, applied twice daily until improvement (typically within one week)
Superior efficacy to lower potency steroids, with shorter treatment duration. Most helpful in early disease; once vesicles are established there is less benefit.
Poison ivy dermatitis is caused by this type of hypersensitivity reaction, which develops 12-24 hours after exposure.
Type IV (cell-mediated) hypersensitivity
Patients using DEET-containing insect repellant should be counseled to avoid wearing clothing containing this common material, due to the risk of permanent fabric damage.
Rayon / spandex
In adult patients presenting with acute diarrhea, these two clinical "red flag" features typically prompt further diagnostic workup including stool studies and possible imaging.
Bloody stools and signs of systemic toxicity (high fever, leukocytosis, or hypotension)
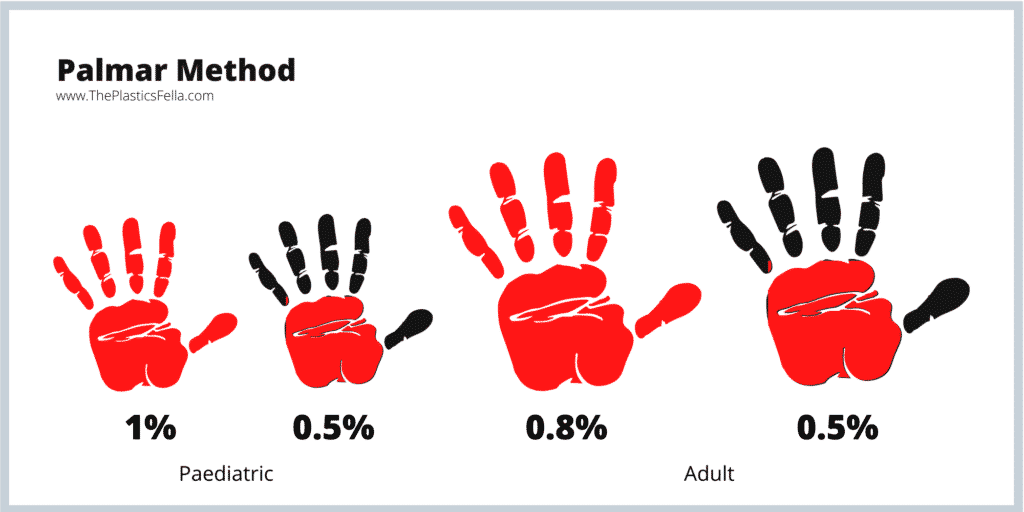
To minimize the risk of sunburn, an adult patient wearing a bathing suit should apply this quantity (in tsp or mL) of sunscreen every X hours.
9 tsp or 45mL every 1-2 hours
1 teaspoon (visually measured) of sunscreen to the face and neck area, a total of 2 teaspoons to the front and back torso, 1 teaspoon to each upper extremity, and 2 teaspoons to each lower extremity.
A standard sunscreen bottle will be consumed after 2-4 applications.
Patients presenting with this itchy rash should be instructed to take these steps to minimize the risk of further breakouts.
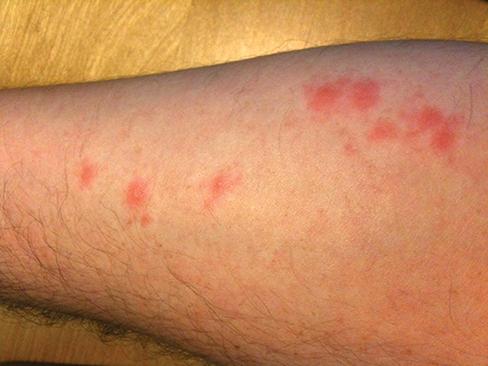
Inspect mattresses, wash or dispose of bedding and clothing.
Systemic corticosteroids are indicated when poison ivy dermatitis involves more than this percentage of body surface area.
10%
A single dose of doxycycline 200mg is recommended for Lyme disease prophylaxis if an Ixodes tick has been attached for X hours and prophylaxis can be started within Y hours.
What is X and Y?
X: attached for ≥ 36 hours
Y: prophylaxis started within 72 hours.
Doxycycline 100mg BID for 10 days is used for treatment of early uncomplicated disease.
Empiric antibiotic therapy for acute gastroenteritis is typically avoided, but may be indicated in immunocompromised patients or if this invasive bacterial etiology is suspected.
Shigella, Salmonella, Campylobacter, or enterohemorrhagic E. coli (excluding STEC due to HUS risk)
According to the Wilderness Medical Society, this is the most effective field treatment for exertional heat stroke.
Cold water immersion
While frequently described as a "spider bite," this skin finding is actually most concerning for this diagnosis.
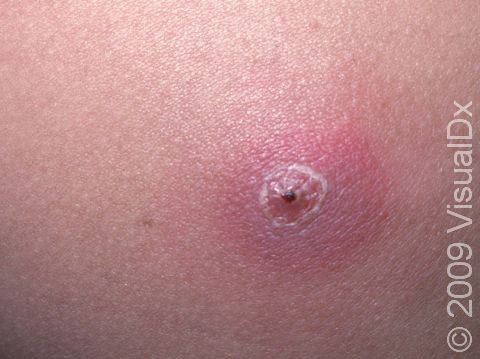
Furuncle.
Disposing of poison ivy by burning can release smoke containing this substance, which may trigger acute laryngeal edema, bronchospasm, and respiratory distress.
Urushiol
Anaphylaxis following a bee sting is characterized by the presence of these symptoms (name diagnostic criteria).
1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to several hours) with involvement of the skin, mucosal tissue, or both (eg, generalized hives, pruritus or flushing, swollen lips-tongue-uvula) AND AT LEAST ONE OF THE FOLLOWING:
A. Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, hypoxemia)
B. Reduced BP* or associated symptoms of end-organ dysfunction (eg, hypotonia, collapse, syncope, incontinence)
2. TWO OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING that occur rapidly after exposure to a LIKELY allergen for that patient (minutes to several hours):
A. Involvement of the skin mucosal tissue (eg, generalized hives, itch-flush, swollen lips-tongue-uvula)
B. Respiratory compromise (eg, dyspnea, wheeze-bronchospasm, stridor, hypoxemia)
C. Reduced BP* or associated symptoms (eg, hypotonia, collapse, syncope, incontinence)D. Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms (eg, crampy abdominal pain, vomiting)
3. Reduced BP* after exposure to a KNOWN allergen for that patient (minutes to several hours):
A. Infants and children - Low systolic BP (age-specific)* or greater than 30% decrease in systolic BP
B. Adults - Systolic BP of less than 90 mmHg or greater than 30% decrease from that person's baseline
This antibiotic regimen is recommended for treatment of suspected infectious diarrhea after travel to Southeast Asia.
1. Azithromycin 500 mg PO daily for 1–3 days [Preferred in Southeast Asia, India, or for pregnancy; effective against Campylobacter and resistant strains]
2. Ciprofloxacin 500 mg PO BID for 1–3 days [Good for E. coli, Shigella, Salmonella; not reliable in South/Southeast Asia due to resistance]
3. Levofloxacin 500 mg PO daily for 1–3 days [Similar to ciprofloxacin; may be used when azithromycin is contraindicated]
4. Rifaximin 200 mg PO TID for 3 days. [Non-absorbed; effective only for non-invasive, ETEC-type diarrhea; not effective if fever or blood in stool]
The presence of these two clinical features differentiates heat stroke from heat exhaustion.
Altered mental status and core temperature above 40°C (104°F)
The rash below is classically associated with gardening. It is caused by this infectious agent, and is treated with this therapy (identify diagnosis, medication, and duration).

Sporotrichosis (caused by Sporothrix fungus)
Treated with itraconazole for 2-4 weeks after lesion resolution (often 3-6 months total).