daily changes in the level of ocean water
Double your points: How does the moon "produce" light?
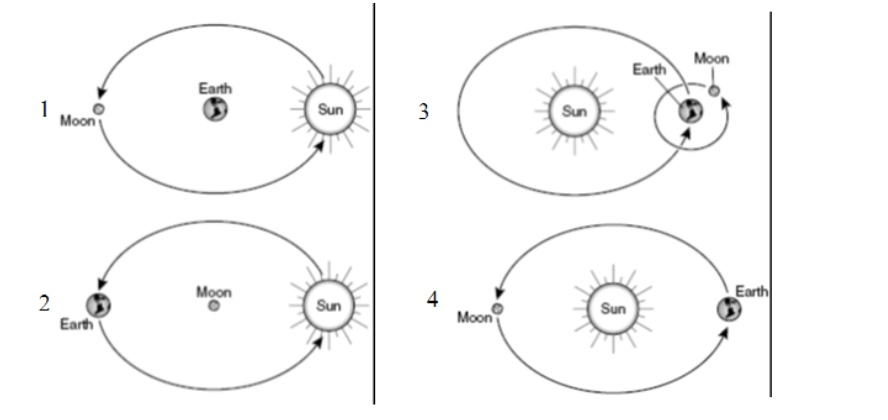
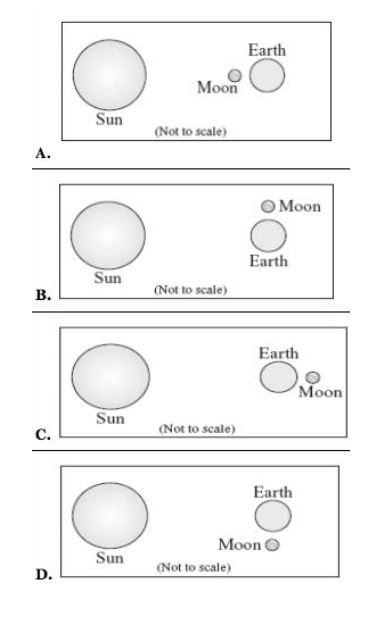
Which picture best describes the Sun, Earth and Moon relationship?

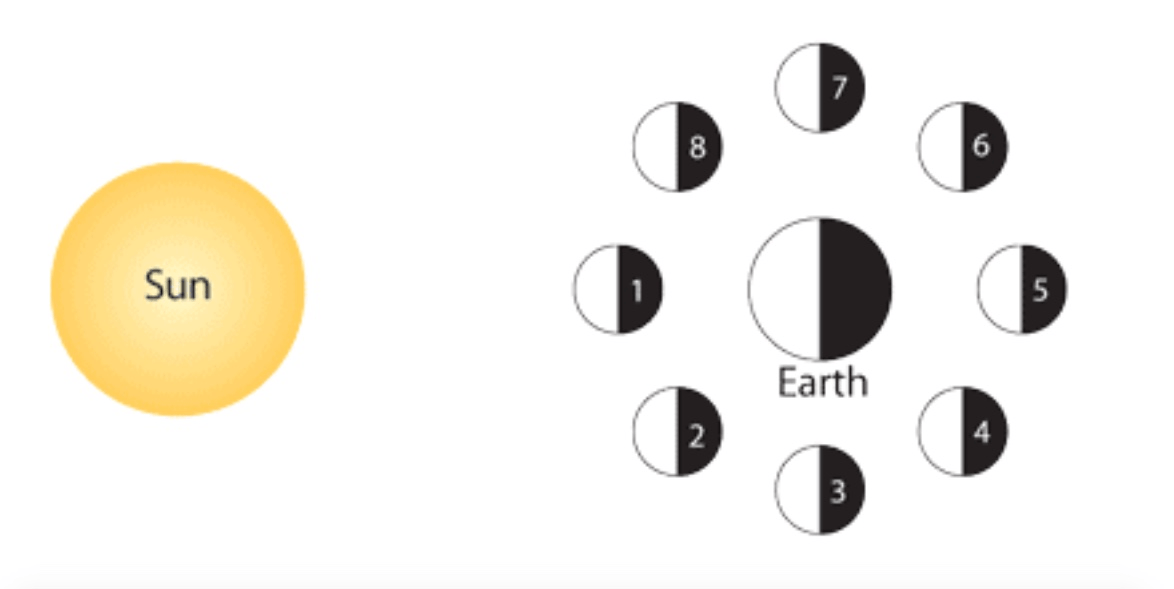
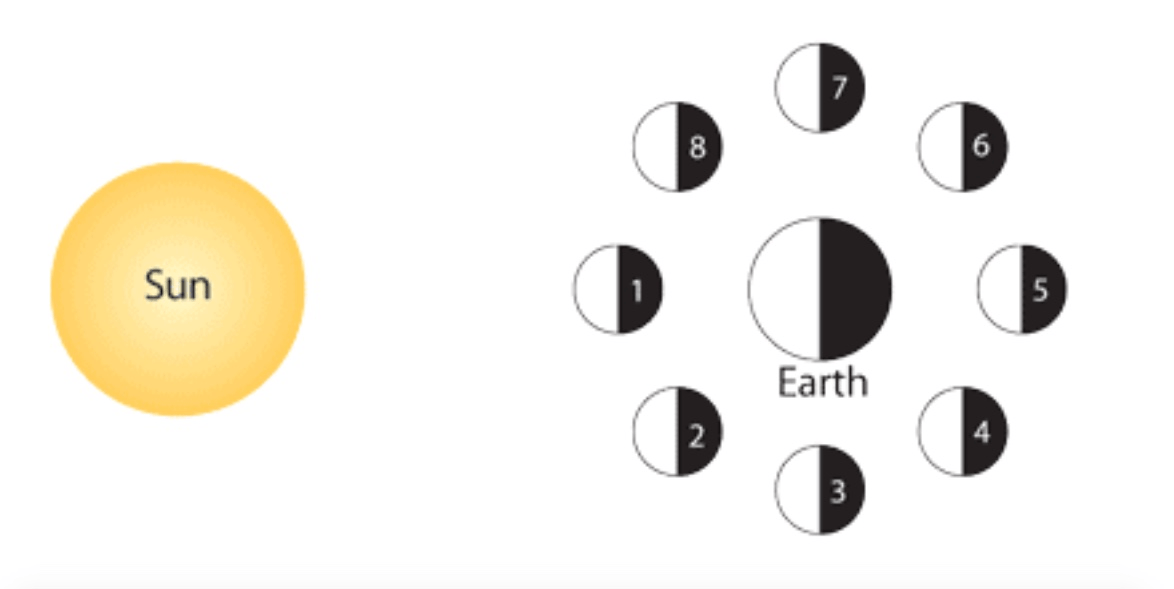
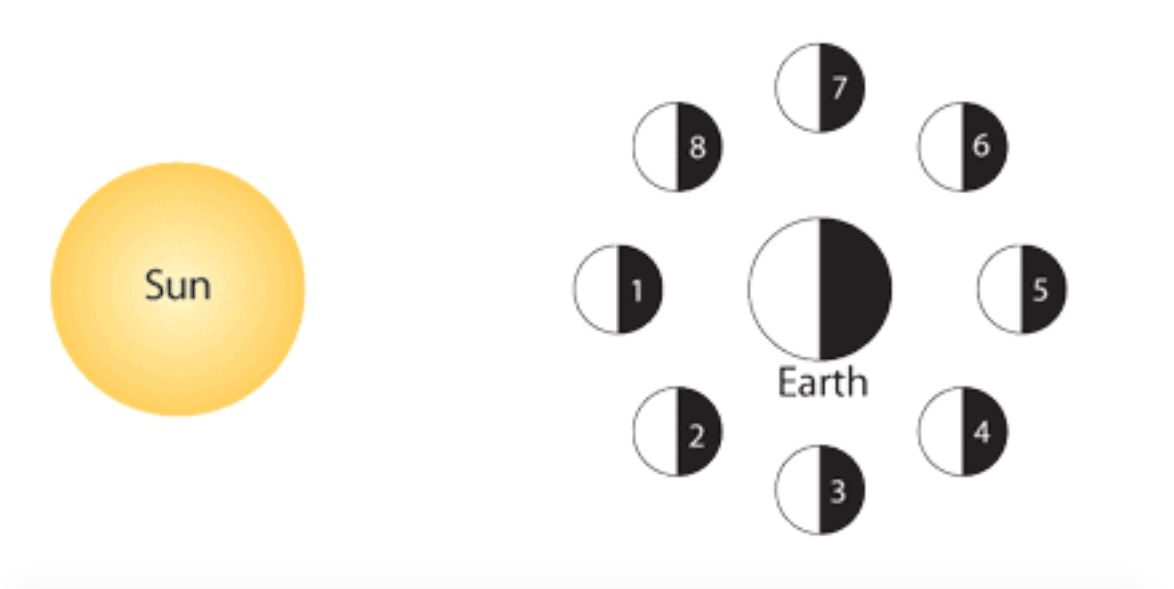
In the diagram below, what moon phase occurs at location 2?
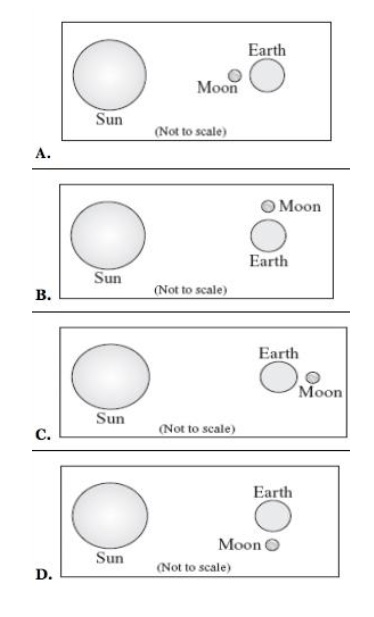
Which two arrangements of the Sun, Earth and Moon would produce a neap tide?
If you saw a waxing crescent in the sky tonight, predict what moon phase you would see in 14 days.
In the diagram below, what moon phase occurs at location 4?
the partial or total blocking of light of one celestial object by another
What do we call it when ocean levels fall to their minimum point in any day?
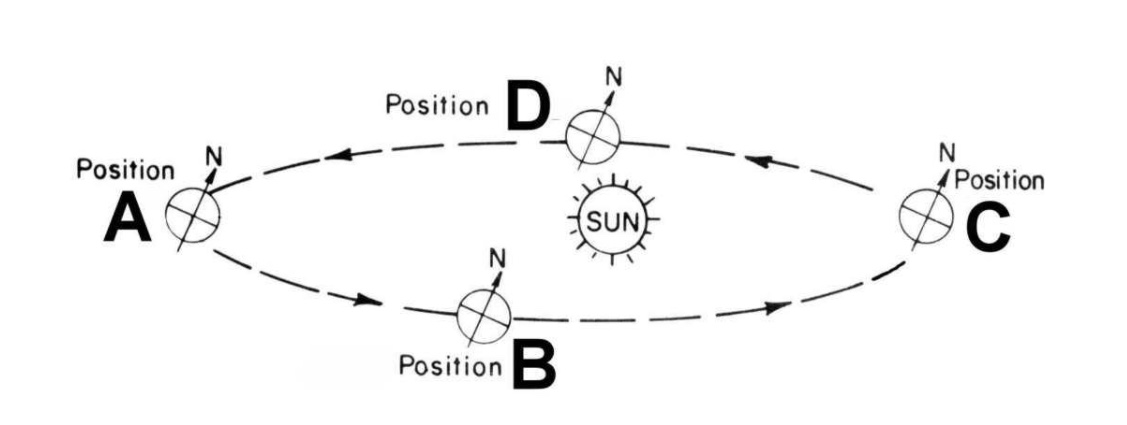
December 22nd is usually the what in the Southern Hemisphere?
Double your points: What is it in the Northern Hemisphere?
In the diagram below, what moon phase occurs at location 7?
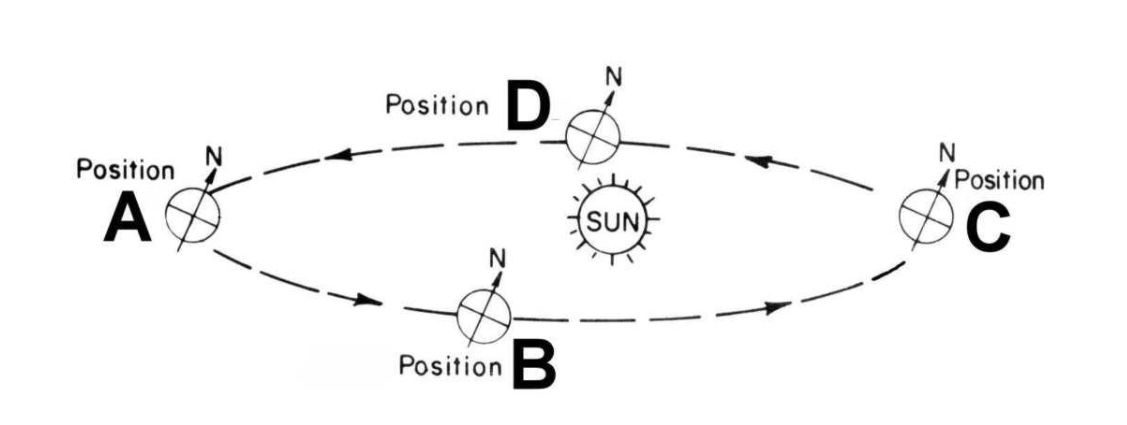
What location would produce summer in the Southern Hemisphere below?
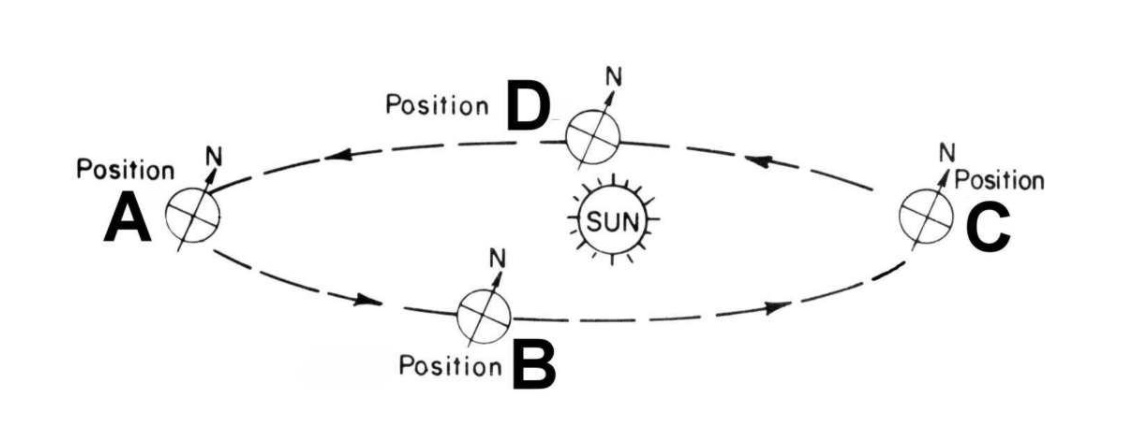

What location would produce spring in the Northern Hemisphere below?
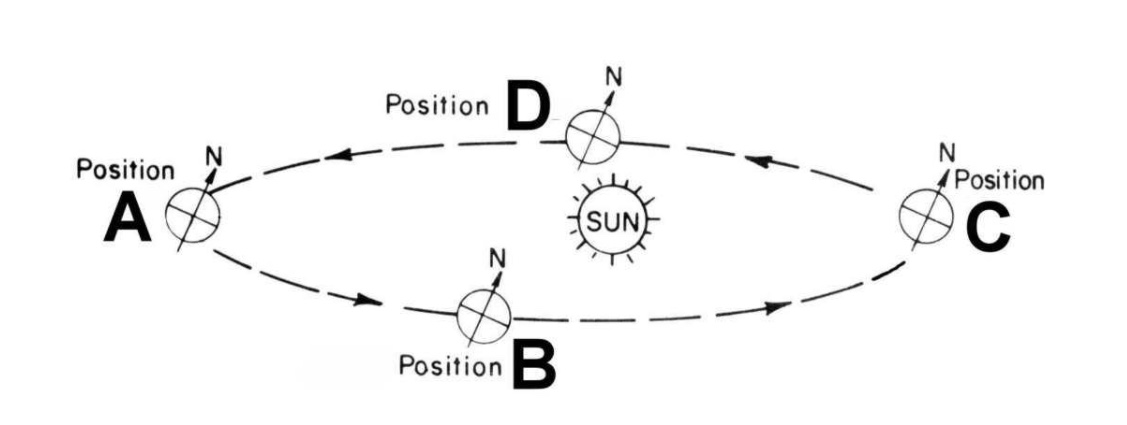
The orbital velocity of the inner planets has to be greater than the orbital velocity of the outer planets for them to stay in orbit because they have _?_.
Which object has the greatest effect on ocean levels?
What location would produce winter in the Northern Hemisphere below?
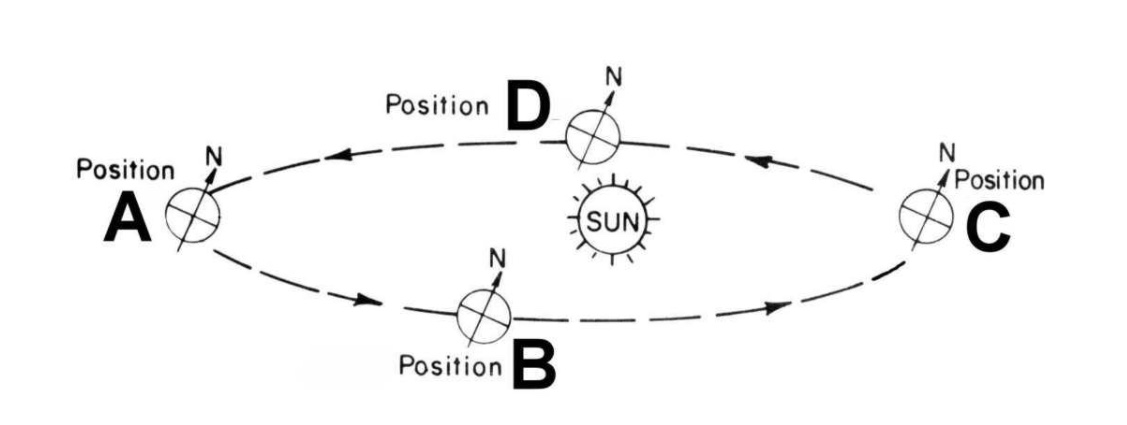


The Earth revolves _?_ and rotates _?_.
How long does is it between high tides?
approximately 12 to 12.5 hours
What location would produce fall in the Northern Hemisphere below?
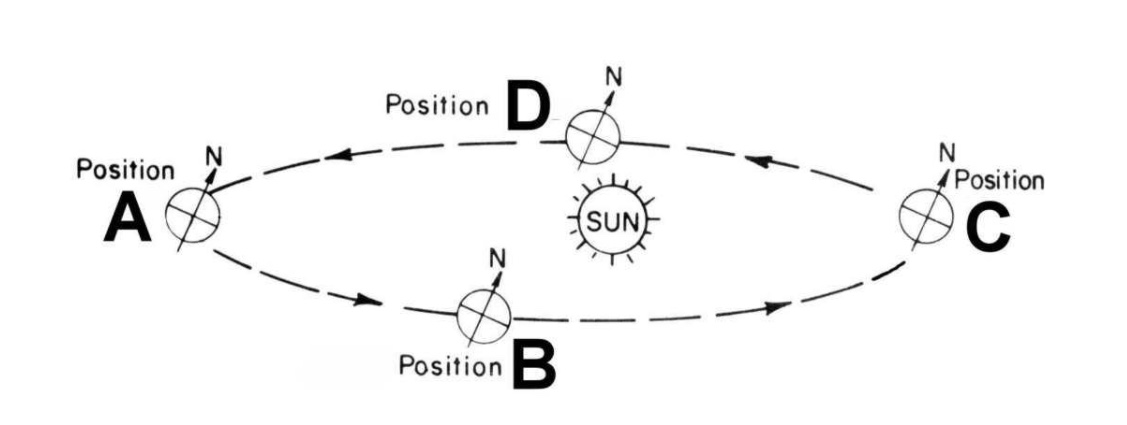


Explain what would happen in the Earth - Sun relationship if the mass of the Sun doubled. Explain in detail why this would happen.
2 low
What location would produce fall in the Southern Hemisphere below?