The amount of goods available.
What is Supply?
The economic rule stating that individuals cannot keep buying the same quantity of a product if its price rises while their income stays the same.
What is Real Income Effect?
Keeps a price from falling below a given point, lowest price that one can legally pay for some good or service.
What is Price Floor?
A person may buy a certain type of cereal for a while. Later, they may by less, or buy a different cereal due to the decreased level of satisfaction from the first cereal.
What is Diminishing Marginal Utility?
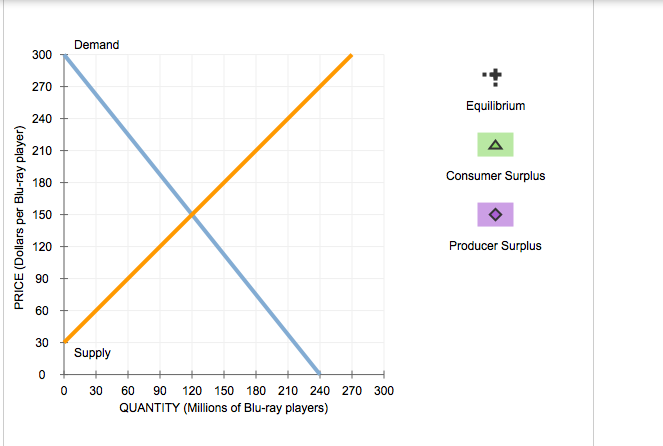
What is Surplus?
An economic principle referring to a consumer's desire and willingness to purchase goods.
What is Demand?
States that if one input in the production of a commodity is increased while other inputs are held fixed, a point will eventually be reached at which additions of the input yield progressively diminishing increases in output.
What is Law of Diminishing Return?
A situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied.
What is Shortage?
At $3 per cookie, 500 cookies are demanded and 100 are supplied.

What is Law of Diminishing Return?
The claim that, other things being equal, the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises.
What is Law of Demand?
Tastes and Preferences, Number of Consumers, Price of Related Goods, Income, Future Expectations
What is The Shifters of Return?
A situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded.
What is Surplus?
Minimum wage, the lowest amount that employers can legally pay their employees.
What is Price Floor?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/IntroductiontoSupplyandDemand1_2-578635efad694c929704cbaf6884fb55.png&usqp=CAU)
What is Demand?
States that producers offer more of a good as its price increases and less as its price falls.
What is Law of Supply?
Price of Resources, Number of Producers, Technology, Taxes and Subsidies, Expectations
What is The Shifters of Supply?
The measure of change in the quantity demanded for a good or service.
What is Elastic ?
Caps on the costs of prescription drugs and lab tests.
What is Price Ceiling?
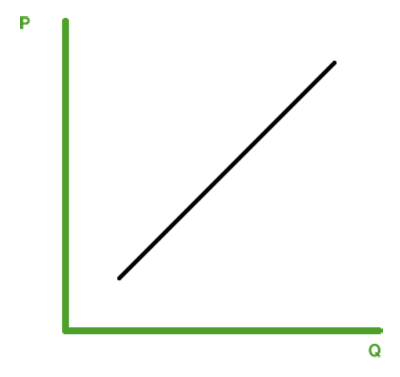
What is Supply?
The principle that consumers experience diminishing additional satisfaction as they consume more of a good or service during a given period of time.
What is Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility?
Keeps a price from rising above a certain level, legal maximum that one pays for a good or service.
What is Price Ceiling?
What is Inelastic ?
A consumer may choose to spend less on popular clothing because their income has dropped.
What is Real Income Effect?
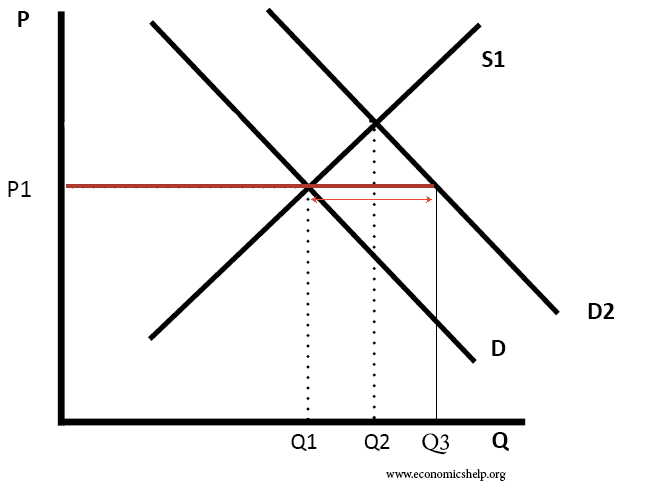
What is Shortage?