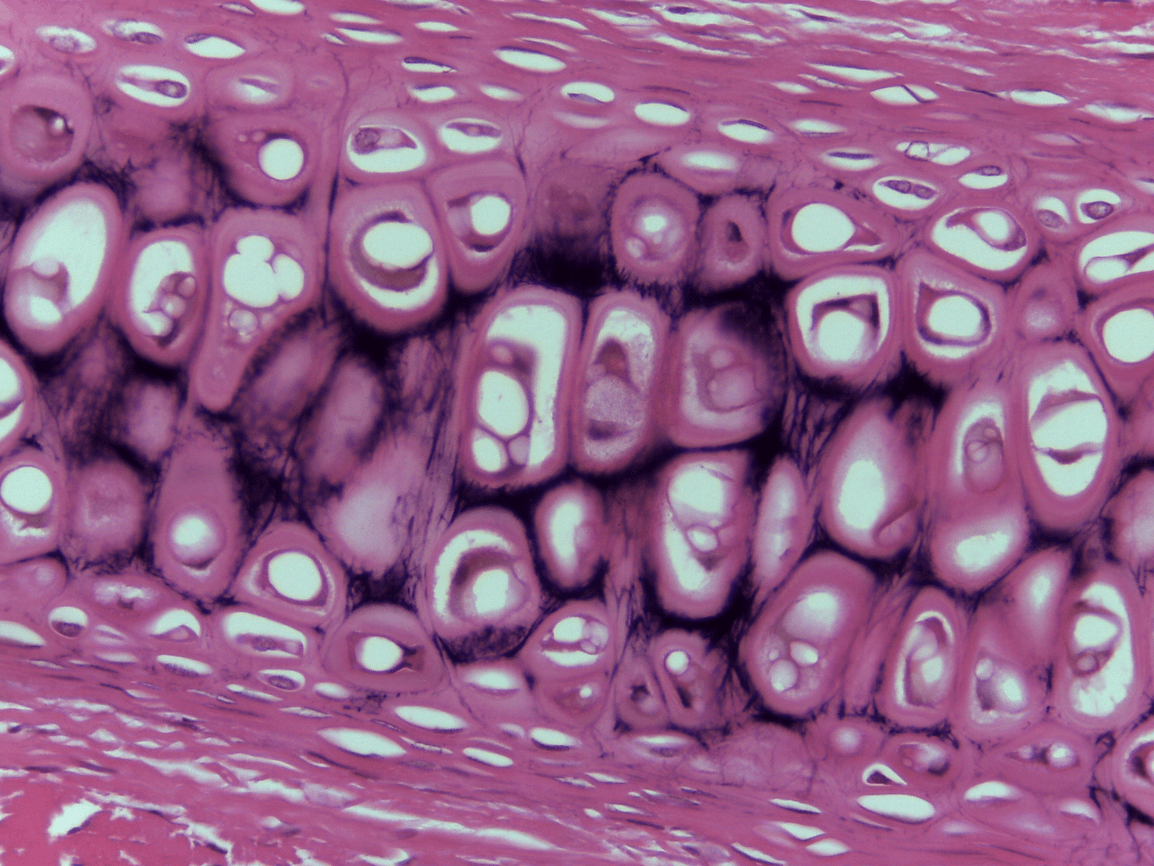
Hyaline CT
Menisci of the knee and intervertebral disks
protection with flexibility
withstand compression
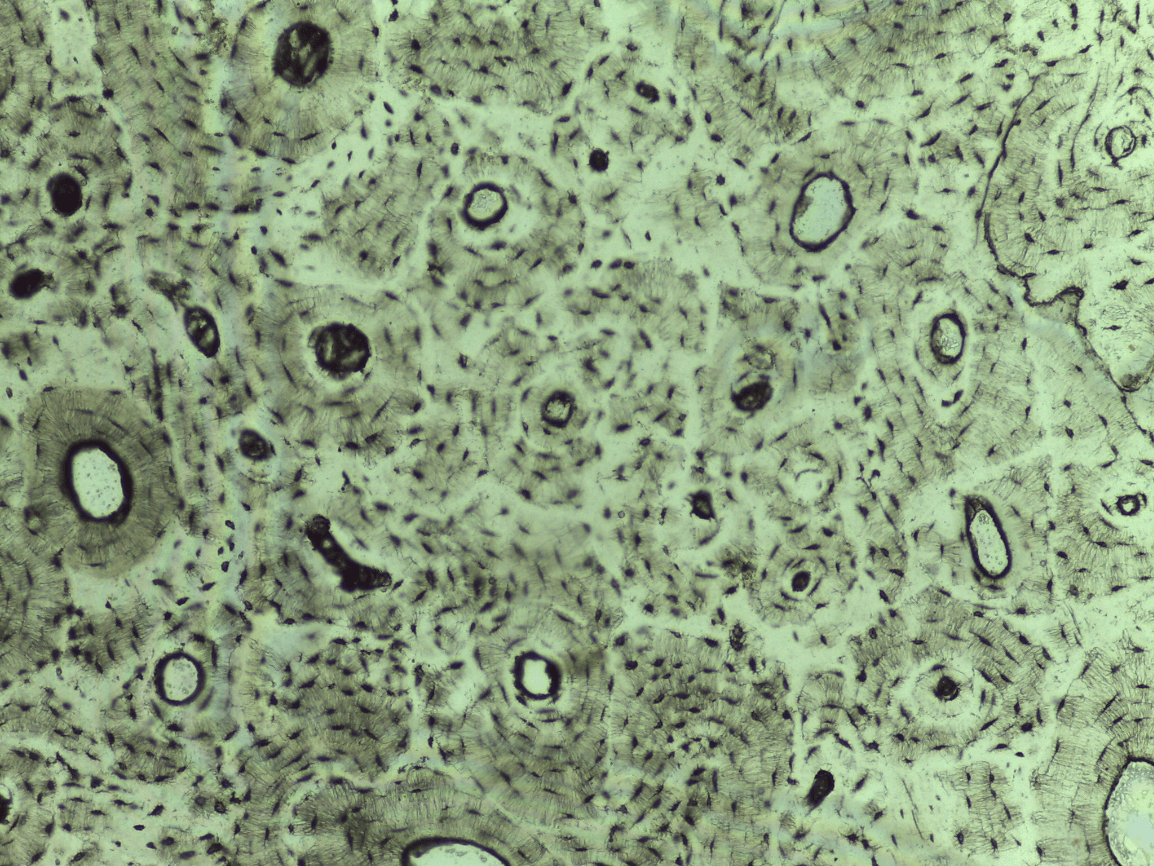
Haversian system
lamallae
osteocytes
What tissue is this and what is its function?
Cardiac Muscle
keep your heart pumping through involuntary movements, pacemaker cells control the contractions of your heart
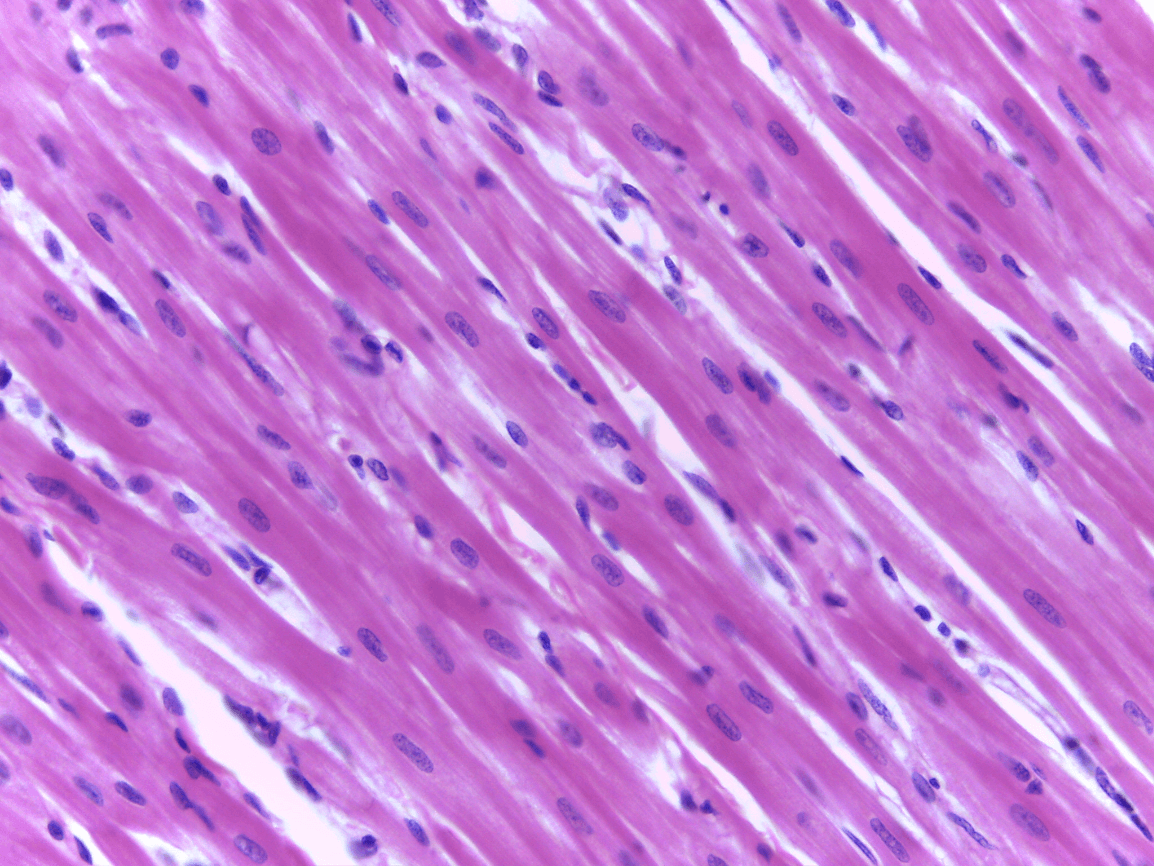
Cardiac Muscle
Hollow Organs and blood vessels
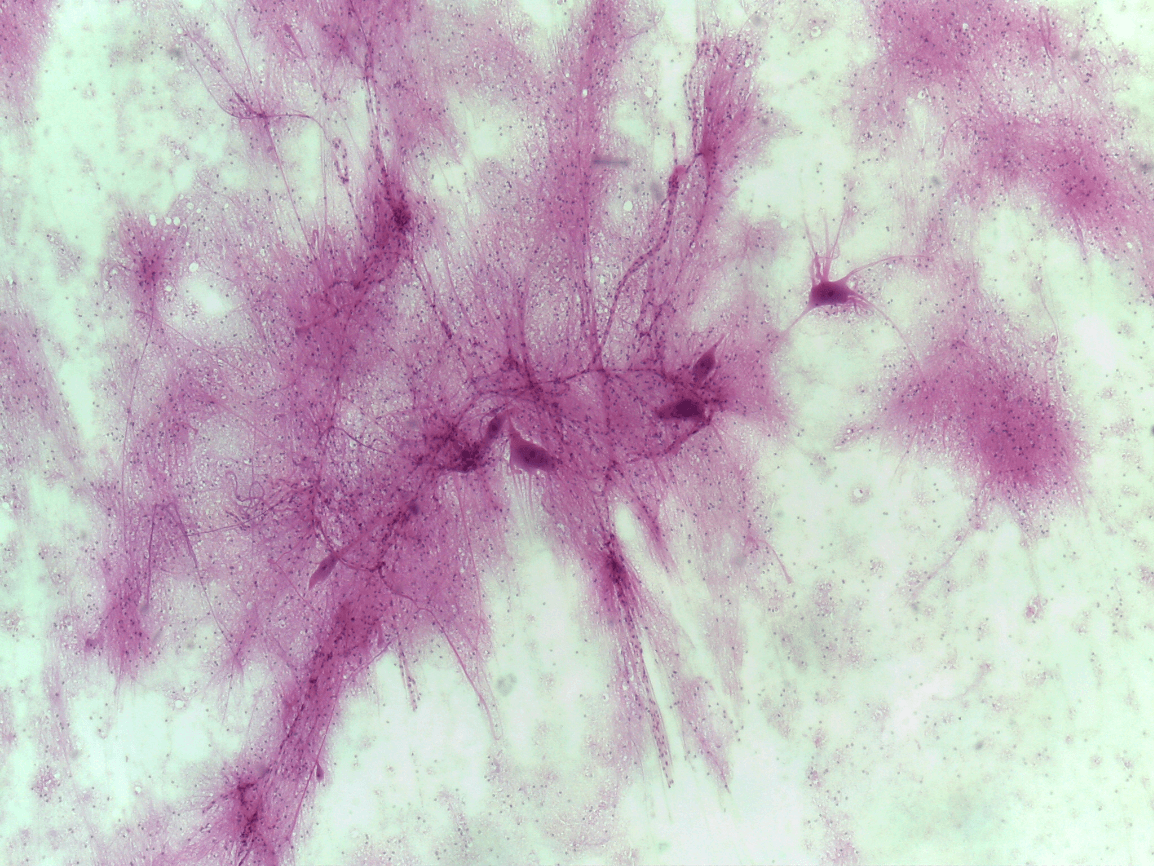
coordinating and controlling many body activities. It stimulates muscle contraction, creates an awareness of the environment, and plays a major role in emotions, memory, and reasoning
What is the black material in this tissue?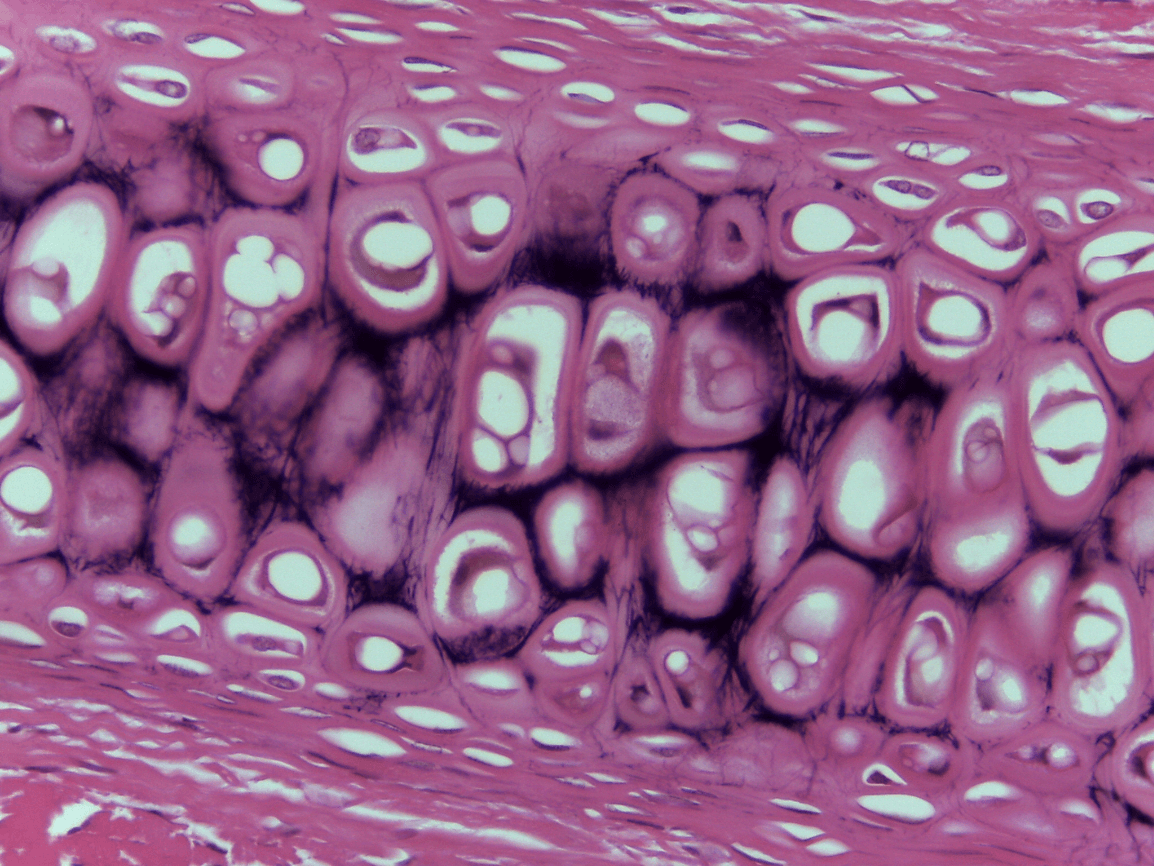
Elastic fibers
Cardiac Muscle
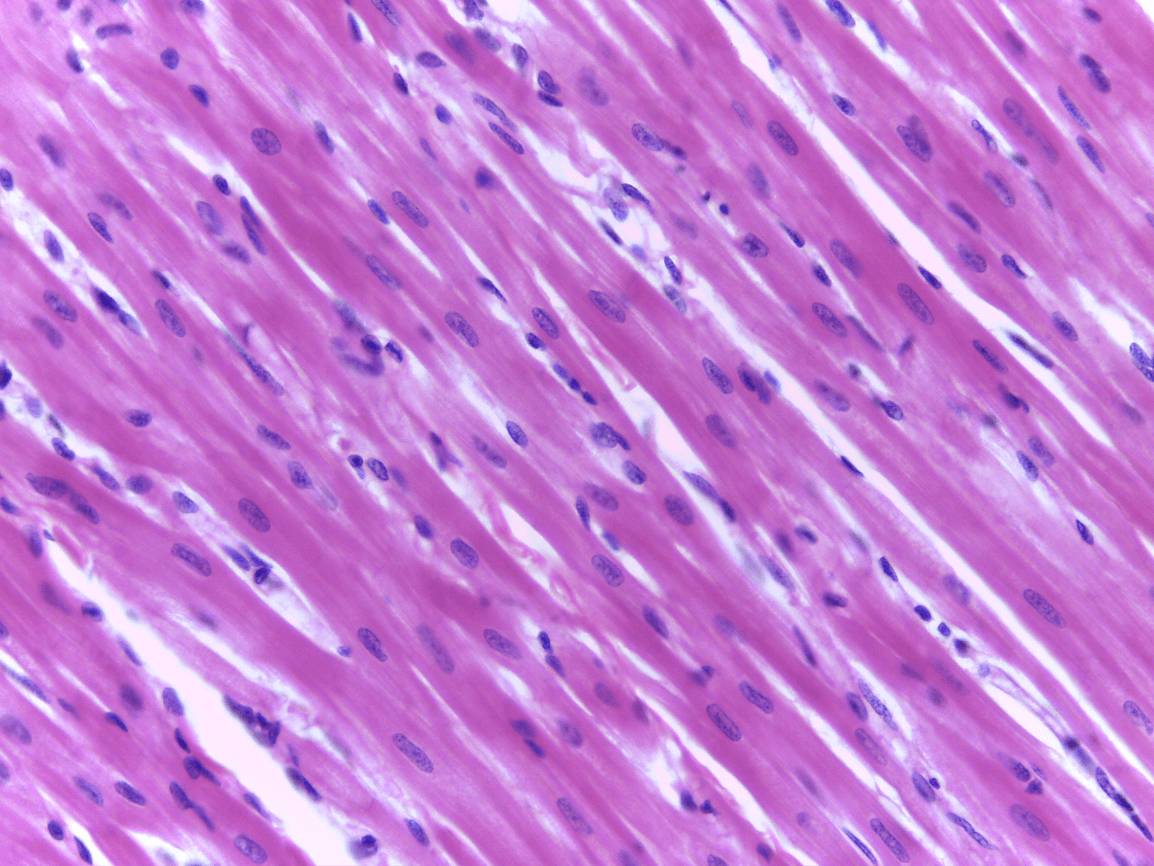
the heart
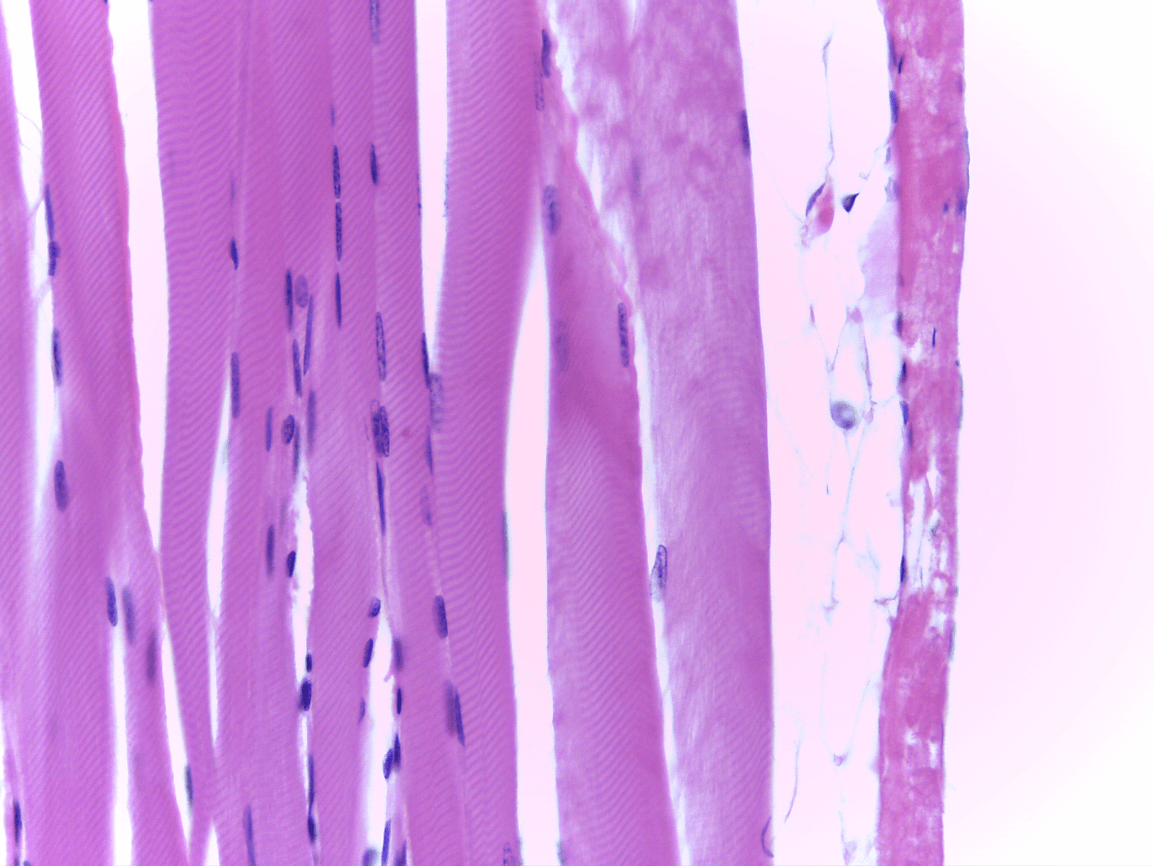
voluntary muscle contraction

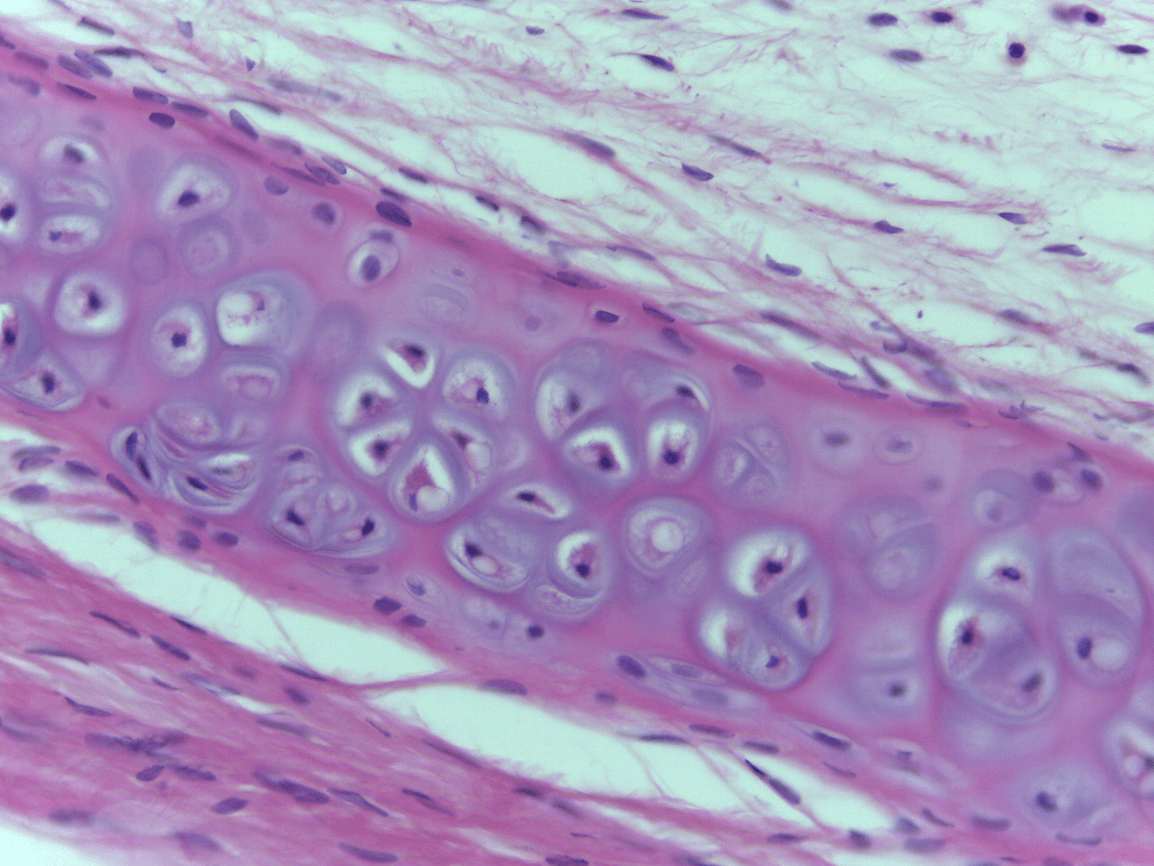
chondrocytes (take care of matrix) (bubbles seen)
Lacunae is where the cytes live in (outer part) inner part is the chondrocyte
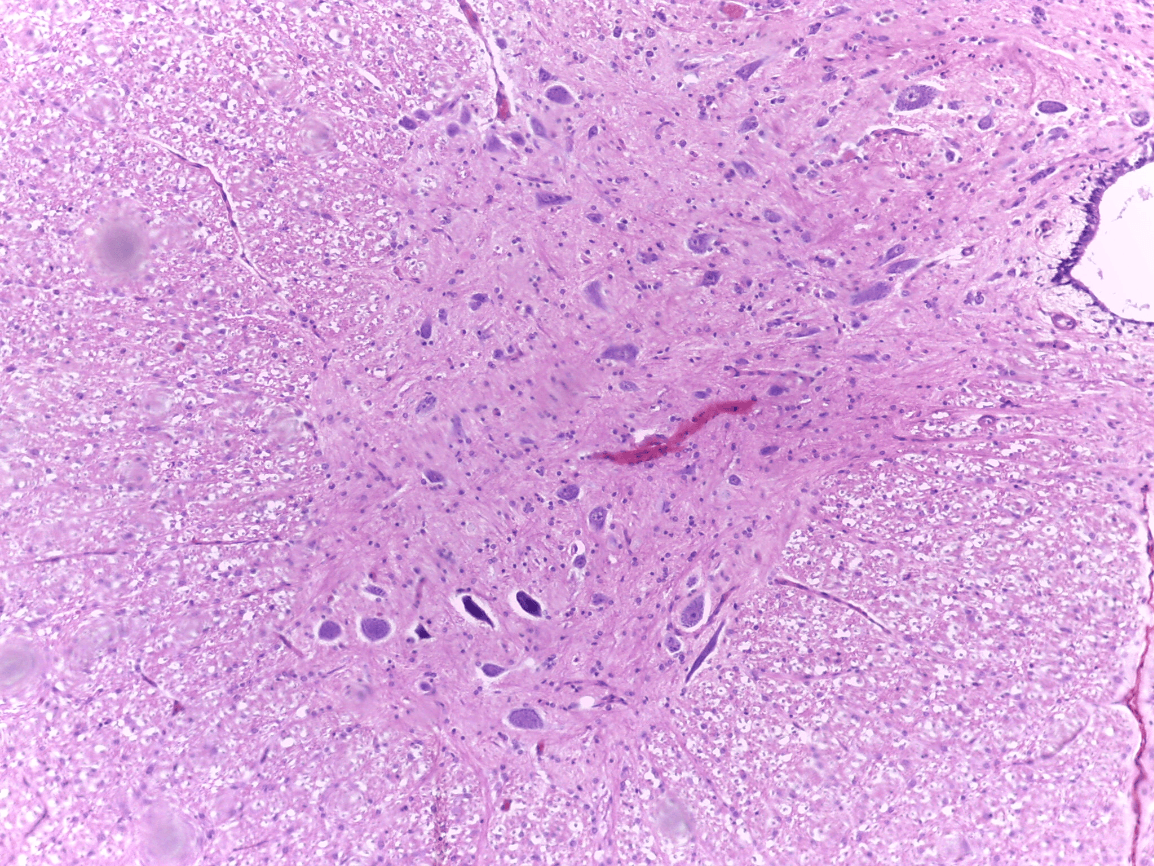
anterior horn of the gray matter
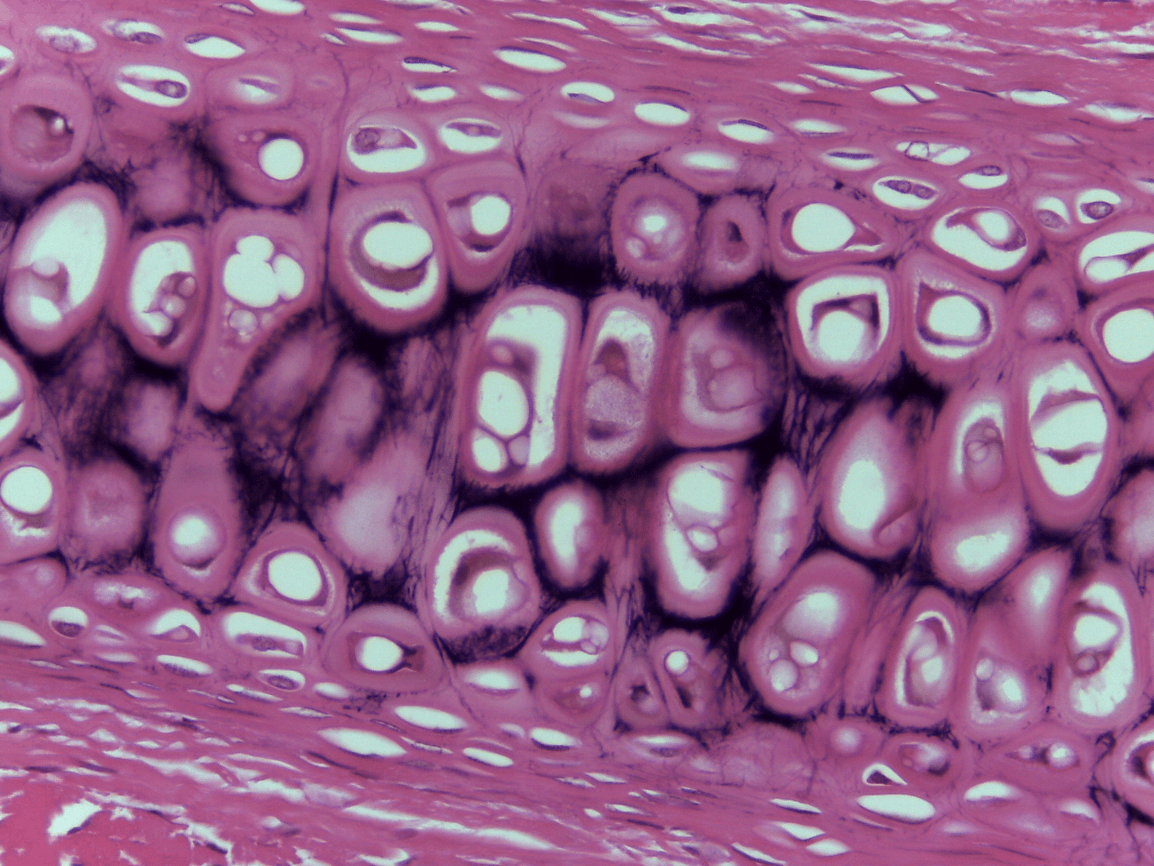
Elastic Cartilage CT
the outer portion of your bone
create a firm but flexible structure
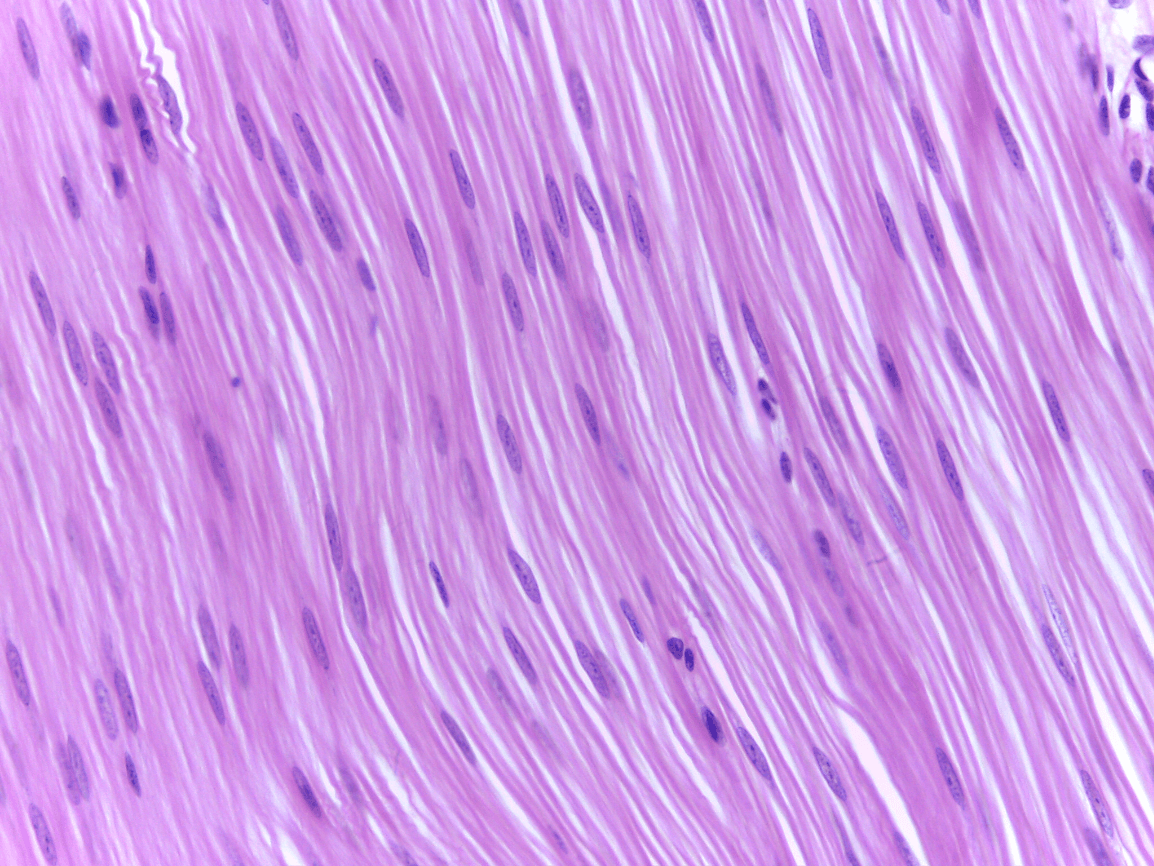
No striation, single centrally located nucleus
What four tissue types can you see here from superficial to dense? (two are the same)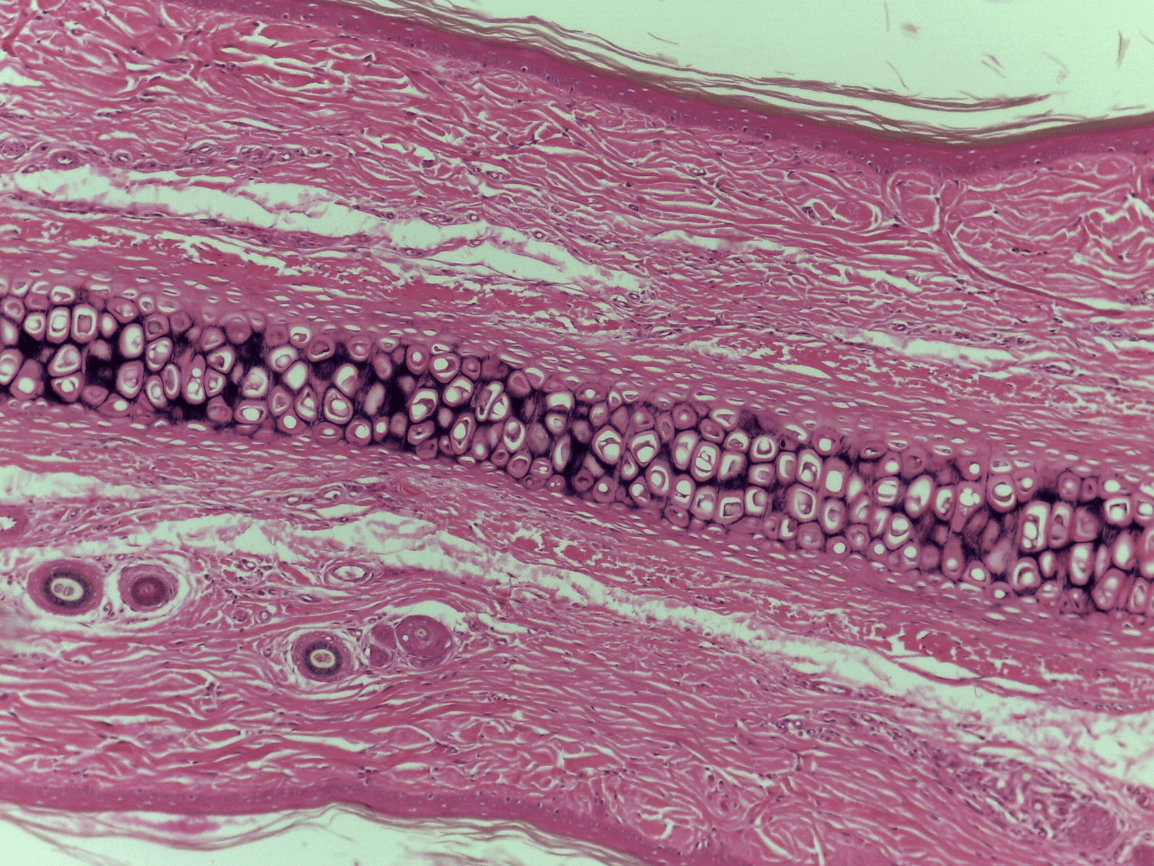
1.) Keratinized stratified squamous ET
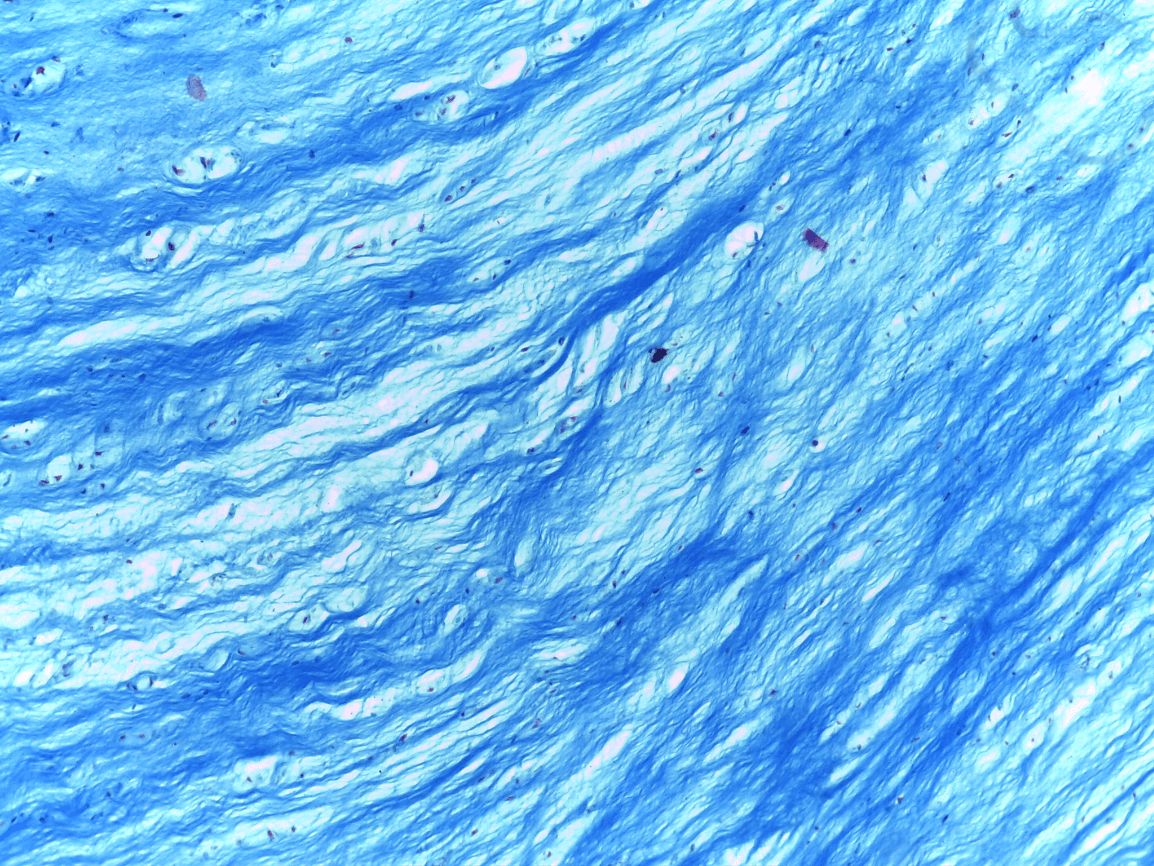
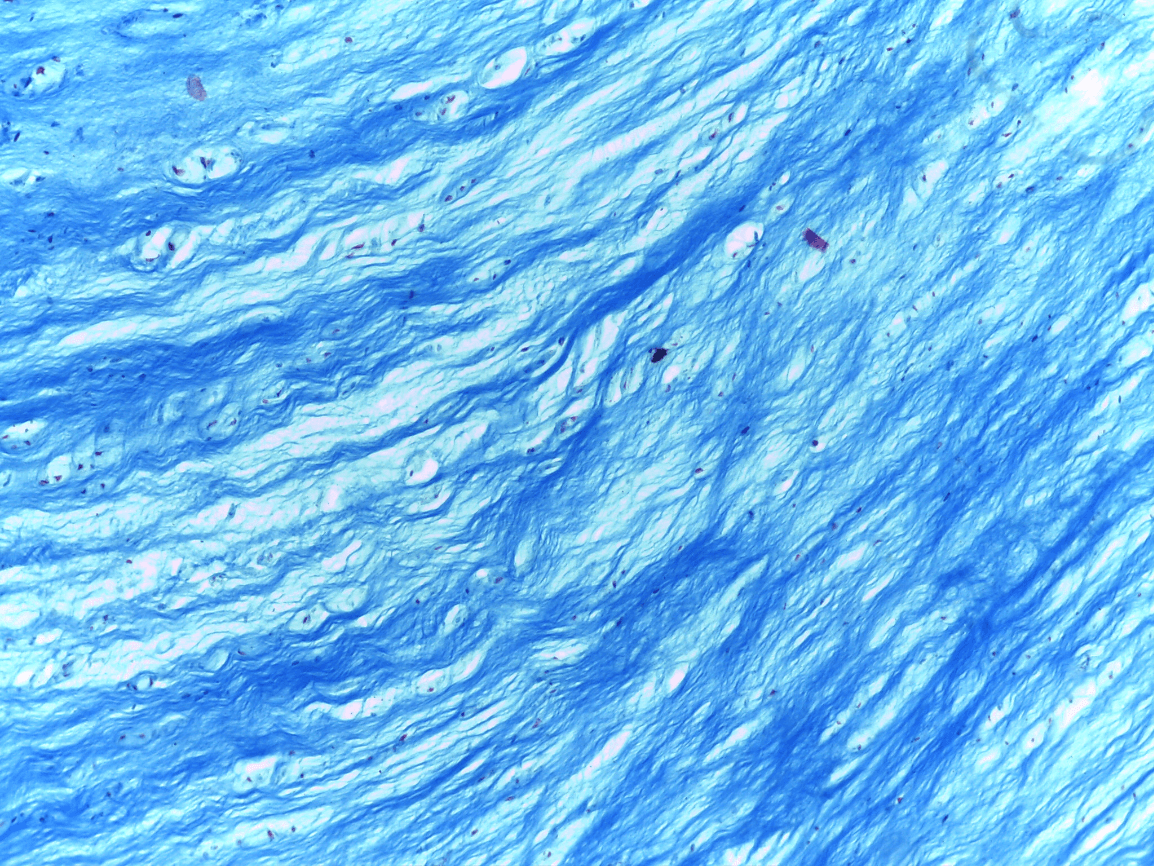
2.) Dense irregular CT
3.) Elastic cartilage CT
4.) Dense irregular CT
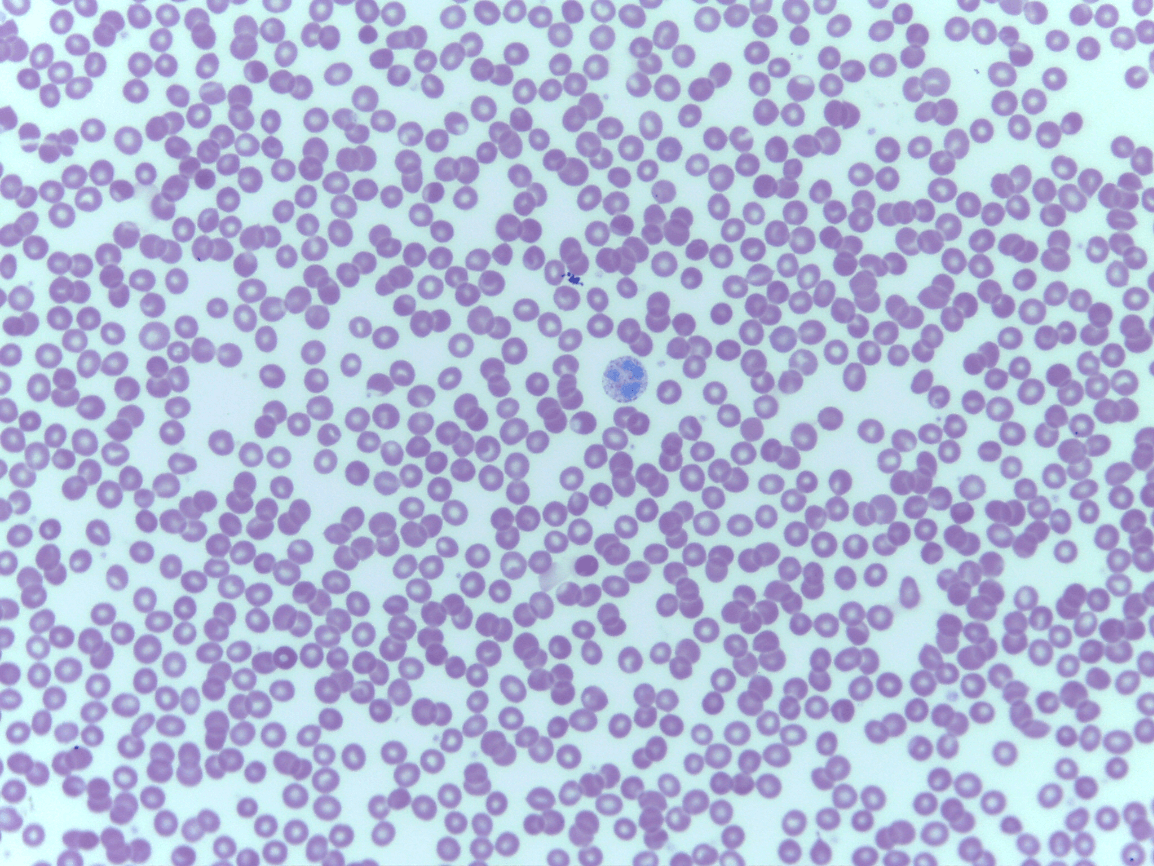
Blood
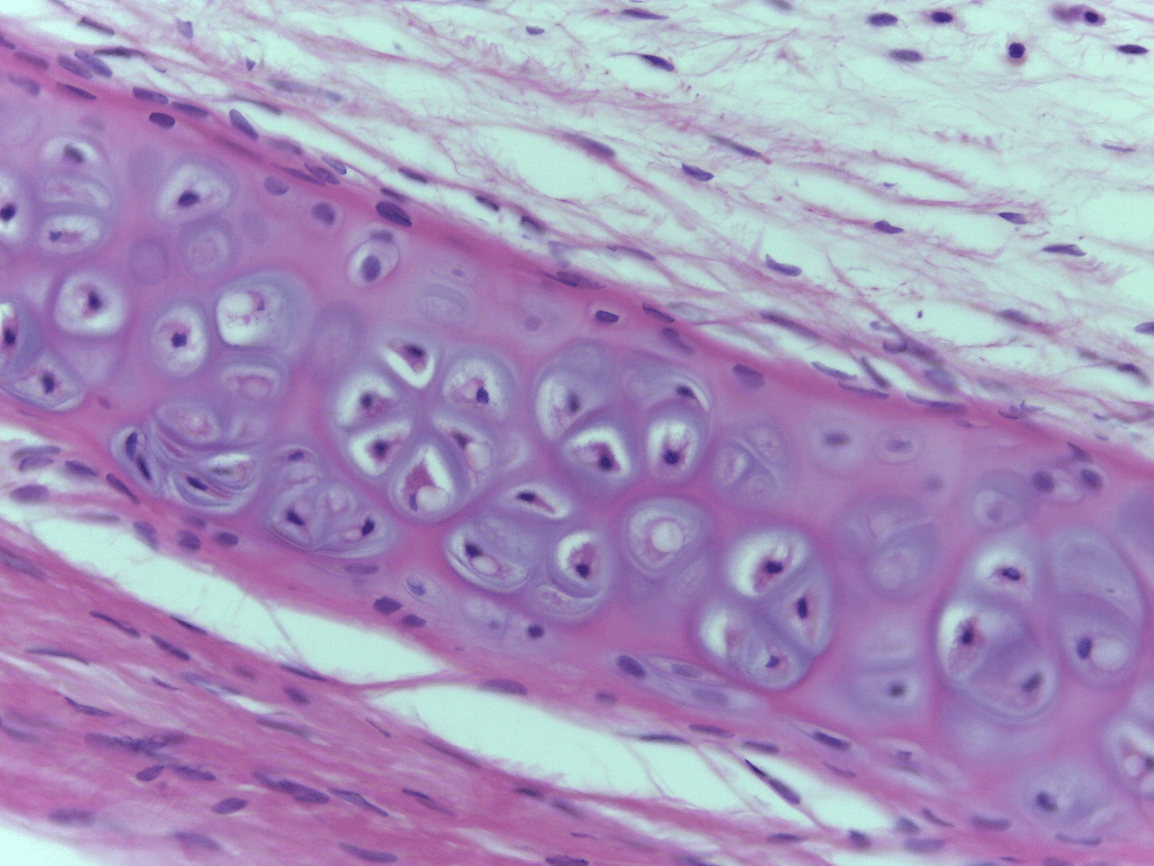
reduce friction, create firm but flexible structure
branching of muscle cells, intercalated discs
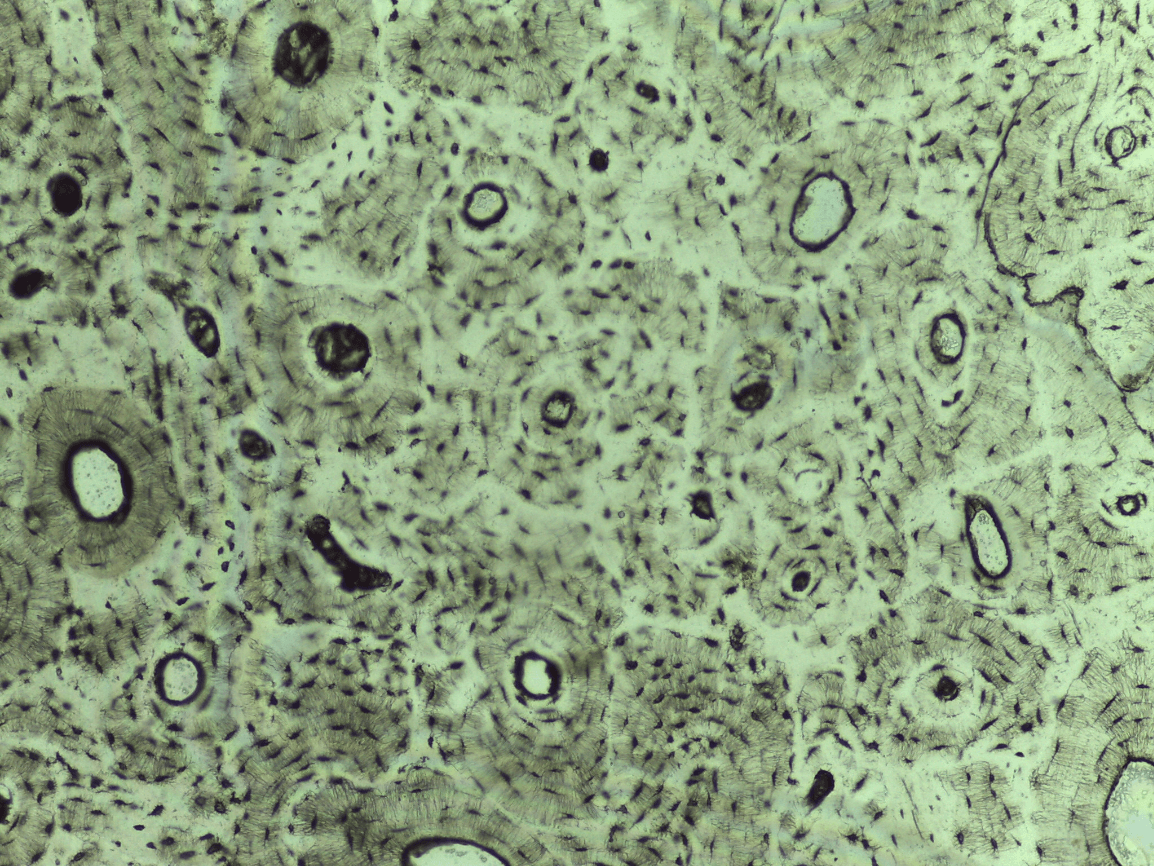
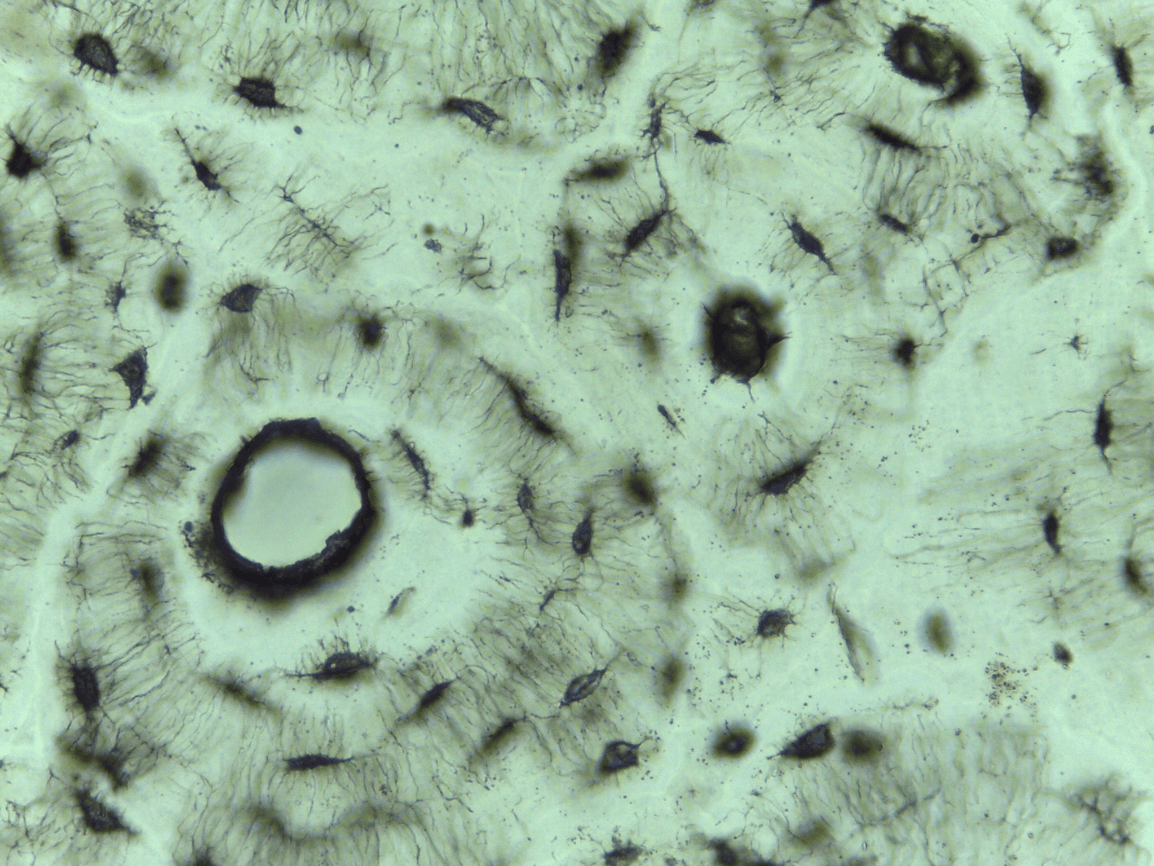
can you identify the 6 main features of bone ct?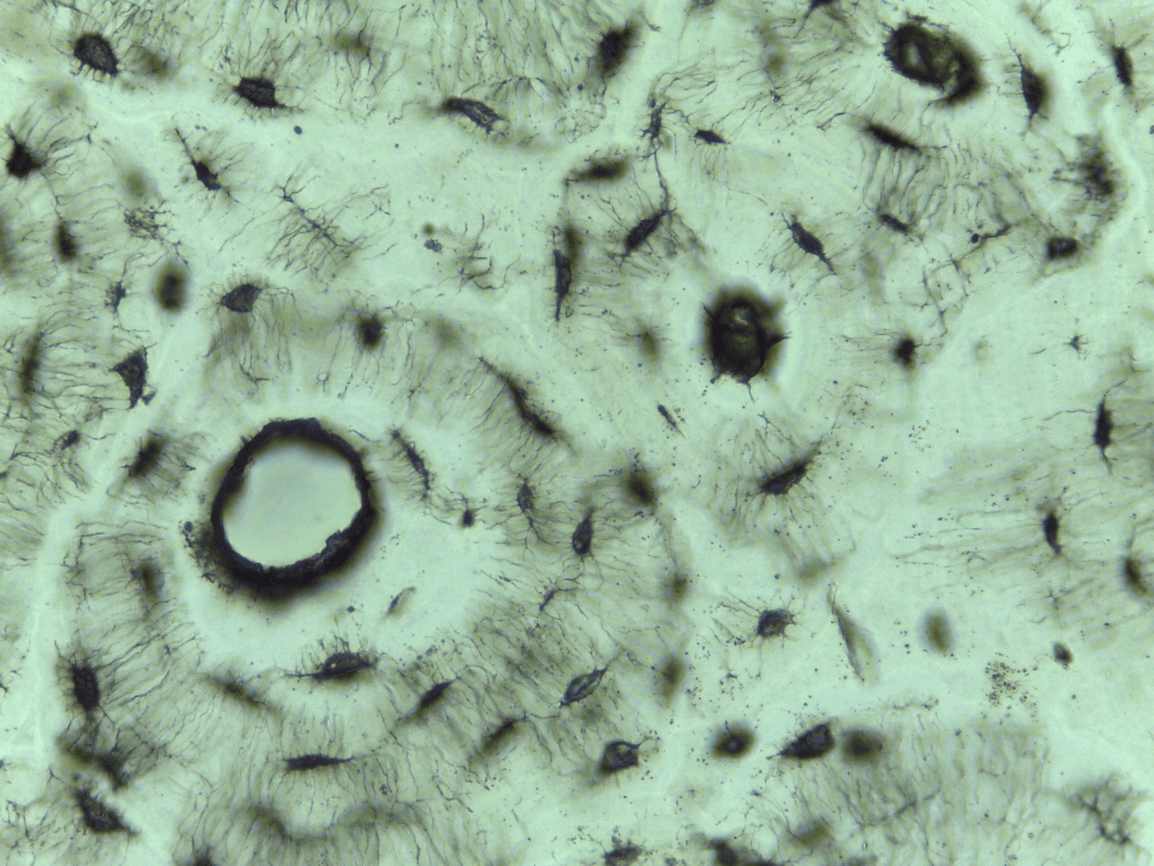
-Haversian system
-lamellae
-central or Haversian canal
-osteocytes
-lacunae
-canaliculi
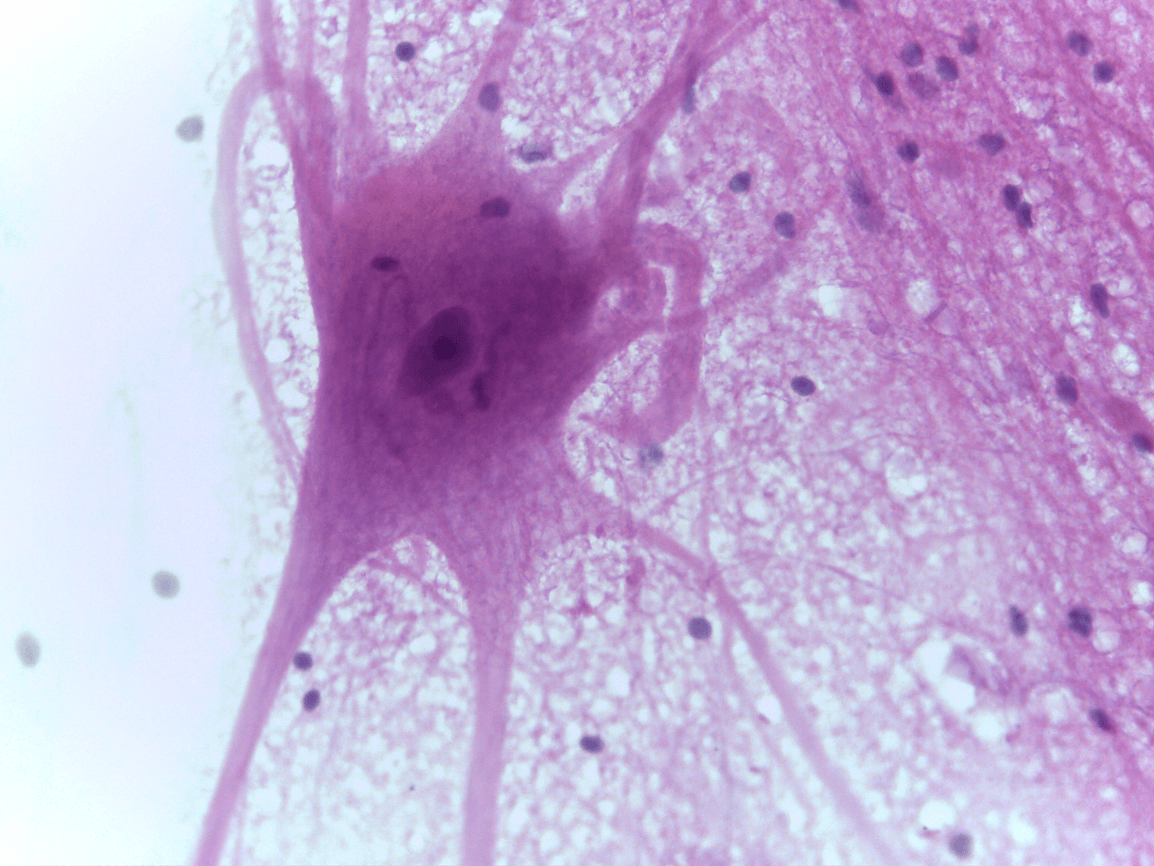
Nervous tissue

Chondriocytes
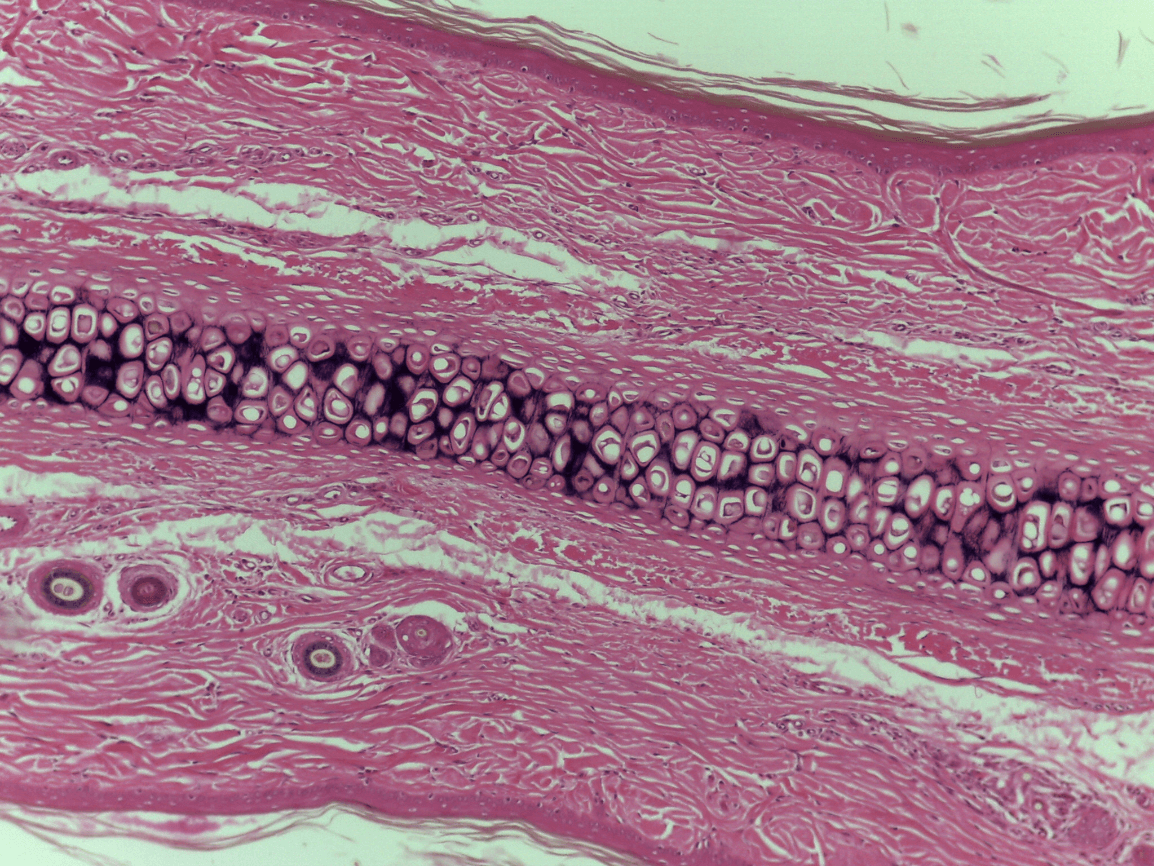
Elastic Cartilage CT
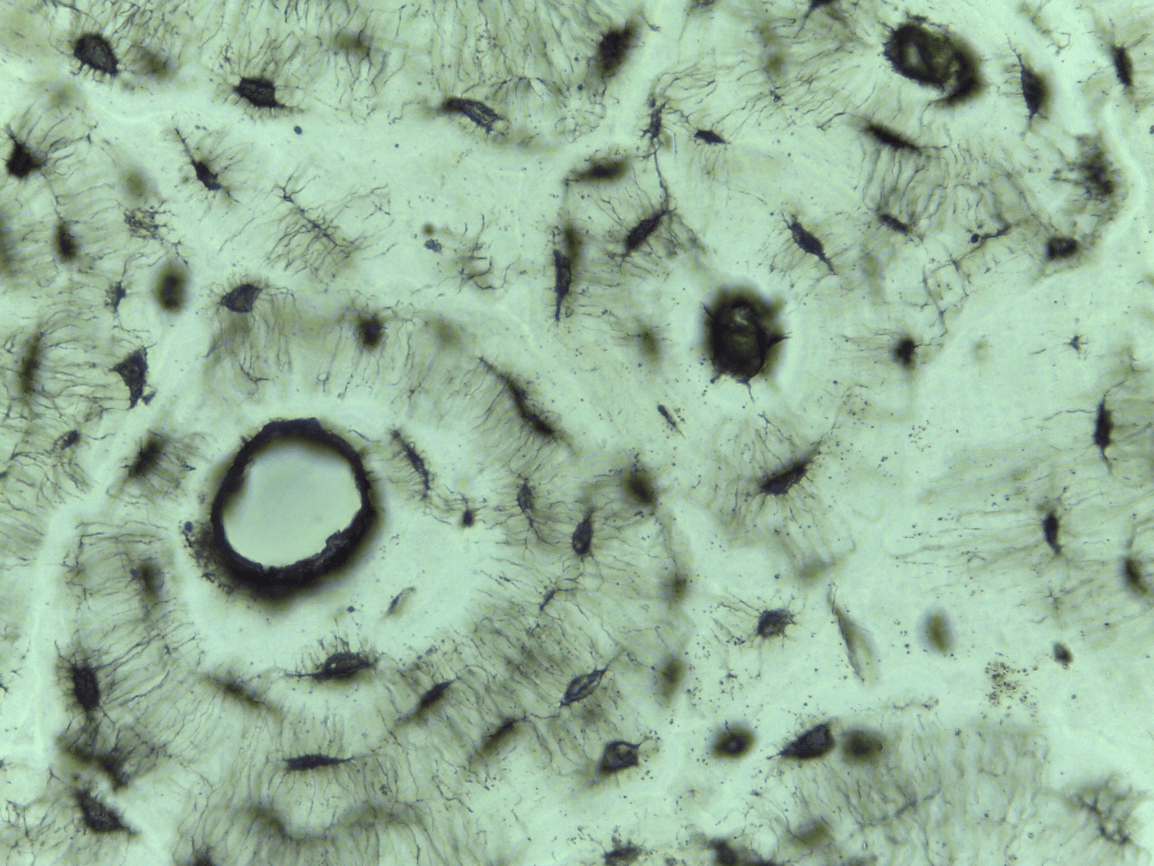
Outer portion of your bone
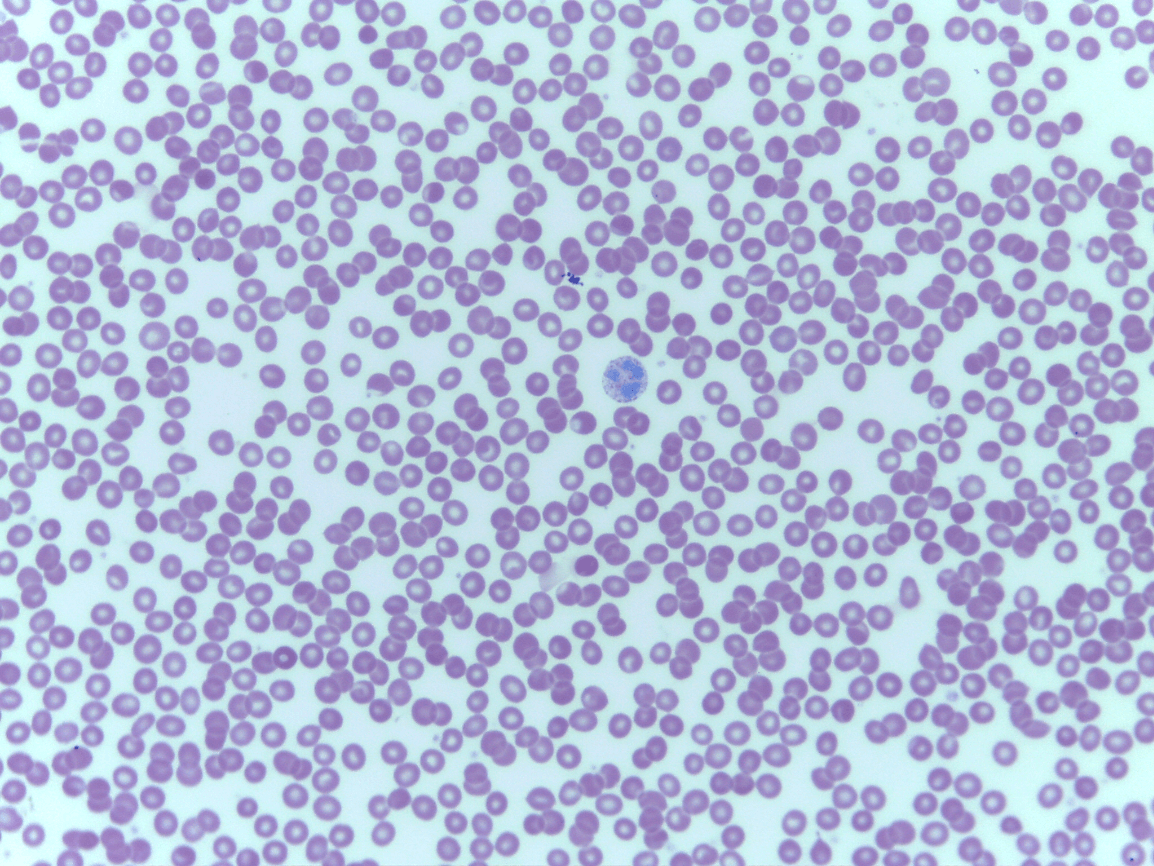
supplying nutrients,gases (O2 andCO2) essential for the cells for their living
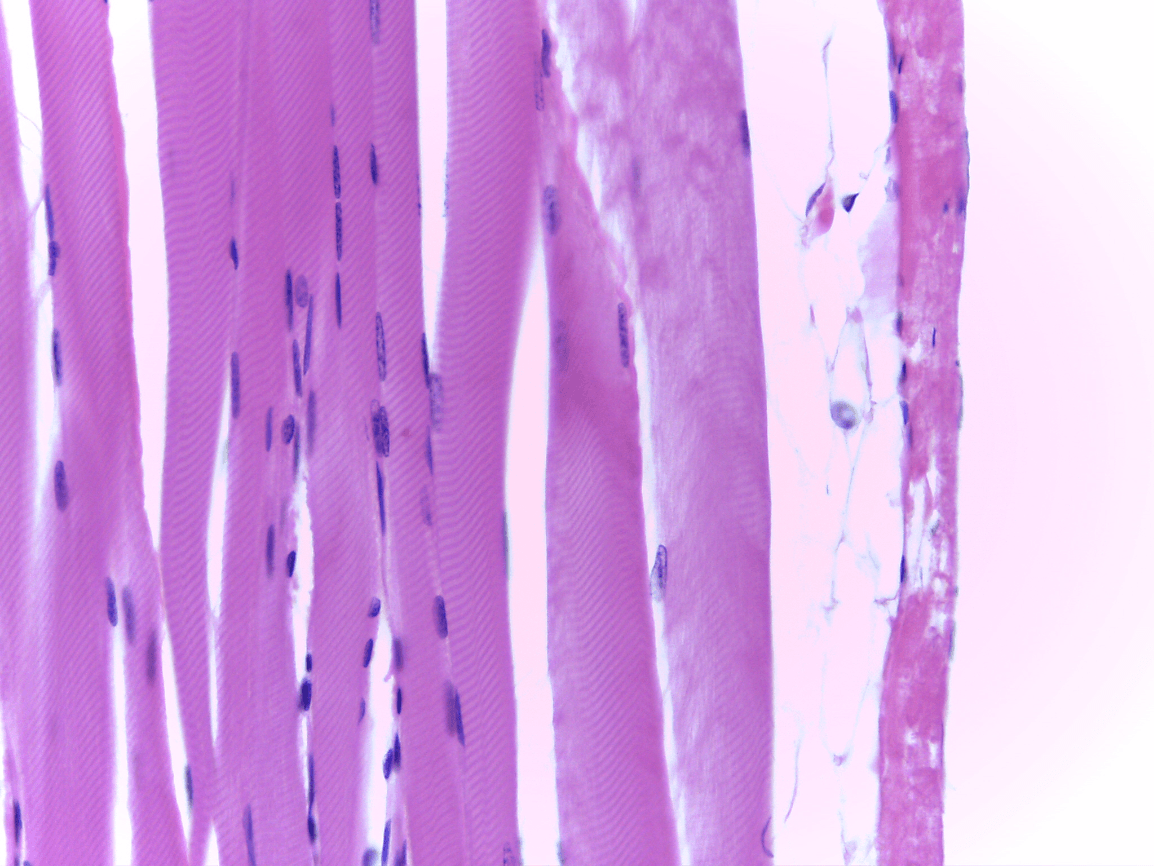
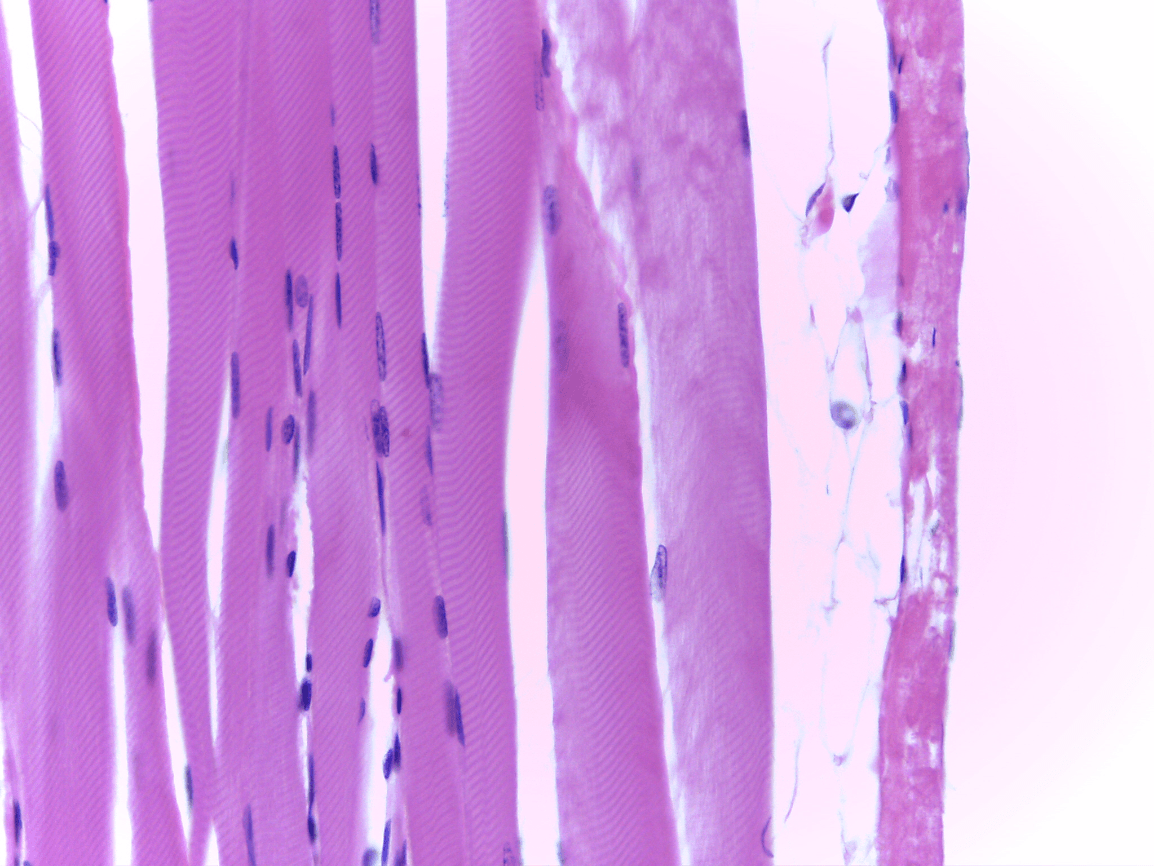
multiple nuclei, striations
What tissue type is this and what is its function?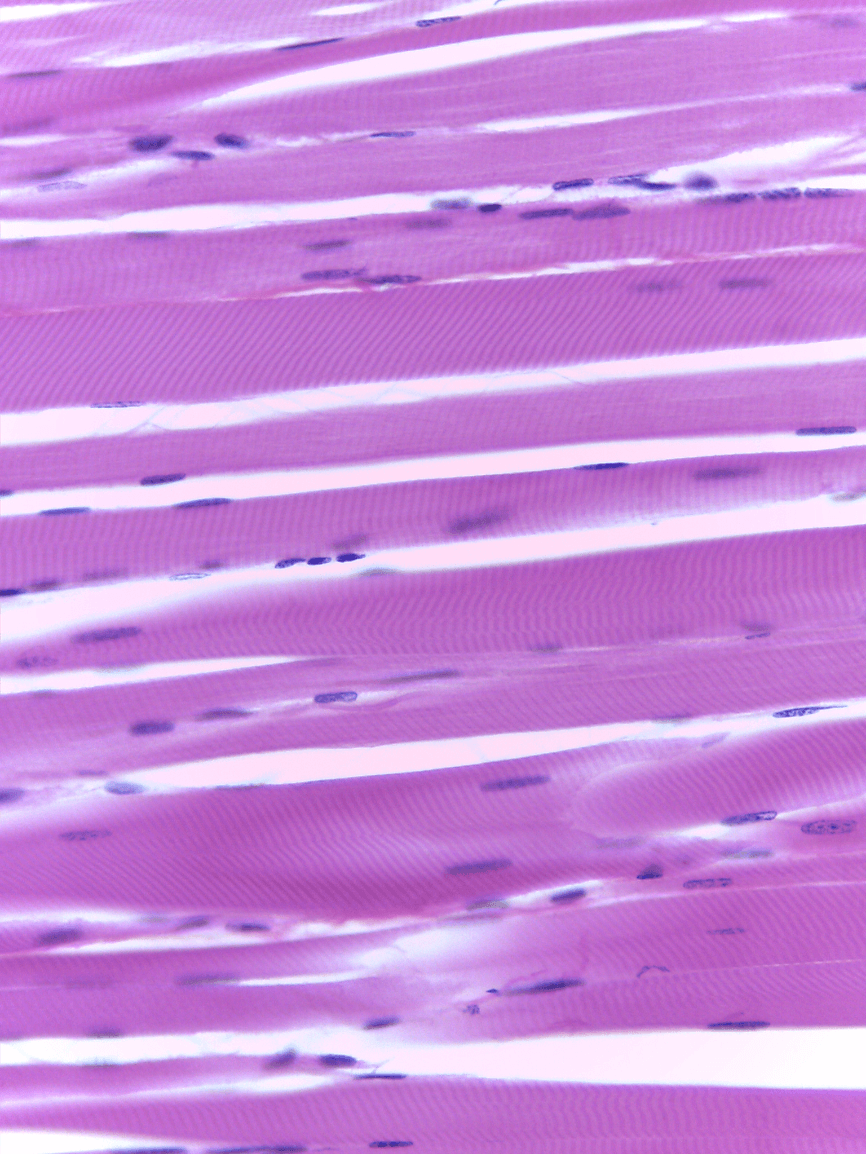
Skeletal
voluntary movement, posture, movement, ventilation, facial expressions
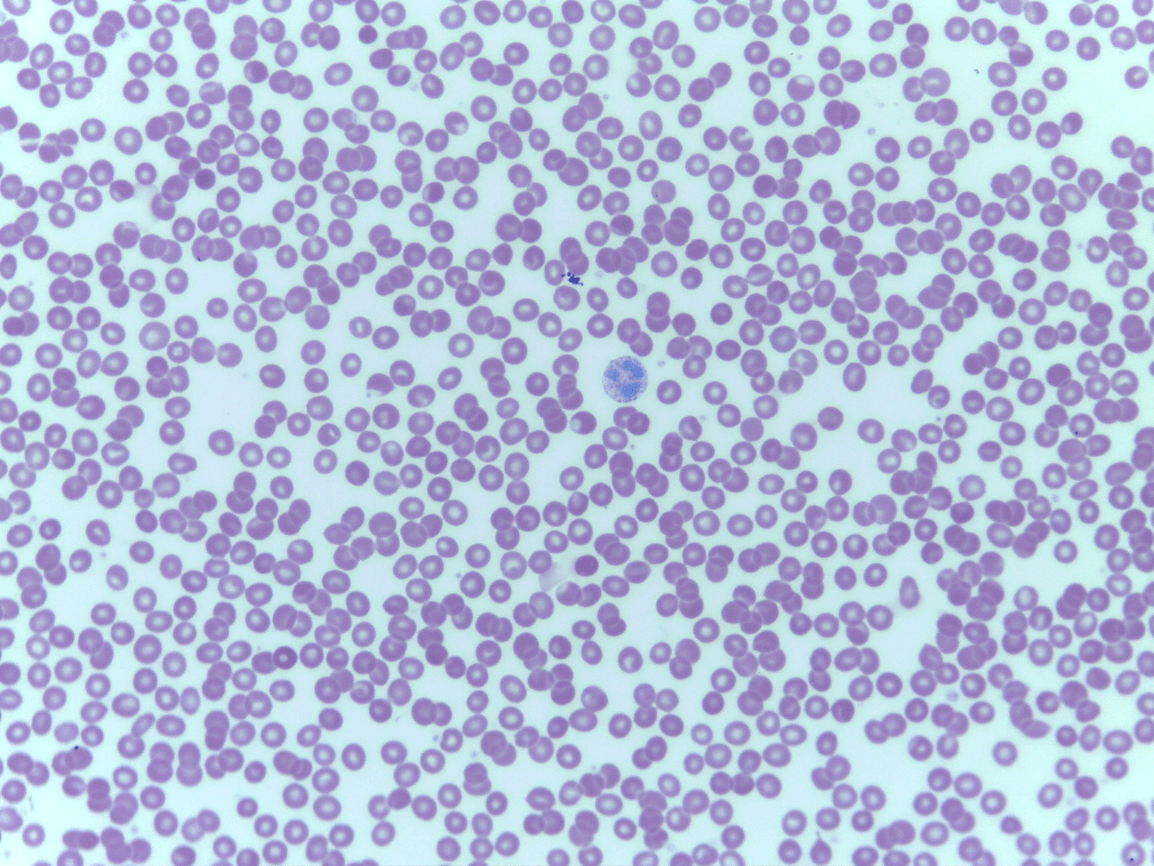
Fluid CT
Connected to Bones
keep your heart pumping through involuntary movements, pacemaker cells control the contractions of your heart
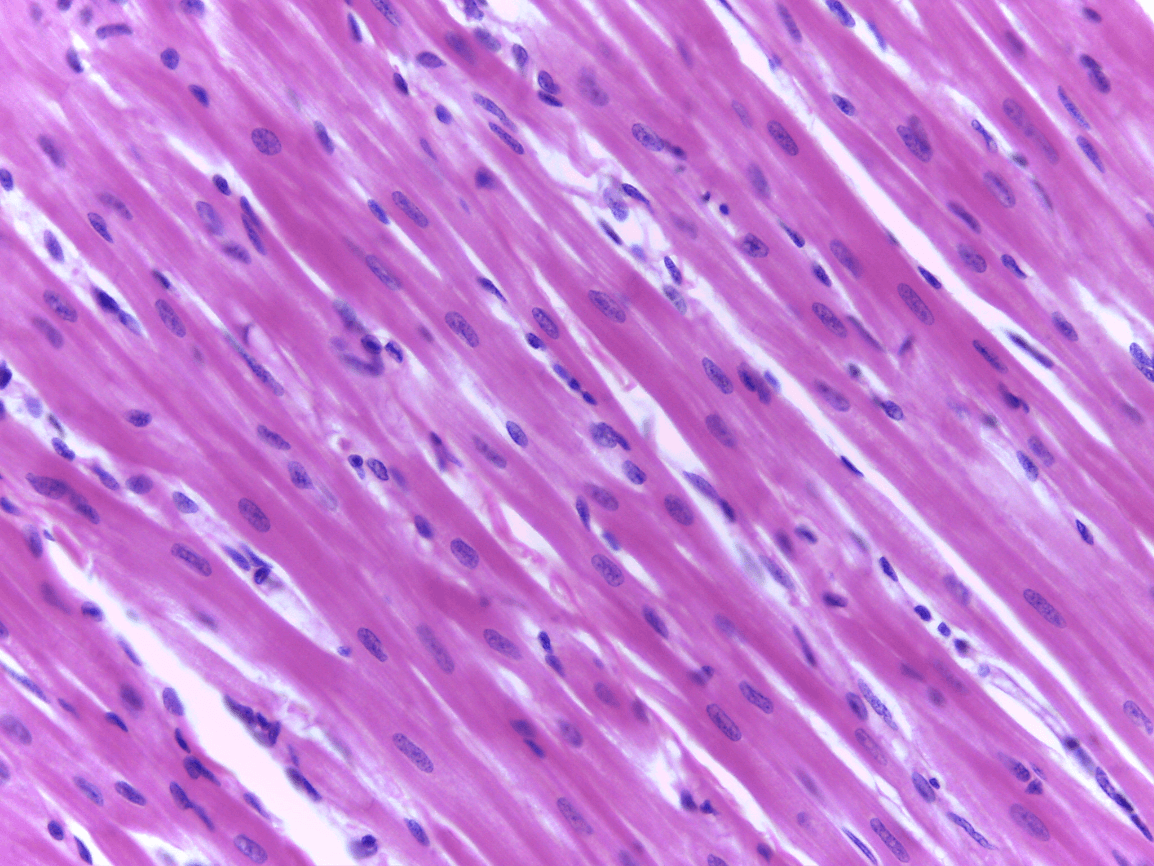
branching of muscle cells, intercalated discs
What are you looking at?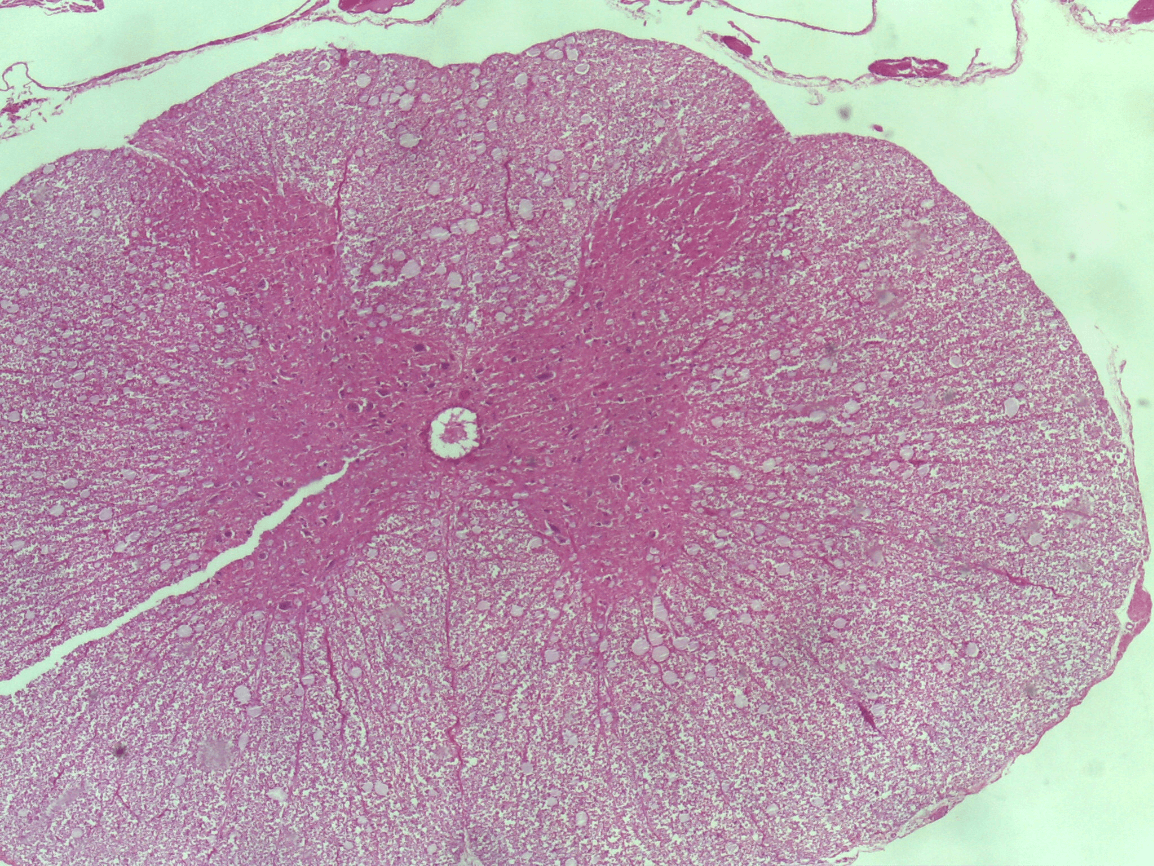
Spinal Cord with a view of the central canal and grey matter (butterfly) and white matter
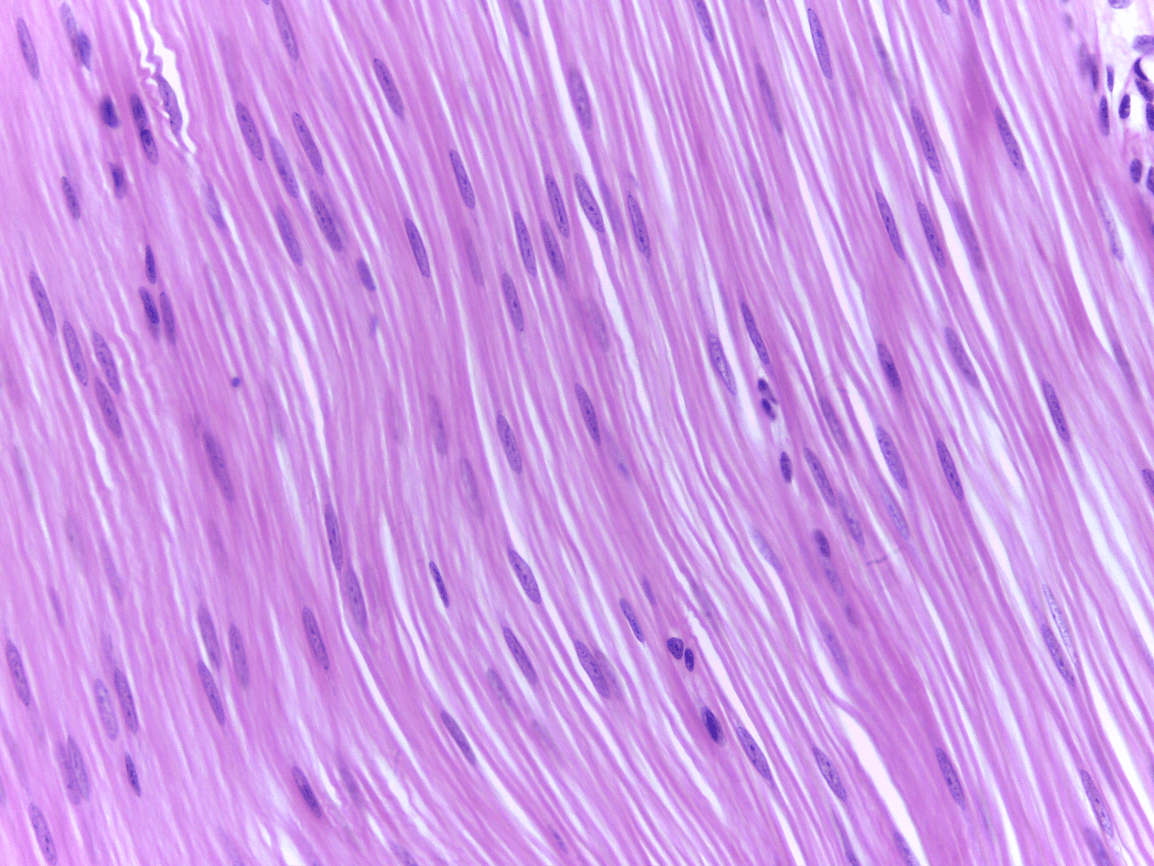
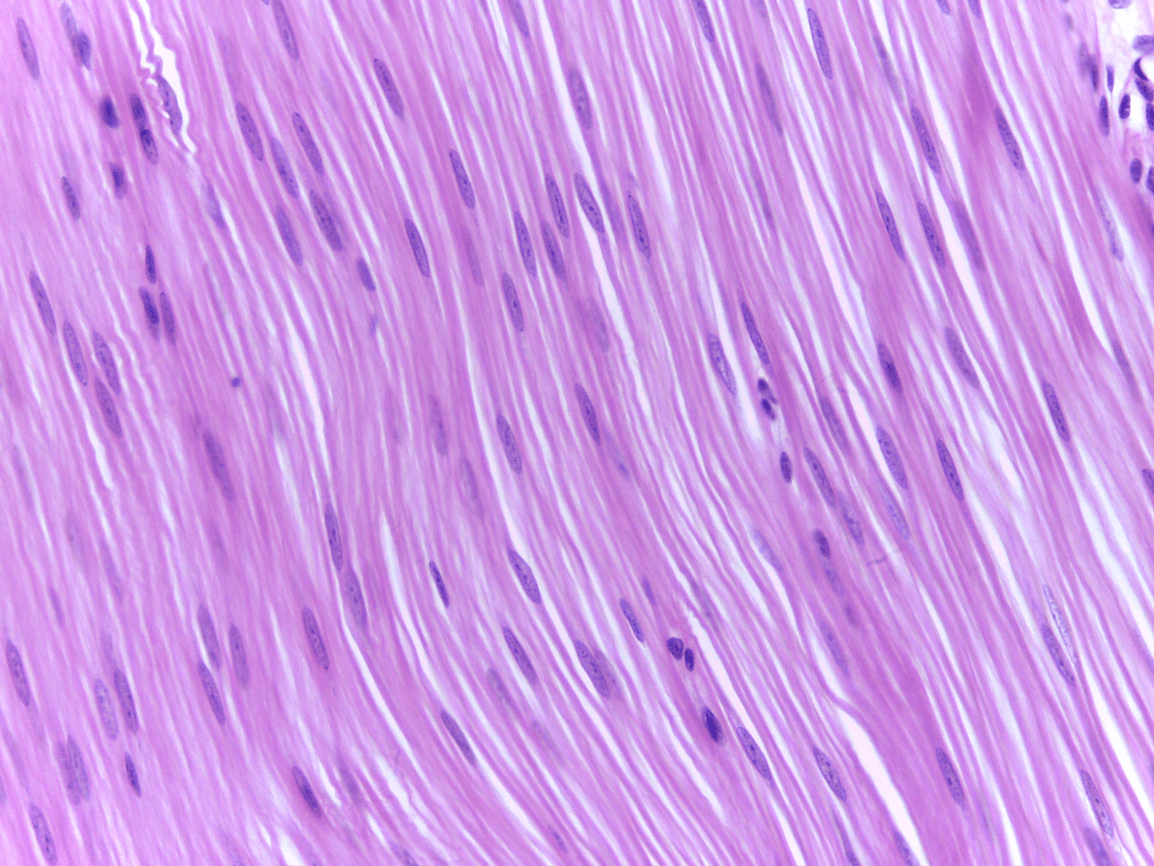
Smooth Muscle
The heart
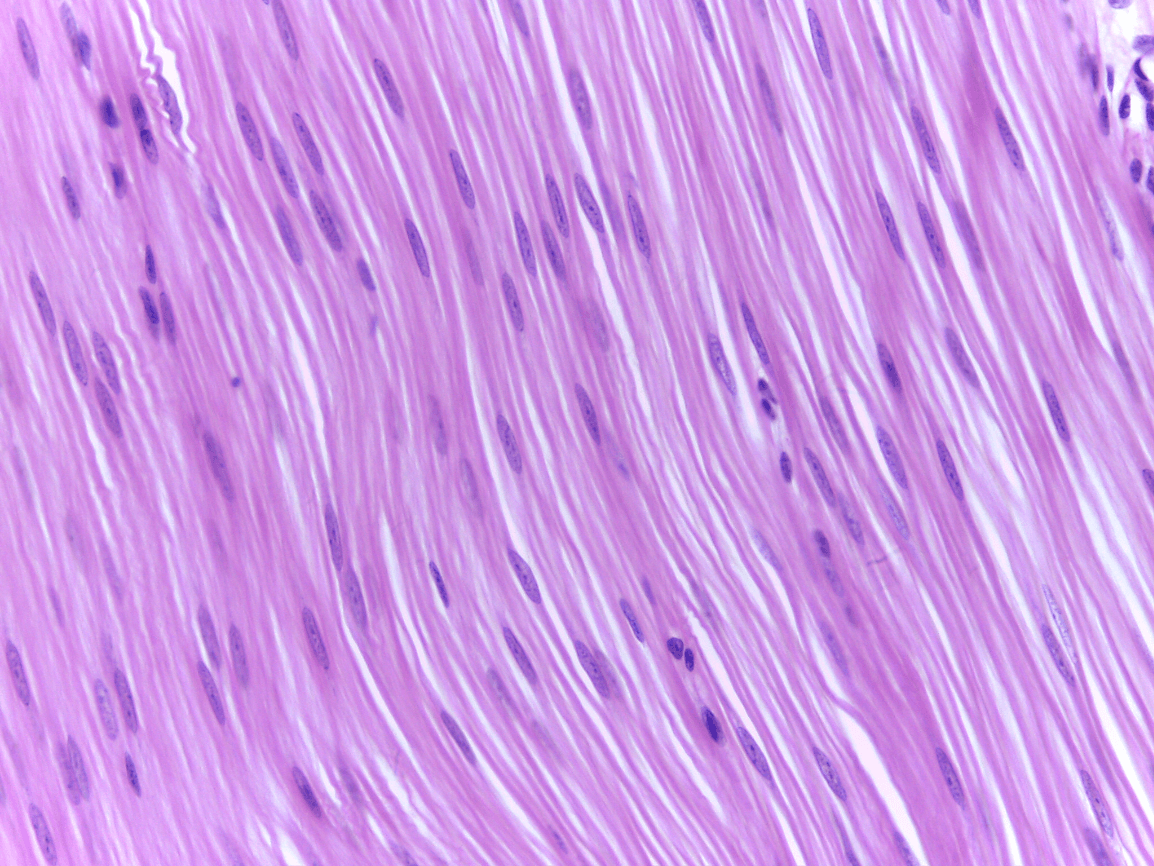
involuntary muscle contraction
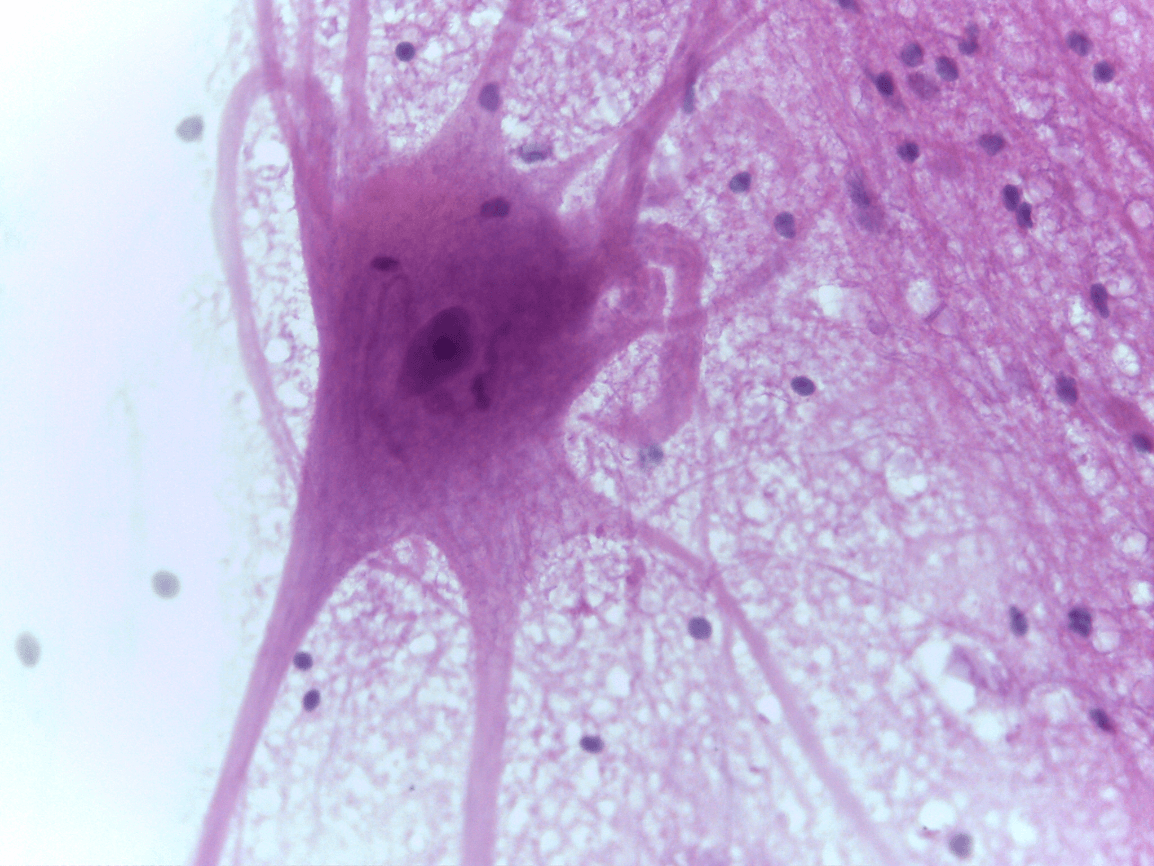
axon and dendrite
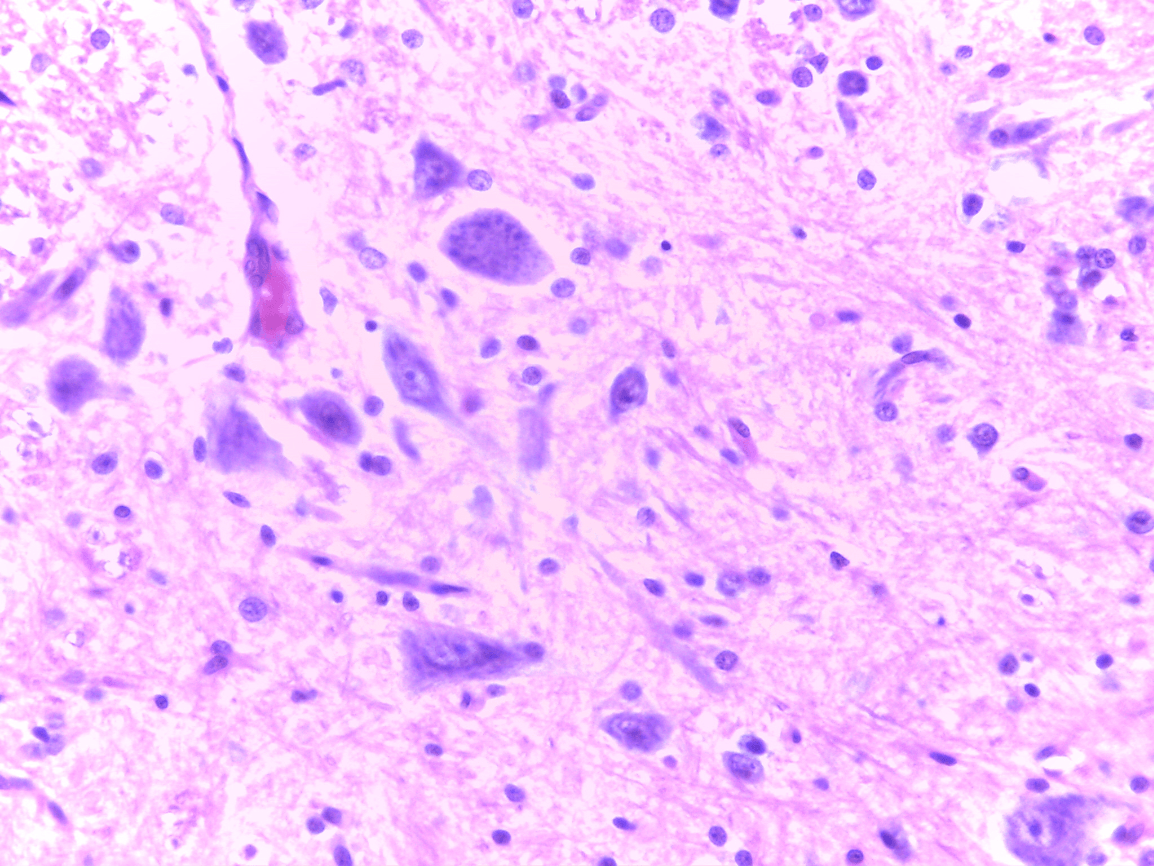
anterior horn of the gray matter
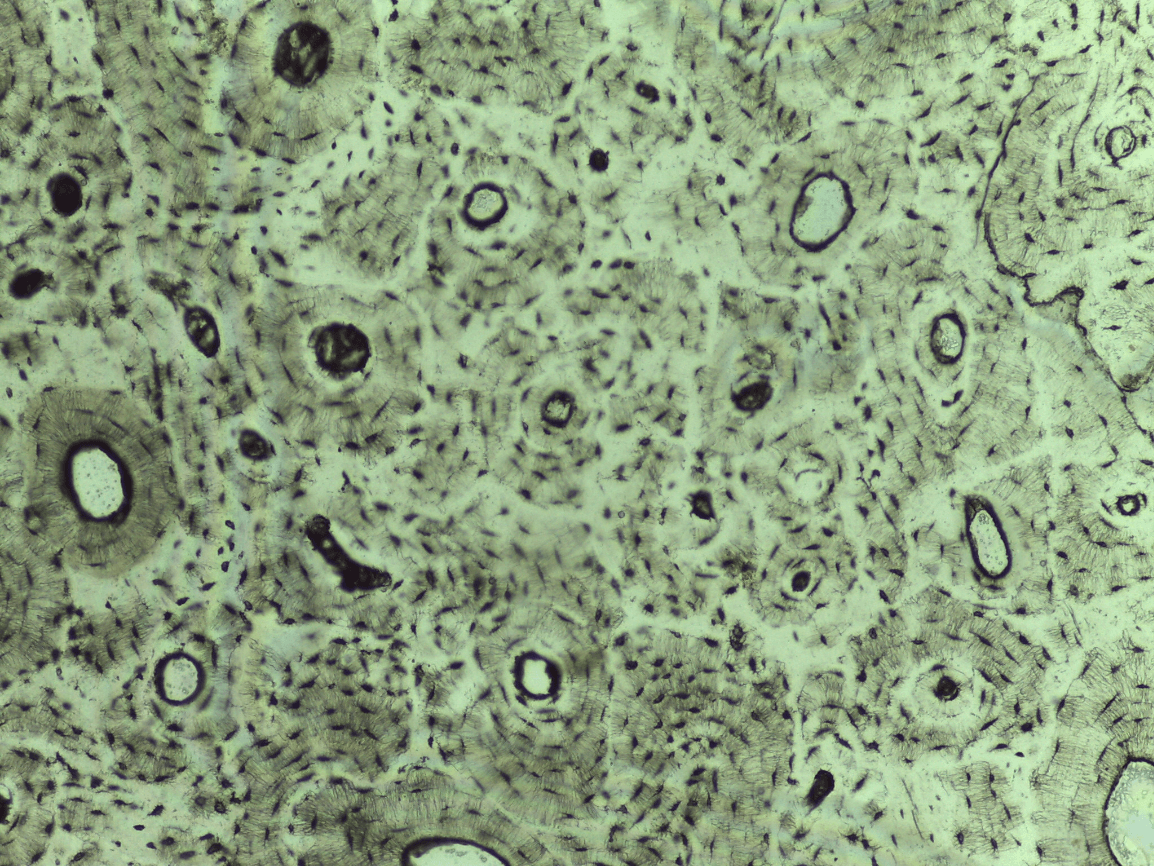
Compact bone CT
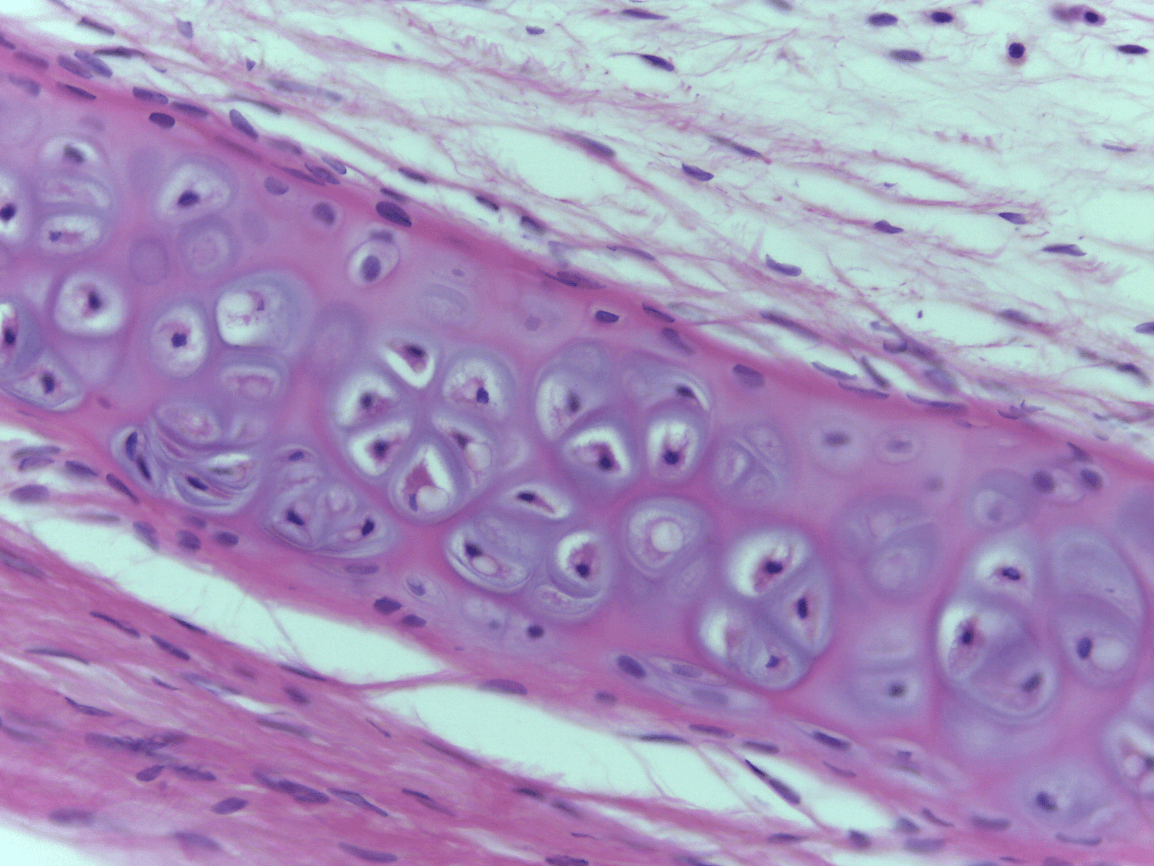
Trachea
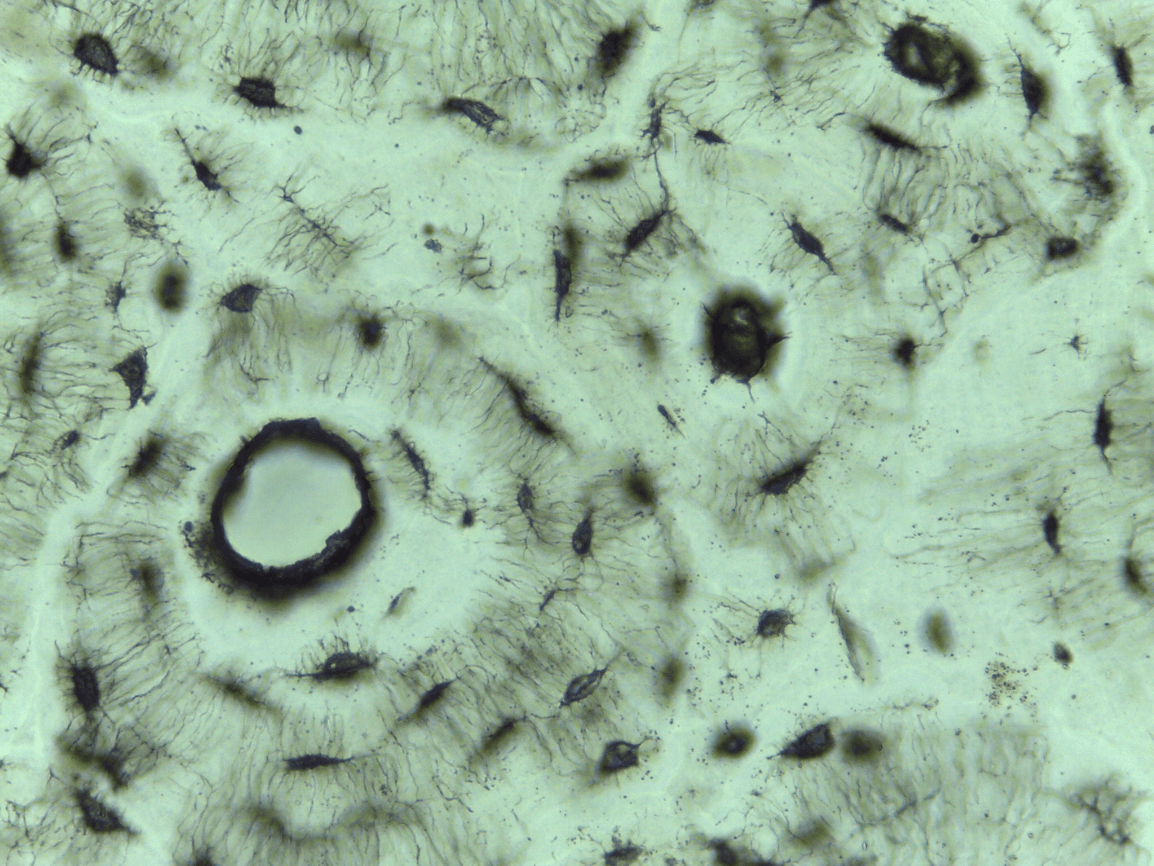
storing minerals, providing internal support, protecting vital organs, enabling movement, and providing attachment sites for muscles and tendons

Lacunae and chondrocytes
What tissue type is this?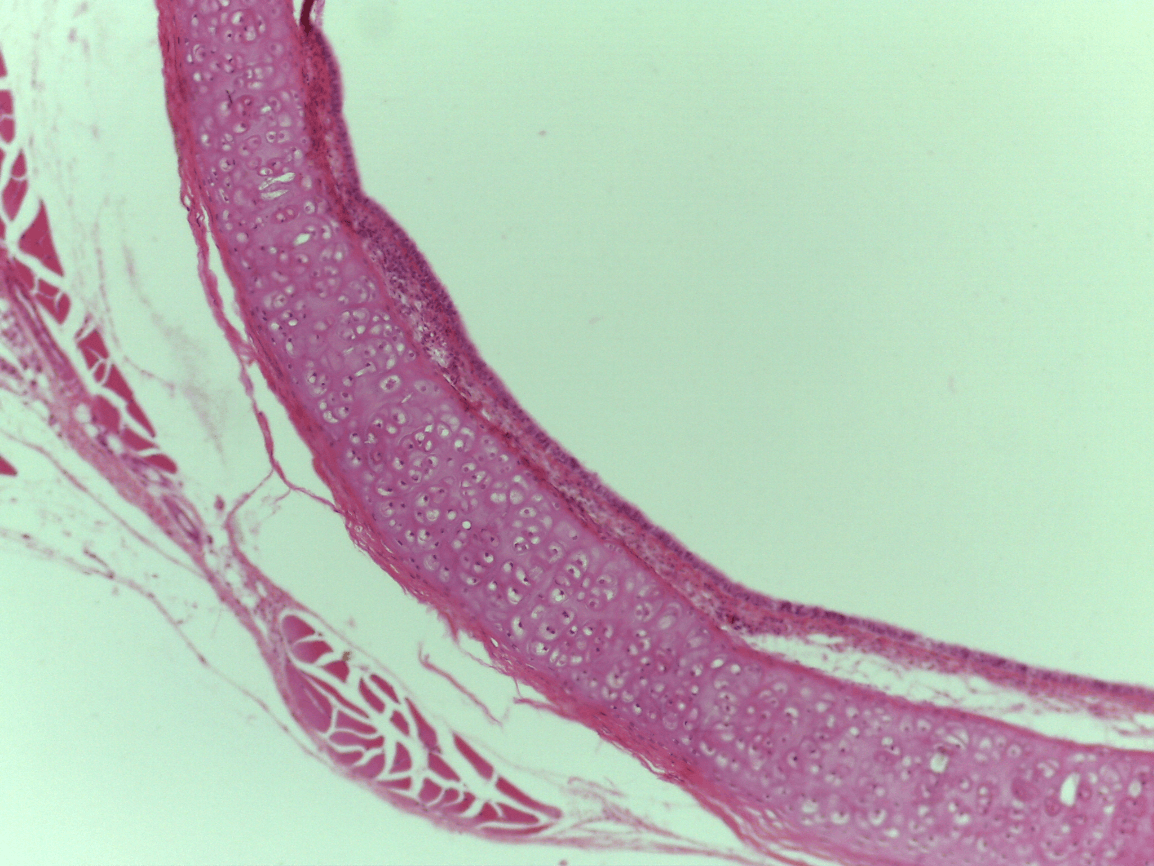
Hyaline CT
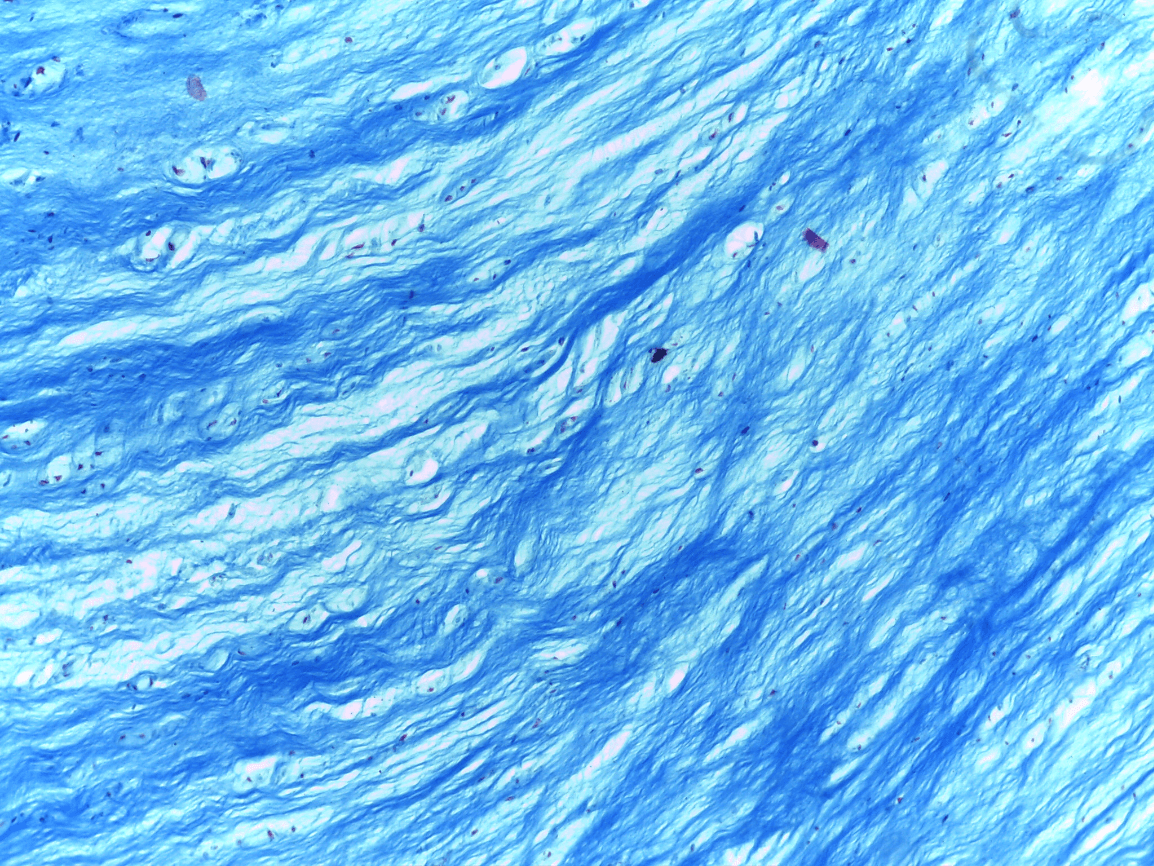
Fibrocartilage
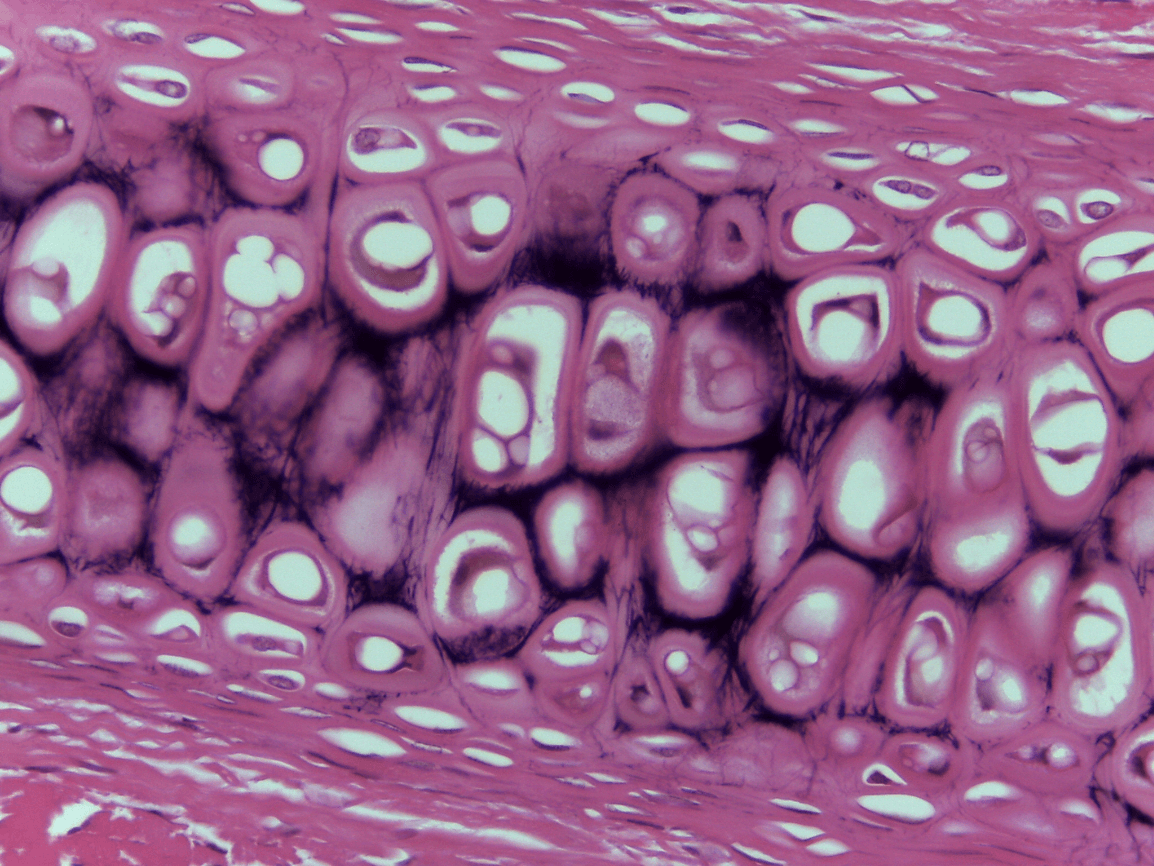
external ear
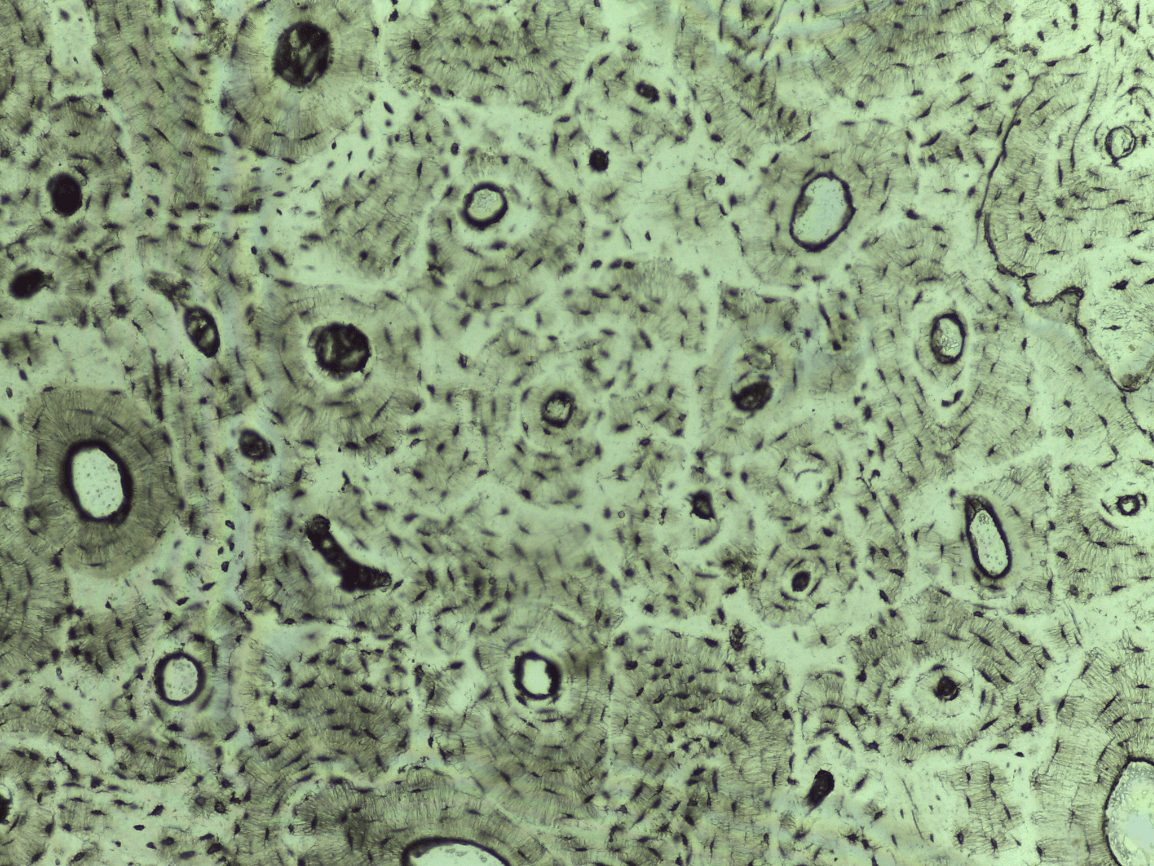
storing minerals, providing internal support, protecting vital organs, enabling movement, and providing attachment sites for muscles and tendons
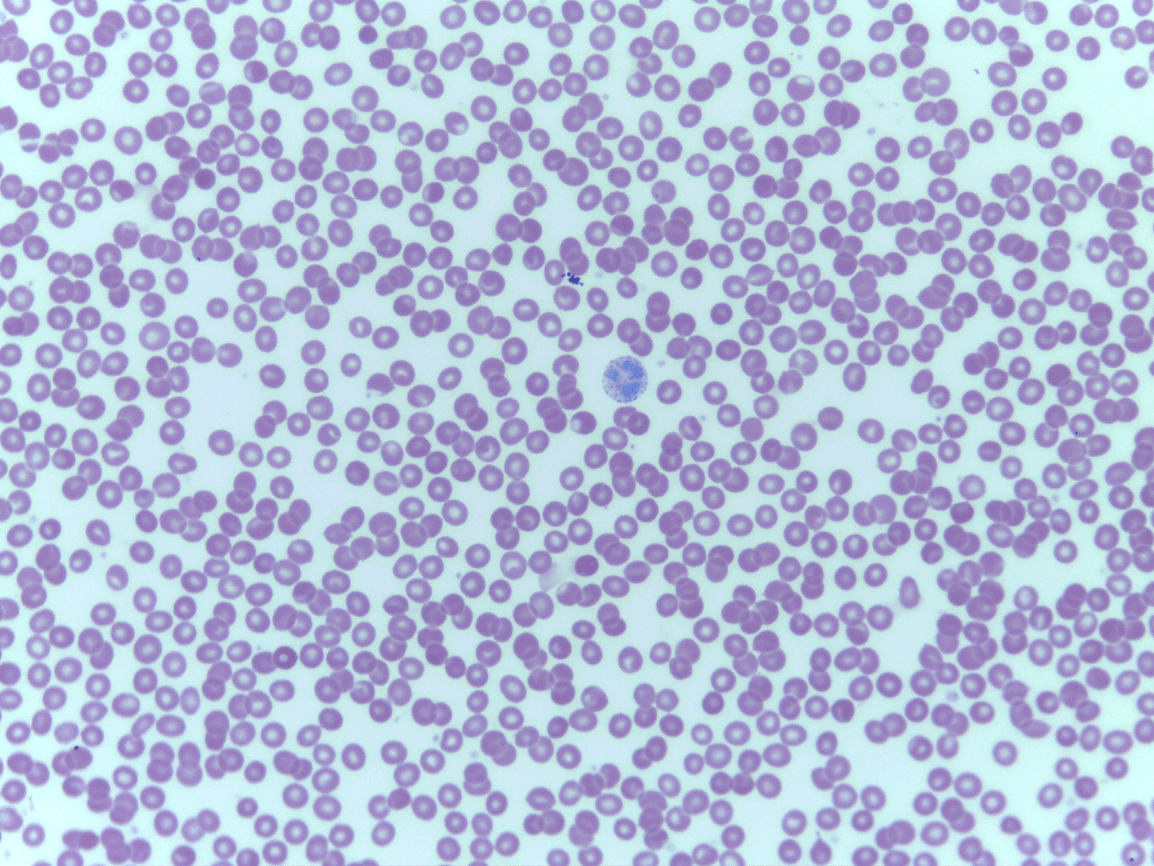
Erythrocytes and leukocytes
What tissue type is this?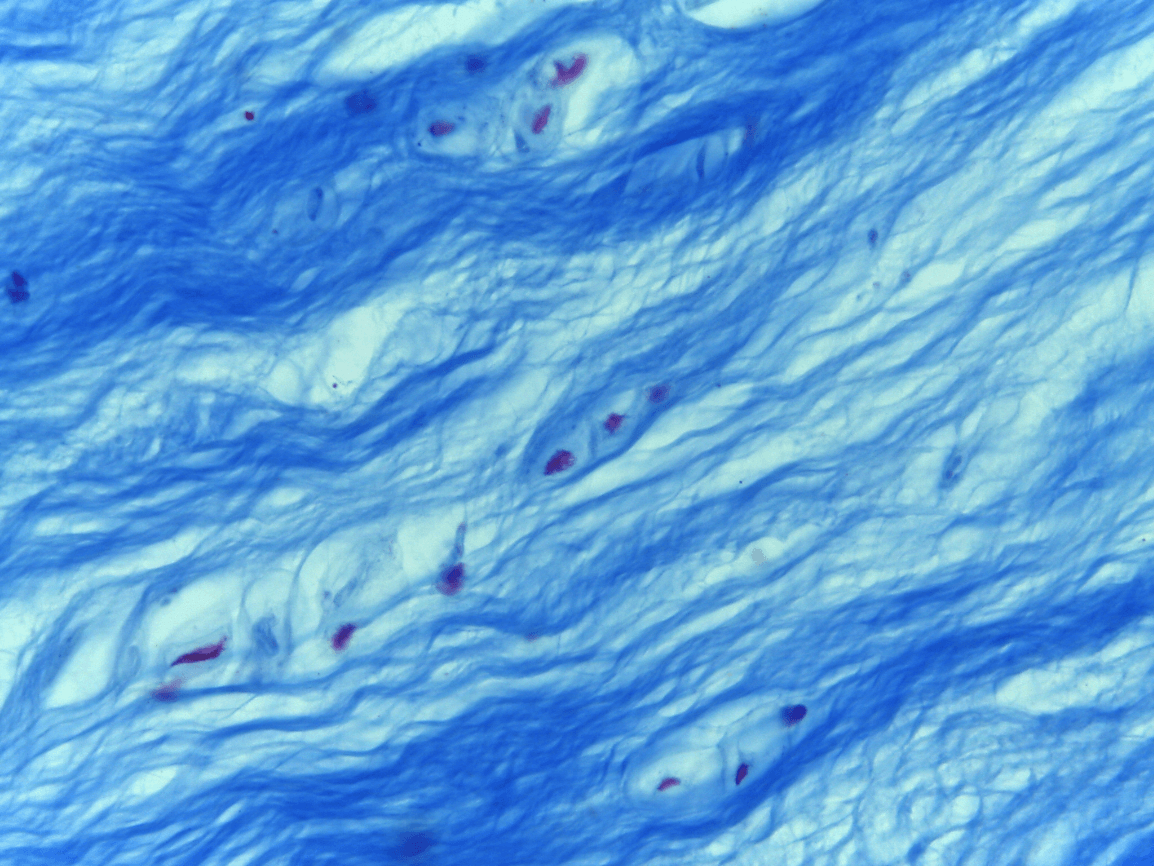
fibrocartilage
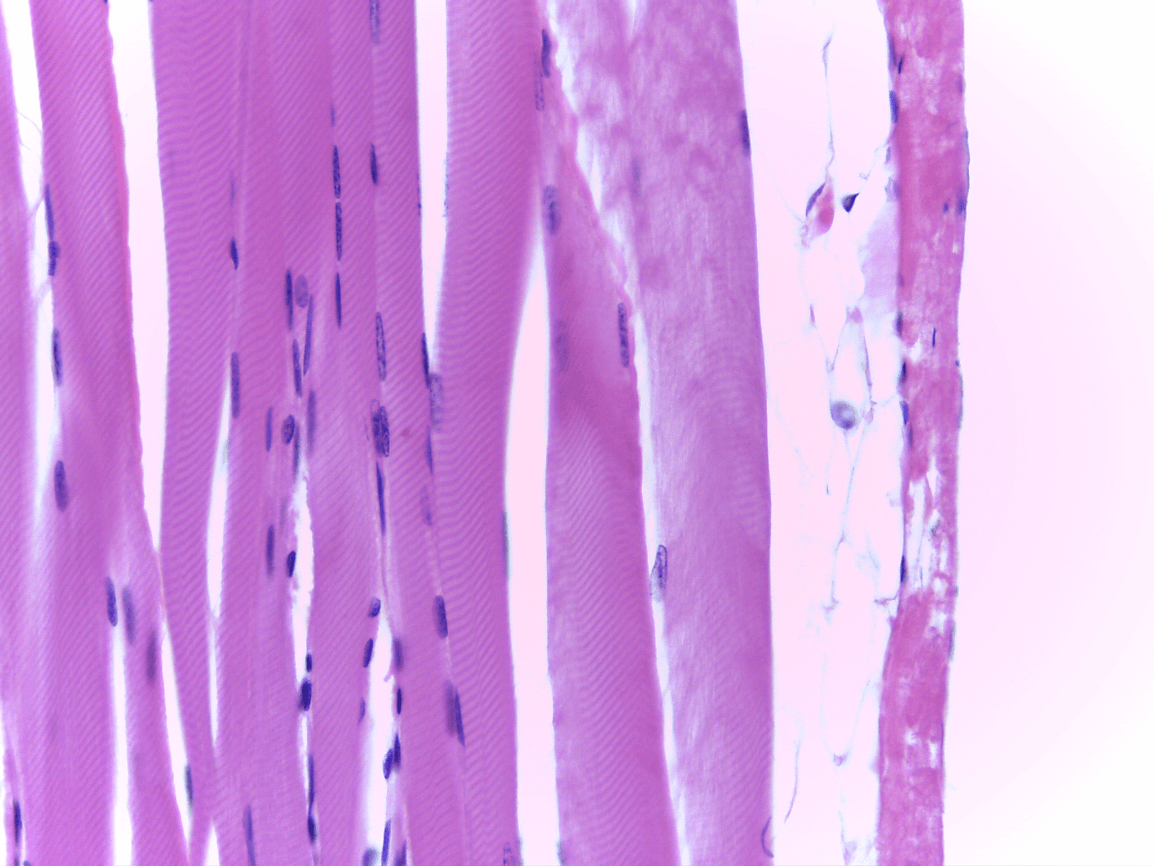
Skeletal Muscle
The heart
keep your heart pumping through involuntary movements, pacemaker cells control the contractions of your heart
What tissue is this and what is its function?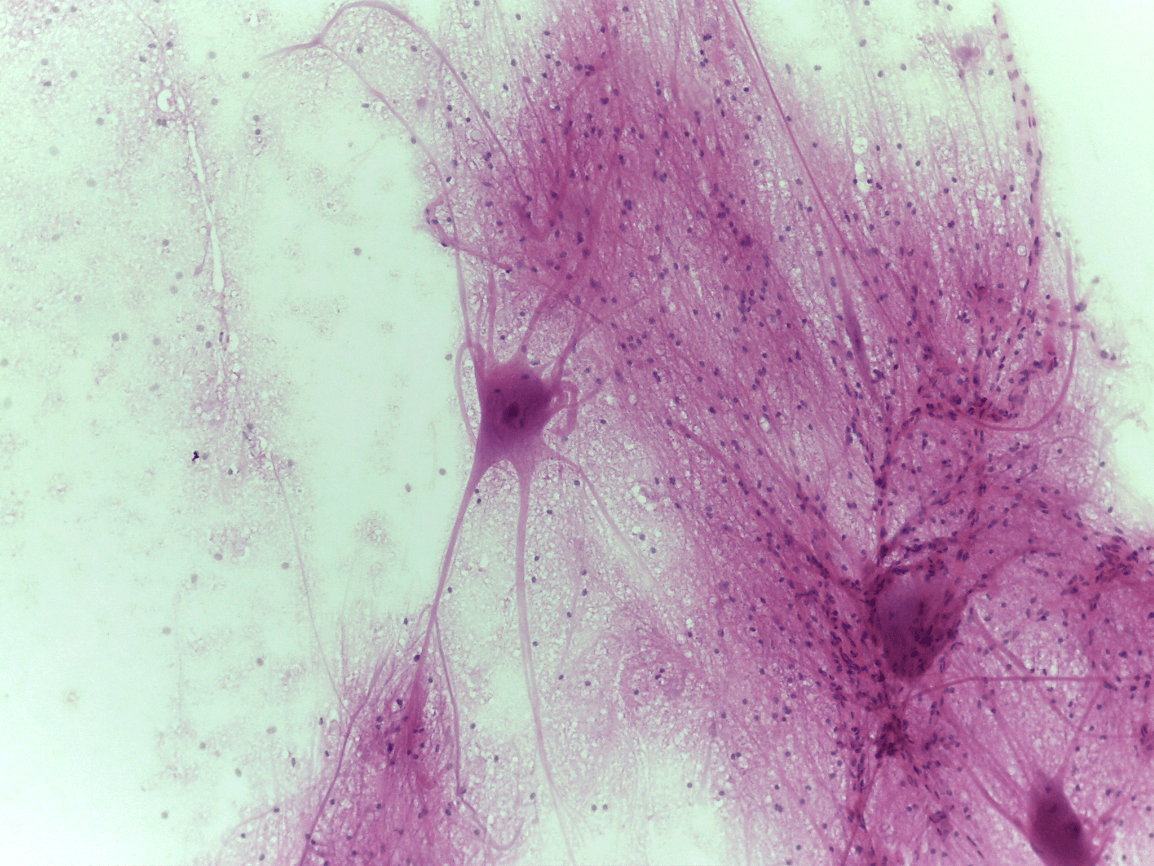
neurons or nerve cells
Function: coordinating and controlling many body activities. It stimulates muscle contraction, creates an awareness of the environment, and plays a major role in emotions, memory, and reasoning
Cardiac Muscle
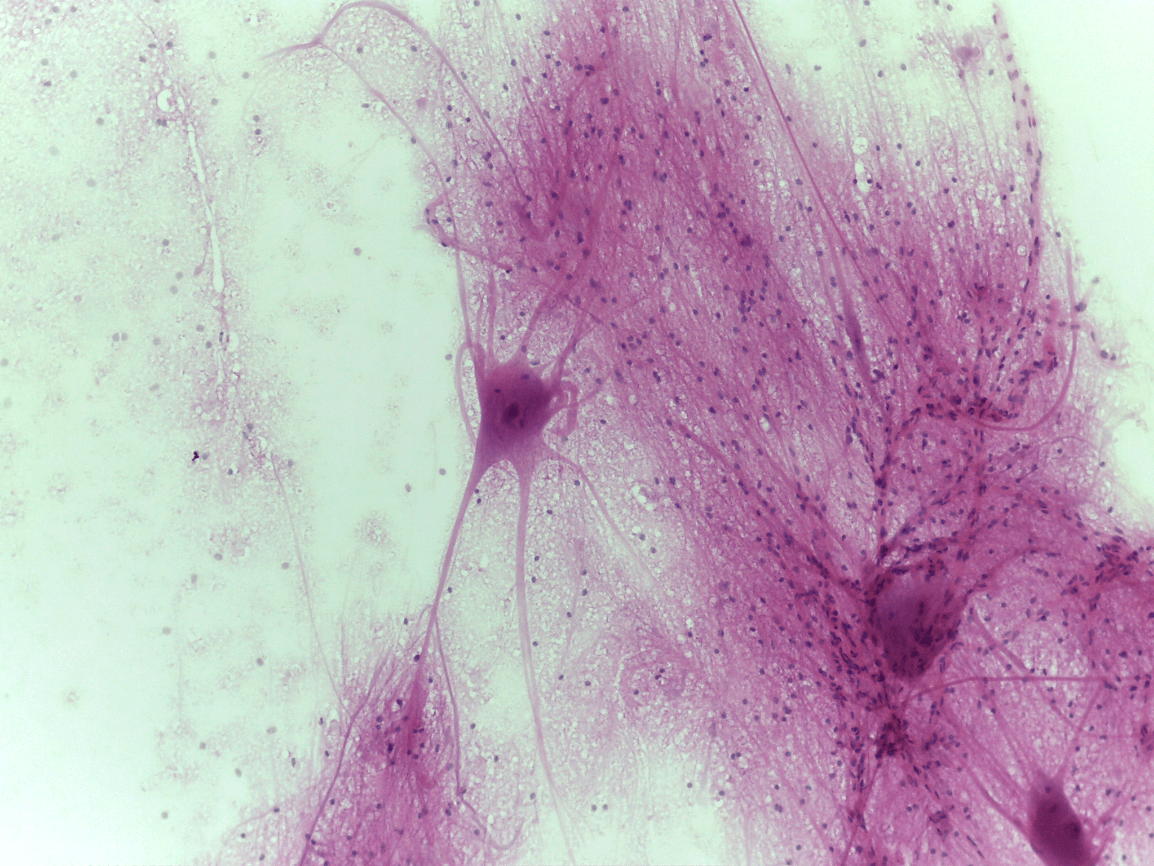
brain, spinal cord, and nerves