Uses ultrasonic energy to fragment the hard lens material, which then can be aspirated from the eye.
Phacoemulsifier
These three orbital bones combine to form both orbits:
The frontal, ethmoid and sphenoid
This is a thin, circular-shaped, contractile curtain suspended in the aqueous humor posterior to the cornea and anterior to the crystalline lens. It is perforated at the center by a circular aperture called the pupil. It comes in different colors.
Iris
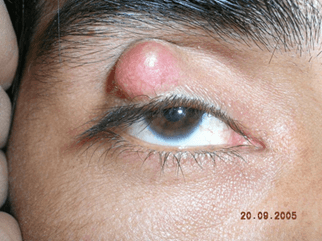 This is an inflammatory, benign growth that originates in a sebaceous gland of the eyelid:
This is an inflammatory, benign growth that originates in a sebaceous gland of the eyelid:
Chalazion
This medicine is used to dilate the pupil for examination of the retina, to prepare the eye for ophthalmoscopy, and to optimize removal of a diseased len
Mydriactics
What is taking place?
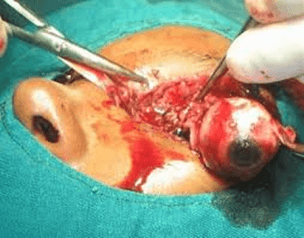
Enucleation
This cranial nerve, both in name and number is for sight:
Cranial nerve II - Optic
Each retina contains about 6 million of these and about 120 million of those:
Cones and Rods
This is an abnormal inversion of the lower eyelid. This causes the eyelashes to rub against the cornea, resulting in irritation, pain, and chronic tears. The most common cause is the weakness and imbalance of the eyelid muscles, due to either age or trauma:
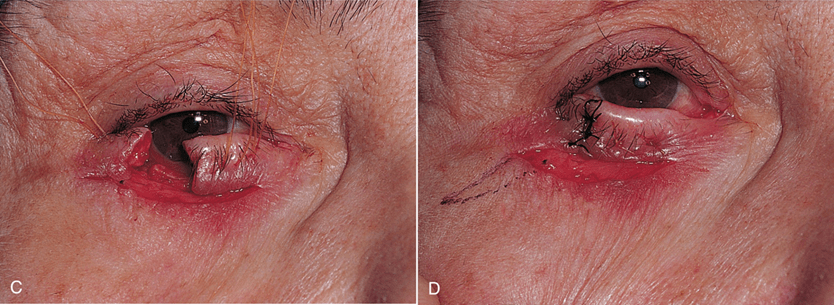
Entropion
These are pupil-constricting agents that act on the sphincter of the iris, and include pilocarpine hydrochloride (Isopto Carpine) and carbachol (Carbacel).
Miotics
Dermatochalasis is corrected with this procedure:
Blepharoplasty
This is the mucous membrane covering the eye.
Conjunctiva
The anterior chamber contains this fluid:
Aqueous humor
This is true drooping of the upper lid due to weakness of the levator muscle.
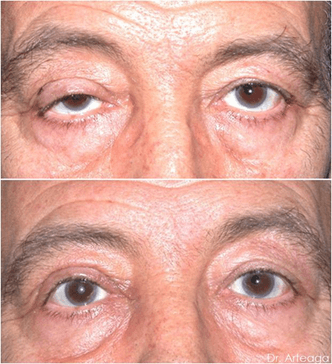
Ptosis repair
This is the standard, approved eye prep antiseptic:
Diluted povidone iodine
What just happened?
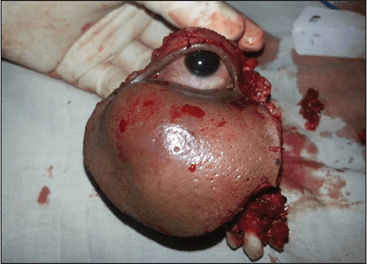
Exenteration
This is opaque, forming the posterior five-sixths of the globe.
Sclera
This is what's replaced in cataract surgery:
The lens
This is is a benign growth of conjunctival tissue over the corneal surface:
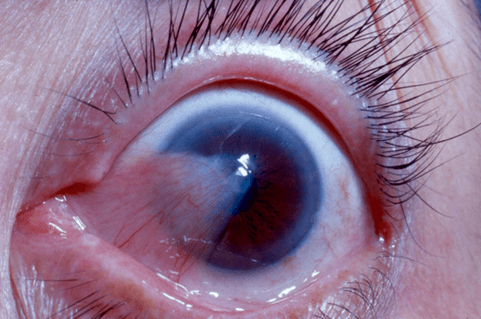
Pterygium
Mydriatic drugs include:
Phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine, Mydfrin)
This is a complex process in which the lens continually changes shape to keep the image focused on the fovea:
Refraction
These are the six muscles of the eye:
Superior rectus, inferior rectus, lateral rectus, medial rectus, superior oblique and inferior oblique.
The posterior chamber of the eye contains this fluid:
Vitreous humor
The technical name for this surgery:
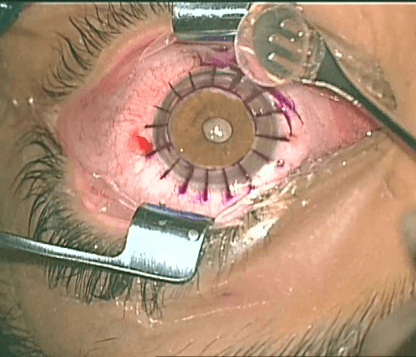
Keratoplasty (corneal transplant)
Topical anesthetics include these two:
Tetracaine hydrochloride (Pontocaine) and Proparacaine hydrochloride (Ophthaine)
This intrinsic eye muscle rotates the eye downward and away from the midline:
Superior oblique
This is the transparent part of the external tunic of the eye and forms the anterior sixth of the globe
Cornea
This is a thin, dark-brown, highly vascular membrane that makes up the posterior five-sixths of the eye. It is pierced from behind by the optic nerve and is firmly adhered to the sclera. It is thicker behind than in front. The inner surface attaches to the retina and consists mainly of a dense capillary plexus. Along with the ciliary body and the iris, this makes up the middle tunic of the globe.
Choroid
In this surgery, a surgeon attaches a piece of silicone or a sponge onto the white of the eye at the spot of a retinal tear:
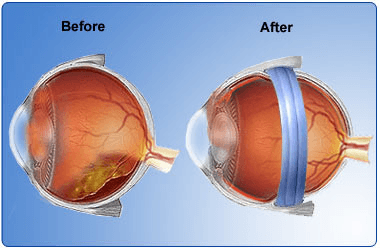
Scleral Buckling
An irrigant used in eye surgery is:
Balanced Salt Solution