These are the classifications of this hernia: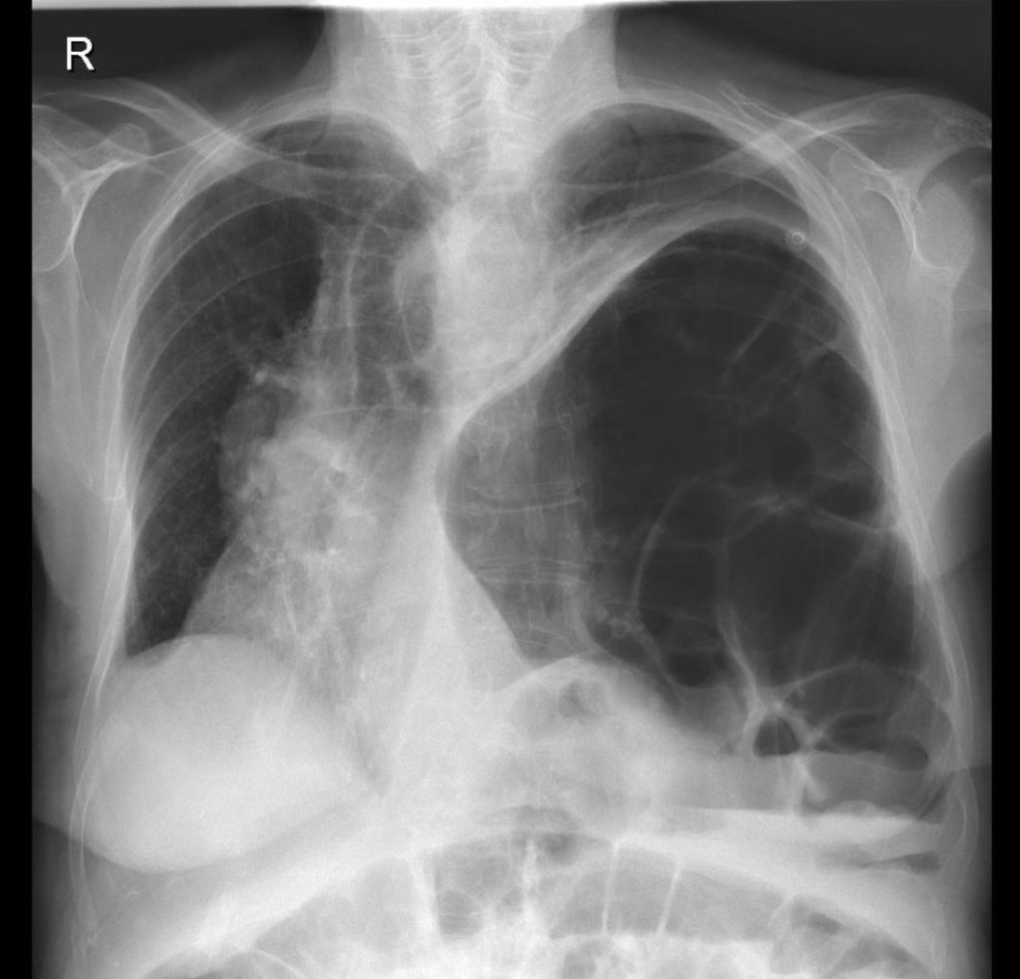
What is a hiatal hernia:
type I: sliding type
type II: paraesophageal
type III: mixed I & II
type IV: another organ besides stomach
You use this formula to calculate the fluid resuscitation requirement in a 2nd degree (or greater) burn covering >20% BSA.
What is the Parkland formula?
4 cc/kg x % BSA
give within 24 hours (1/2 within first 8 hours)
**LACTATED RINGERS**
These are some of the risk factors for developing a ventral hernia.
What are:
- obesity
- old age
- male gender
- sleep apnea
- emphysema
- prostatism
- ascites
- pregnancy
These are the classic signs of an extremity compartment syndrome.
What are:
- paresthesia
- pain
- poikilothermia
- pallor
- pulselessness
- paralysis
These are the borders of the inguinal canal.
What are:
- Anterior: aponeurosis of external oblique
- Posterior (floor): transversalis fascia, conjoined tendon
- Superior: arching fibers of internal oblique/transversus abdominus
- Inferior: inguinal ligament
"Man I got killed last night. I had 3 POCs, a level 2 trauma, and I had to put in a difficult Foley"
Who is Nigel?
This is where you would find a spigelian hernia.
What is the spigelian fascia?
Aponeurotic layer between the rectus muscle medially and semilunar line laterally--almost always below the arcuate line.
This is the additional caloric and protein need that a burn patient requires.
What is...
calories: 25 kcal/kg/day + 30 kcal x %burn
protein: 1 g/kg/day + 3 g x %burn
Ventral hernias greater than this size benefit from mesh repair.
What is 2 cm?
**Recurrence rate after primary repair:
- less than 2 cm: 5-7%
- greater than 2 cm: 10-50%
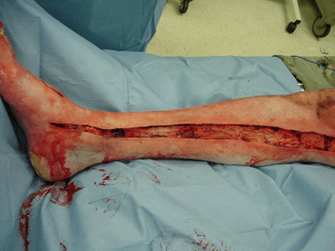
These are the locations where you make your skin incisions during a fasciotomy of the leg.
What are:
- medial: 1 thumb posterior to tibia (releases superficial/deep compartments)
- lateral: 1 finger anterior to fibula (releases anterior/lateral compartments)
These structures are found within the spermatic cord.
What are the:
- testicular artery, deferential artery, cremasteric artery
- genital branch of genitofemoral nerve, sympathetic nerves
- vas deferens
- pampiniform plexus
- lymphatics
"I was the first one to present stenting popliteal aneurysms 45 years ago at the SVS conference in Las Vegas"
Who is Dr. Ascher?
This is the most common place to find a Littre hernia.
What is the inguinal canal?
This degree of burn is moist, erythematous, and blanches with digital pressure.
What is 2nd degree burn?
1st degree: erythema, involves epidermis only
3rd degree: pale, black, or deep erythema; no signs of blanching with digital pressure (absent perfusion); dry
These are some indications where laparoscopic/robotic hernia repair would be favored over open repair.
What are:
- severe obesity
- uncontrolled diabetes/smoking
- multiple hernias
- recurrent hernia after open repair
What is an escharotomy?
This is the definition of a Lichtenstein repair.
What is a tension-free inguinal hernia repair with mesh sewn from the conjoined tendon to the inguinal ligament?
"This guy is uneducated!"
Who is Gumer?
This is the traditional treatment for an Amyand's hernia.
What is an appendectomy and inguinal hernia repair?
You should be concerned for this in a nonhealing burn or unstable scar.
What is Marjolin's ulcer? (highly-malignant squamous cell CA)
**Curling's ulcer: gastric ulcer that occurs with burns
This is usually the initial treatment for infected PTFE mesh.
What is mesh explantation?
**PTFE has poor tolerance of infection and usually doesn't respond well to antibiotic treatment
Foot eversion is a consequence of injuring this nerve during fasciotomy.
What is the superficial peroneal nerve? (lateral compartment)
This is the difference between a Bassini and a Shouldice repair.
What is:
- Bassini: sewing conjoined tendon to inguinal ligament
- Shouldice: same thing, but multiple layers
"Put it this way, he was most likely shot by his ex girlfriend with a 0.38 while standing in the kitchen"
Who is Dr. Glinik?
It's the hernia pictured here:
What is a Richter's hernia?
These are the advantages of:
- split thickness skin graft
- full thickness skin graft
What is
- STSG: better graft survival (easier imbibition, neovascularization)
- FTSG: less wound contraction, for palms/back of hands
These are the steps to an anterior component separation.
What is: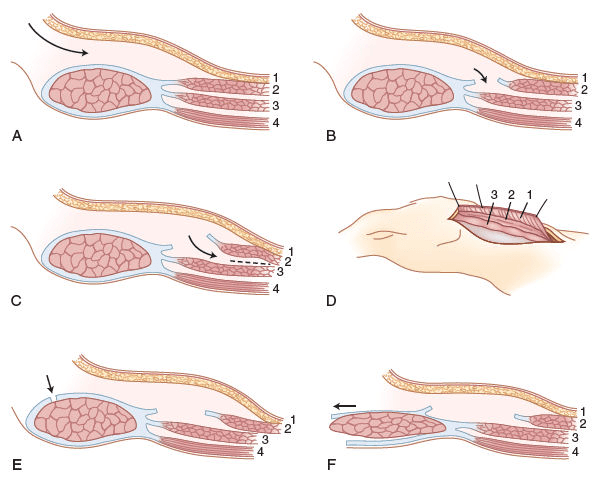
- dissect skin and subcutaneous fat
- incise external oblique 1 cm lateral to rectus
- separate external oblique and internal oblique
- continue dissection to posterior axillary line
These are the incisions for a compartment release of the forearm.
What are:
- S-shaped volar release
- longitudinal dorsal release
- (optional) mobile wad release
Suspect injury to this nerve if the patient complains of pain here after laparoscopic hernia repair.
What is the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve?
(probably from tack placed too far laterally)
"Book it for robotic man tell the patient it is a very advanced surgery"
Who is Dr. Nazir?