According to ACC/AHA/HRS SVT arises from ____.
His bundle or above
This arrhythmia gradually increases in a rate over approximately 30 seconds to several minutes, in contrast to atrial tachycardia that is an abrupt onset and termination.
inappropriate sinus tachycardia
When the flutter wave in V1 is upright, in what chamber does the circuit most likely originate?
Left Atrial circuit
PSVT is a clinical syndrome characterized by sudden onset and termination of rapid palpitations documented as a regular narrow comlex tachcyardia. It implies the presence of ___, ___ or ____
AVNRT,AVRT, or less frequently AT
The most common form of tachycardia associated with an accessory pathway is _____?
Orthodromic AVRT
The 2019 and 2023 atrial fibrillation guidelines recommen this drug class for non-valvular atrial fibrillation
DOAC
In a hemodynamically stable patient not on anticoagulation, TEE should be performed prior to cardioversion if afib has been present for longer than THIS amount of time.
What is 48 hours? Or if the duration is unclear and the patient is not already anticoagulated
The two most common ablation energy sources are:
radiofrequency energy and cryoenergy
Patients with this clinical syndrome can have very rapid ventricular rates (250-300 beats/min) which can result in loss of consciousness or precipitate ventricular fibrillation?
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
b. Comment: Conduction through the accessory pathway which has a short refractory period
The majority of atrial tachycardias originating from the left atrium are traced back to this specific anatomical feature.
Pulm veins
The most important differentiation factor on ECG between AT and AVNRT and AVRT?
RP relationship
What class of antiarrhythmics should be avoided in AFLutter?
What is Class 1C agents, risk of slowing atrial rate an facilitating 1:1 AV conduction with concomitant profound conduction slowing in the ventricle.
According to the AHA/ACC/HRS practice guidelines, however, 1C AADs should be avoided or used with caution in patients with CAD, or in the presence of sinus node or atrioventricular node dysfunction, heart failure, atrial flutter, infranodal conduction disease, Brugada syndrome, or liver disease.
When SVT occurs with abberancy, you are more likely to see RBBB pattern than LBBB pattern because?
Longer refractory period of the right bundle compared to the left.
What is the underlying diagnosis based on this ECG?
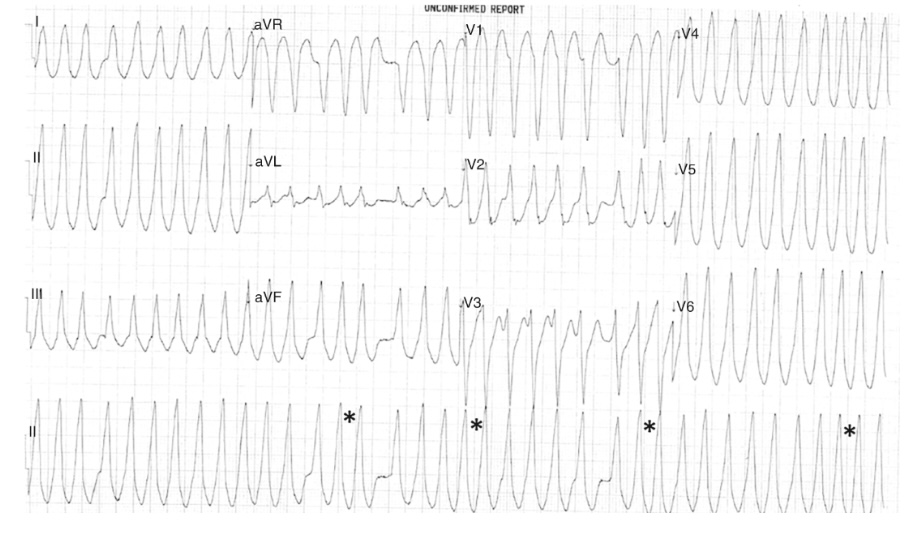
Answer: Pre-excited atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response (irregularly irregular, wide complex tachycardia with varying QRS morphologies)
rapid ventricular response (irregularly irregular, wide complex tachycardia with varying QRS morphologies)
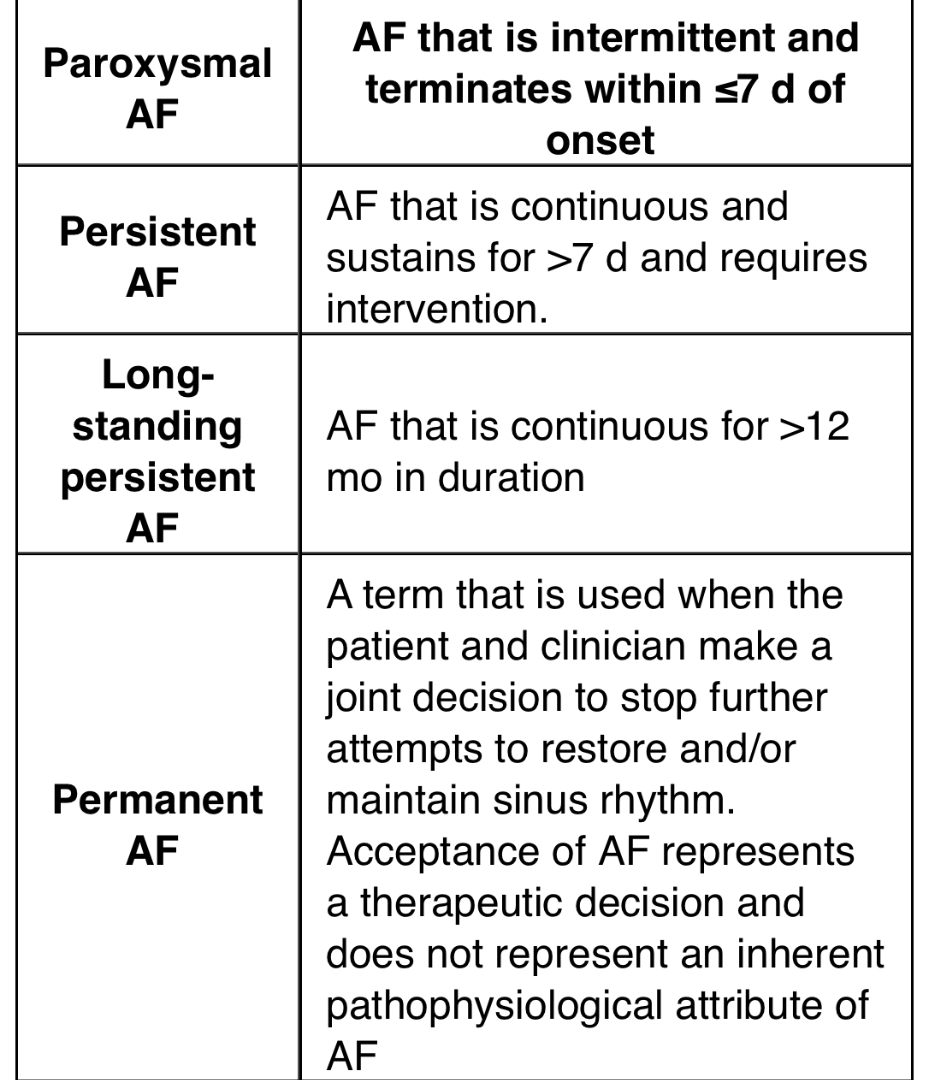
Define paroxysmal, persistent, long standing persistent, and permanent atrial fibrillation
IV options for pharmacologic cardioversion include amiodarone and THESE two medications.
What are ibutilide and procainamide?
Success rates in episodes < 2-3 days: ibutilide (60-70%), amio (40-50%), procainamide (30-40%)
Ibutilide should only be used if LVEF > 35%, and it lowers the defibrillation energy requirement for cardioversion, improving the success rate of transthoracic cardioversion.
Head-to-head comparisons of the safety and efficacy of radiofrequency ablation versus cryoballoon ablation have shown:
Superiority of RF ablation
Superiority of cryoablation
Similar outcomes
More cardiac tampondade with cryoablation
C. Similar outcomes
What is the pharmacologic treatment for hemodynamically stable patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in rapid atrial fibrillation? (2)
a. Procainamide, Ibutilide
b. Comment: Hemodynamic instability: electrical cardioversion. Digitalis and CCB are contraindicated in WPW and Afib. Long term: catheter ablation
During and shortly after episodes of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), increased urine output, known as polyuria, occurs due to the release of this hormone.
atrial natriuretic peptide.
This arrhythmia relatively uncommon that occurs in the context of pulmonary disease, pulm HTN, CAD and valvular heart disease.
What is multifocal AT
What is the treatment of choice for atrial flutter?
Catheter ablation
What is the treatment of choice for frequent episodes, unpredictable episodes, or very symptomatic episodes of AVNRT?
Catheter Ablation
At 5 years, none with catheter ablation have recurrent arrythmia vs. 75% in medical arm by 2 years. Long term success rates about 95%.
Anatomically, accessory pathways are most commonly located where?
Along the mitral annulus (left free wall pathways [60%]). Approximately 25% are in the septal region of the tricuspid or mitral annulus, and a minority are on the right free wall.
What is the specific reversal agent for the factor Xa inhibitors and what can be given in cases where the specific reversal agent is not available
Andexanet alfa and prothrombin Complex concentrate
Oral options for pharmacologic cardioversion without structural heart disease include THESE two medications (i.e. “pill-in-the-pocket”).
What are propafenone (300-600mg) and flecainide (100-200mg)?
Give BB prior to flecainide
First administration should be under surveillance to monitor for pronounced postconversion pause
Name 4 potential complications of AF catheter ablation:
stroke (0.5%), cardiac tamponade (0.5% to 1.5%), phrenic nerve injury (0.2%), femoral vein-related complications (1%), pulmonary vein stenosis (0.5%), and death (0.1%). (4 of any of the above complications would be correct)
These are the only two rhythm-control agents recommended for patients with HCM and a wall thickness > 15mm
Dronedarone, amiodarone
Due to prominent structural atrial abnormalities in patients with HCM, Afib is likely to recur. Ablation is also an option
What characteristic of the RP interval helps to differentiate AVRT and AVNRT from Atrial tachycardia.
What is R-P interval (Constant in AVRT &AVNRT while variable in AT)
It is defined as a tachycardia that can be induced and terminated with programmed stimulation and has a P wave morphology identical or similar to the that of the sinus P wave.
sinus node reentry
Antiarrythmic of choice for atrial flutter in patients with low LV function.
Amiodarone
The pwave occurs at the tail end of the QRS, producing a pseudo right bundle branch block apperance in V1 and pseudo S wave in inferior leads. This appearance has been reported to indicate ___ with an accurancy of 100%.
typical AVNRT
An accessory pathway may conduct in the antegrade direction, the retrograde direction or both. When an accessory pathway conducts only in the retrograde pathway it is termed _____.
Answer: Concealed because the surface ECG appears normal. The anterograde conduction pathway is termed manifest due to it appearing on the ECG.
What is the name of the cardiac device approved for soft tissue approximation (not stroke prevention) and has been used off-label in clinical practice in the United States and elsewhere for LAA occlusion.
LARIT (Sentreheart, Redwood city)
THIS landmark trial randomized patients with AF to catheter ablation or medical therapy and showed no difference in the primary composite endpoint, but a lower rate of the secondary endpoint for death or CV hospitalization among the ablation group.
What is the CABANA trial?
Primary endpoint: composite of death, disabling stroke, serious bleeding, or cardiac arrest
Seconday endpoint: death or CV hospitalization, 51.7% ablation vs 58.1% medical therapy
What is the only proven benefit of AF ablation?
improvement in quality of life
This is the best anticoagulation strategy for patients during pregnancy
Warfarin from the second trimester until 1 month before the due date, LMWH during the first trimester and during the final month of pregnancy
b. Comment: Warfarin doses < 5mg are acceptable during the first trimester.
Focal atrial tachycardia, mimicking sinus rhythm (similar pwave), often originates from this specific anatomical structure.
crista Terminalis (Particulary superior crista)
It is the initial management of a focal AT in the emergency department
adenosine? 6 to 12 mg IV
What is the specific site of ablation for cavo-tricuspid dependent flutter?
Across the CTI from the annulus to the eustachian ridge at the anterior margin of the IVC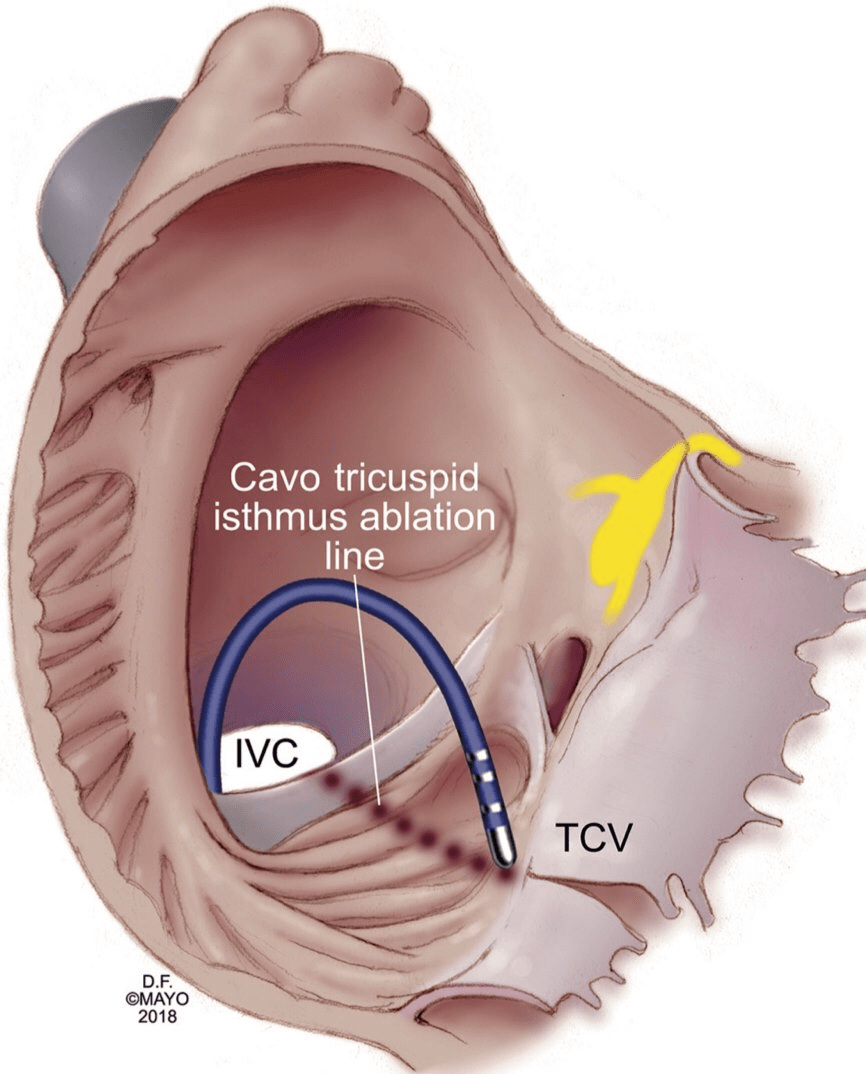
Name three EKG features that are highly suggestive of AVNRT vs. Atrial Tachycardia. HINT: Initiation, VA relationship, Termination
1) Initiated by an atrial ectopic followed by a long PR interval (atrial ectopic comes early and blocks the fast pathway (due to longer refractory period), conducts down the slow pathway with a long PR, activity then travels retrograde via the fast pathway and tachycardia is initiated
2). When cycle length variability occurs, the presence of a FIXED VA relationship (fast pathway conduction) strongly suggest AVNRT rather than AT
3). Terminates with a Pwave as the final event
Name 3 medications that can be used when there is a concealed accessory pathway AVRT.
Beta-blockers, non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, Class IC agents
What clinical trial showed that left atrial appendage ligation plus pulmonary vein isolation was not superior to pulmonary vein isolation alone at preventing recurrent atrial fibrillation?
aMAZE trial
The 2014 and 2019 ACC/AHA/HRS AF guidelines advise the optimal metric for rate control is a resting heart rate less than THIS.
What is less than 80 bpm?
Less than 110 bpm is a Iib recommendation based on a single European clinical trial.
Catheter ablation for a patient with symptomatic paroxysmal AF who has not responded well to least one antiarrhythmic medication versus another patient who is medication-naïve has the following class of recommendation:
A. Both class I
B. Both class II
C. Class I for the first patient and II for the second patient
D. Class II for the first and I for the second
C. Class I for the first patient and II for the second patient
Pharmacologic management of atrial fibrillation in pregnancy for a) rate control (2) and b) rhythm control (3)
1) IV metoprolol acutely, PO digoxin long term 2) flecainide and sotalol in structurally normal hearts, amiodarone in structural heart disease
b. Comment: PO beta blockers can be used, but only after the first trimester