Which group is a clade?
Holophyletic
Plesiomorphic, give an example of a Plesiomorphic trait in mammals an why
An ancestral characteristic
Define Taxonomy
the naming of groups of organisms
How should you scientifically name a species?
Genus species
Binomial Classifications
Which of the following is not homologous:
A. Fur in Wolves, Dogs, Coyotes, and Foxes
2. Whale Fin, Cow Leg, Human Femur
3. Wings of Birds, Flaps of Sugar Gliders, and Wings of Butterfly
THREE
All squares are rectangles but not all rectangles are squares. How does this relate to Monophyletic and Holophyletic?
Monophyletic: Rectangle
Holophyletic: Square
Monophyletic lineages can be holophyletic, but all Holophyletic lineages are monophyletic
Apomorphic definition. List an apomorphic trait in this phylogeny 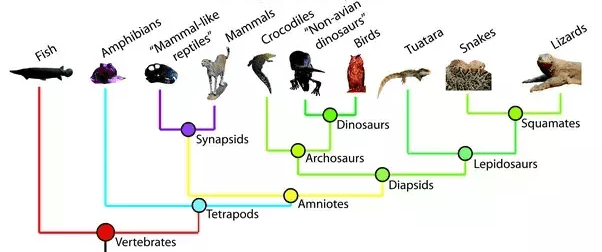
A derived Characteristic
Define Systematics
study of diversification and its relationships
What is the most biodiverse group?
Analogous vs Homoplasy
Analogous structures have similar functions due to different lineages evolving in similar environmental niches. Example: Sharks and Dolphins
Homoplasy: an analogous trait.
"The similar fin structures of sharks and dolphins are considered a homoplasy because they evolved independently in response to the need to hunt in aquatic environments "

Paraphyletic: Includes organisms of a common lineage BUT it does not include all of organisms
Polyphyletic: a lineage or trait found in a bunch of different organisms (bonus give me an example).
Symplesiomorphic definition. give an example of three symplesiomorphic traits you can come up with using this phylogeny 
A shared, ancestral characteristic
Define Classification
assigning organisms to hierarchical groups
List the three domains:
Which are most closely related?
Domains: Archaea, Eukarya, Bacteria
Convergent Evolution is (homologous/analogous) and describes a shared trait (between two/within a) clade(s)
analogous, between
Draw a monophylogeny

Synapomorphic, and give an example
A shared, derived characteristic
"Limbs with digits is a synapomorphy for Tetrapoda, but a symplesiomorphy for all its subclades"
ortholog, defintion
a gene changes, causing speciation.
List the Linnean Classifications
1. Domain
2. Kingdom
3. Phylum (pl. phyla)/division
4. Class
5. Order
6. Family
7. Genus (pl. genera)
8. Species (pl. species)
Divergent evolution
changes due to natural selection and descent with modification into new forms and phenotypes within a clade!
If I circled all the organisms that walk on two legs, what type of group would I make?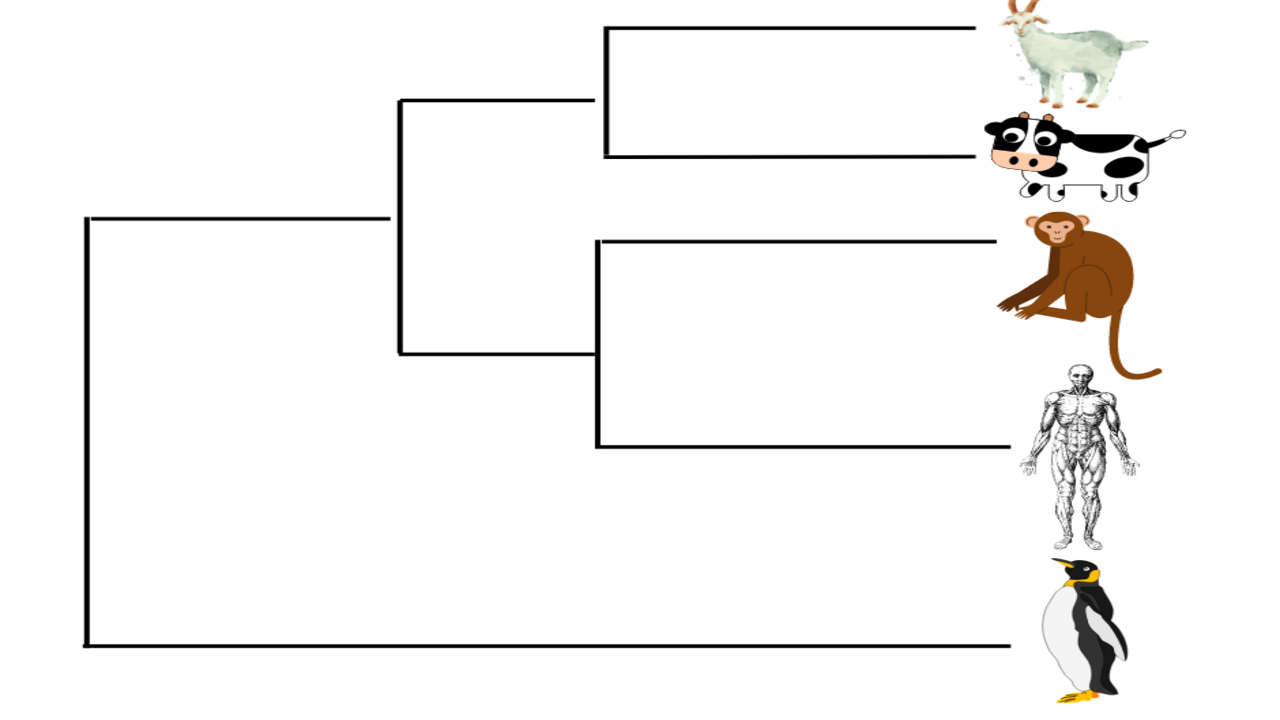
Polyphyletic
Autapomorphic
An unshared, derived characteristic
How does a clade differ from a grade and give examples!
A clade: the lineage of organisms that is derived from a single common ancestor and contains ALL descendants
Grade: a group of organisms that shares similarities but not by shared common ancestry or excluding some descendants
Paralog, definition
formation of two different alleles of a gene WITHIN one species.
What are the two main ways to classify phylogeny and explain them? Give a compelling argument as to which one you love most!
Cladistic: All taxa (NOT TAXONS) should be clades. Monophyletic and Holophyletic.
Evolutionary: Taxa should have a recent common ancestor AND common traits. Paraphyletic taxa.