Should physical restraint be used to enforce compliance? True/False
False.
Crisis is an opportunity for growth? True/False
True.
Please list 2 strategies for emotional first aid.
co-regulate emotions – be a calm presence
maintain the relationship and lines of communication
plan and anticipate – be a coach
Anything that makes challenging behavior and traumatic stress responses more or less likely to happen is called a:
Setting condition
The goal of physical intervention is to:
Reduce risk.
What are the two goals of crisis intervention?
Support and teach.
What are the 5 spaces that make up the therapeutic milieu?
- Physical
- Social
- Cultural
- Emotional
- Ideological
What are the 4 elements of a potentially violent situation?
- The spark
- The target
- The weapon
- The level of stress or motivation
The deprivation of oxygen to living cells is defined as:
Asphyxia
What are the first 3 questions we ask ourselves when facing a potential crisis?
- What am I feeling now?
- What does this child feel, need, expect or want?
- How is the environment affecting the situation?
Name 2 things we monitor for during restraints.
- Make sure the restraint position is correct (child and staff)
- Assure there are no breathing problems
- Observe and Assess:
skin color
respiration (no breathing problems)
level of consciousness (is responsive)
level of agitation (overexertion)
range of motion in the extremities
“You look angry. Let’s go for a walk …” (communicate understanding before making a request) is a example of verbal “what to say” statements you can make when using:
Crisis co-regulation
Name two improper techniques in restraint?
- Pressure on the neck or chest
- Incorrect positioning of the arms
- Obstructing the mouth or nose
- Abnormal positioning of the body
Name 2 of the skills that adults need for successful 'Intentional Use of Self' with children.
- Self-awareness
- Self-regulation
- Relationship skills and attunement
- Self-Care
What are the 3 basic processing regions of the Triune Brain Model?
- Thinking (neocortex)
- Emotional (limbic system/amygdala)
- Survival (brain stem/reptilian)
During a potentially violent situation, name 3 aspects of non-verbal crisis communication that staff should consider.
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Personal space
- Height and gender
- Sensitivity to cultural issues
- States what is expected of the young person
- Is directed by the team leader
- Is supportive of the young person
- Sets the tone for the recovery process
Are principles for what process?
The Letting Go Process (restraint).
List the 3 OUTCOMES for the Recovery Phase of the Stress model of crisis.
- Higher
- Lower
- No change
If the child is exhibiting acute physical behavior and is a safety risk, what 3 conditions have to be present to use a physical restraint?
- Agency policies and state regulations regarding restraint allow it
- The child’s individual crisis support plan prescribes it
- Our professional dynamic risk assessment indicates it
Please provide 3 examples of Pain-Based behaviors:
- Overreaction to situations
- Impulsive outbursts
- Trauma re-enactment
- Defiance
- Inflexibility
- Running away through anger or fear
- Withdrawal
- Self-injury
Please list 3 situations in which restraint, while indicated, should be avoided.
- The staff cannot remain calm and in control; the staff is so angry with or afraid of the child that the staff might intentionally or unintentionally inflict harm as a result of restraint.
- The child is threatening the staff with bodily injury and appears to be capable of inflicting it.
- If sexual stimulation is the child’s motivation.
- If a child begins to act out in public at a location where physical intervention might easily be misinterpreted by the public.
- When the child has a weapon (e.g., a knife, broken glass, etc.) that could cause serious injury
- When the child’s medical condition (e.g., asthma, seizure disorder, a heart problem, sickle cell trait, diabetes, pregnancy) would be aggravated by physical restraint.
- When the restraint may result in serious emotional trauma for the child
- If the child is on certain medication(s)
List 2 effects of anger during a stressful situation.
- Anger can undermine objectivity
- Cognitive abilities are reduced
- Anger is an emotional and physical state
List 3 of the goals of a Life Space Interview (LSI).
- Provide a sense of emotional safety
- Help clarify the event for the child and adult
- Repair and restore the relationship with the adult
- Help the child learn and use emotional regulation skills
- Re-enter the child back into the routine
List 3 strategies to avoid or end the power struggle.
- Listening and validating feelings
- Managing the environment (e.g. removing others)
- Giving choices and time to decide what to do next
- Dropping or changing the expectation
Please list 3 predisposing risk factors that will put a child at greater risk of serious injury during a physical restraint.
- Obesity
- Influence of drugs or alcohol
- Prolonged violent physical agitation
- Underlying natural disease, i.e., enlarged heart, asthma, sickle cell trait, high blood pressure, diabetes
- Hot humid environments
- Individuals taking certain medications
- Effects of severe trauma history
Fill in the blanks for the stress model of crisis
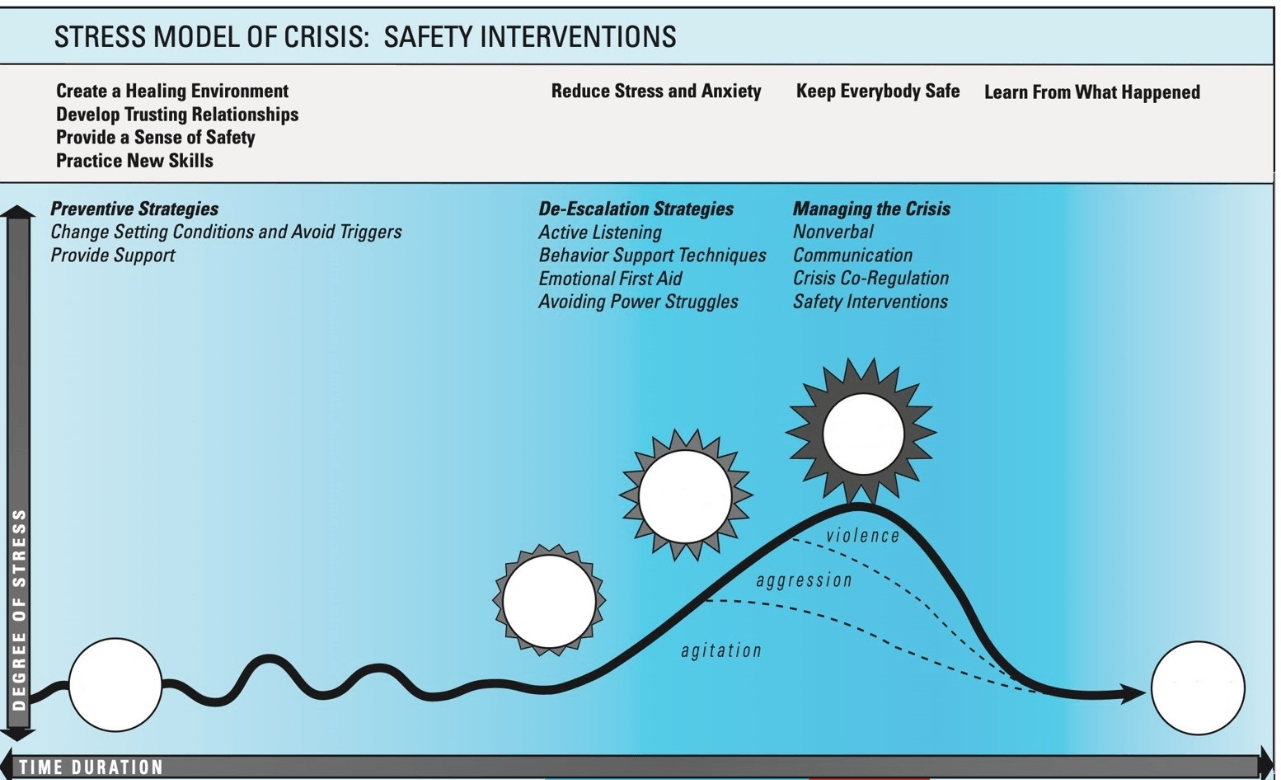
- Baseline
- Triggering event
- Escalation
- Outburst
- Recovery
Please list the steps of a Life Space Interview (LSI) in the correct order.
Identify a place and time to talk
Explore child’s point of view
Summarize the feelings and content
Connect trigger to feelings to behavior
Alternative responses to feelings discussed
Plan developed/practice
Enter child back into the routine
Please list 3 options to manage physical violence that don’t include a physical restraint.
- Eliminate one of the elements of a potentially violent situation
- Use releases and maintain a safe distance with a protective stance
- Leave the situation and get assistance
Please list 5 physical warning signs during a restraint that indicate that the child is in danger.
- Goes limp and ceases to breathe spontaneously
- States they can’t breathe
- Respiration is labored – shortness of breath, gasping, wheezing or coughing
- May make grunting noises
- Gagging or vomiting
- Changes in skin color – pale, gray/bluish, gray/whitish, gray/greenish
- Change in level of responsiveness or consciousness
- Sudden change in struggle
- Bobbing of head, fatigue
- Excessive sweating
- Evacuation of bodily fluids (e.g. urination)
Please list 3 non-verbal crisis co-regulation “help me help myself” strategies to help a potentially violent child.
- Take a deep breath and exhale slowly
- Give the child space and time
- Use silence
- If safe, step out of the child’s sight
- Assume a neutral stance and concerned facial expression
List 2 ways to develop the Cultural Space in an organization or program to decrease the likelihood of challenging behavior or traumatic stress responses.
- Develop culturally competent staff
- Accept and celebrate cultural differences
- Support family connections and involvement
- Allow for diverse staff-child interactions
Please list all 8 behavior support techniques.
- Managing the environment
- Prompting
- Caring gesture
- Hurdle help
- Redirection and distractions
- Proximity
- Directive statements
- Time away