What is an example of a signal in DI?
What is considered mastery? (What is the % range)
A student answers 85-90% of the questions correctly, indicating they can complete the skill independently and are ready to move on.
What does RTI and MTSS stand for?
Response to Intervention
Multi-Tiered System of Support
Provide two examples of precomputation skills for children.
randomly vs. rote counting, one-to-one correspondence, shapes, sizes, etc.
Read the following math lesson component:
Given 15 division problems, students will correctly solve at least 13 problems in 5 minutes.
Question: What Direct Instruction (DI) teaching strategy is this?
State clear objective
After a student has mastered a math skill, the teacher periodically assesses their ability to use the skill in the future to ensure retention.
What type of practice is this?
Distributed Practice
What level is the student receiving math instruction in the general education classroom with no additional supports?
Tier 1
What type of math example is this?
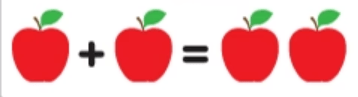
Semi-Concrete
The teacher shows the following image and says "this is a cube."

Questions:
If students have no background knowledge, what could they think a cube is? How can you teach students what a cube is using faultless communication?
Is this math worksheet an example of a mastery measurement or a general outcome measurement? why?
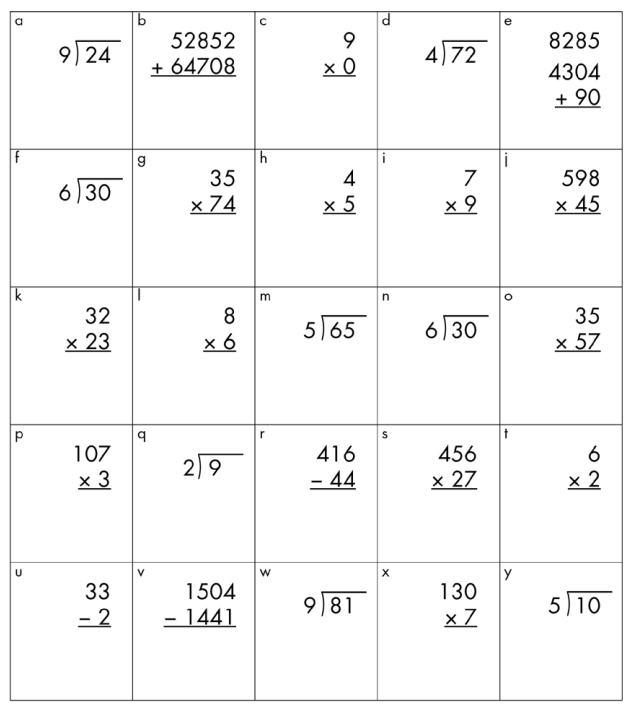
General outcome measurement- It is assessing the students math skills across the entire curriculum (variety of skills/problems)
At what level, can we consider evaluating a student for special education services?
Tier 3
What is the sequential order for teaching students math skills?
1) Precomputation skills
2) Addition
3) Subtraction
4) Multiplication
5) Division
6) Fractions
7) Algebra
8) Problem Solving
Problem: 9X9=
Questions:
1) If a student responds correctly, how should you respond? (Provide example)
2) If a student does not respond or responds incorrectly, how should you respond? (Provide example)
1) Excellent job! 9x9 is 81!
2) Let's try again. If I want to multiple 9 x 9, I'm trying to figure out how much I would have if I had nine groups with nine objects in each. Let me try the finger trick, I get 81! What's 9x9? (Model, Test)
Error Analysis: Review the following work sample
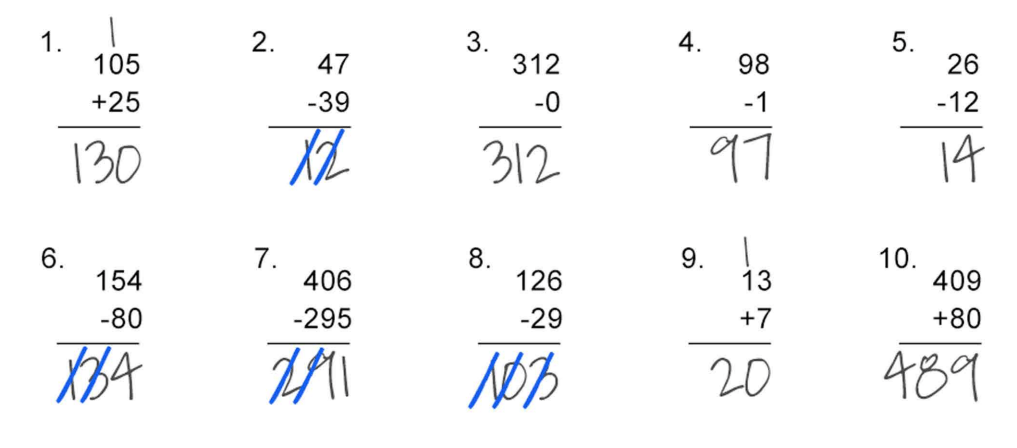
Questions:
1) How many questions did the student answer correctly?
2) How many questions did the student answer incorrectly?
3) What is their overall percentage of accuracy on this assignment?
3) What error are they making?
1) 6 correct
2) 4 wrong
3) 6/10= 60%
4) Difficulty subtracting when the number on top is smaller, not regrouping
After conducting several screening assessments, a group of five students are having difficulty with subtraction problems.
Question:
How could you design a Tier 2 intervention to support these students? Include all required details as if this was happening in the school setting.
2) Determine frequency and duration (weekly for 20 minutes)
3) Identify a specific intervention program to use or evidence-based teaching strategies
4) Collect data on student performance
Provide an example of TWO accommodations and TWO modifications that could support a student with a SLD in math skills.
Accommodations: Extended time, use of calculator, use of number line, use of manipulatives, provided worked example, provided one problem at a time to complete, etc.
Modifications: Reduced problems, worker on prerequisite or simpler skill (single-digit addition versus double), etc.
A student has the following math IEP goal:
Given 10 subtraction problems, Student will independently subtract double digit numbers from double digit numbers with and without regrouping with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Baseline: 100% accuracy on 1 out of 5 trials
Questions:
1) How would you collect progress monitoring data on this goal?
2) If the student does not make progress (achieve the goal), how could you revise it?
3) If the student does achieve the goal (yay!), what could be a new math goal for the student?
1) The student will complete a worksheet that contains 10 double-digit subtraction problems with and without regrouping. The student will complete this same worksheet (different problems) five times during the marking period (biweekly).
2) If the student is not making progress from baseline or regressing, possibly focus in double-digit subtraction without regrouping.
3) If the student achieves this goal, move onto multiplication and division
Math Skill: Algebraic Equations

Question: What is a task analysis? Provide an example of a task analysis to help a student solve this type of problem.
Task analysis- Breaking a problem or skill down into individual steps for a student to complete and thus the teacher can pinpoint where errors are occurring
Example:
1) Identify the variable you are trying to solve (y)
2) Is y on the left-hand side of the equal sign (=) by itself? (If yes, move to step 5, if no continue)
3) Look at the number next to y, is it + or -?
4) To remove the number, we have to perform the opposite operation (+ or -) to move it to the other side of the equation (=)
5) Add or subtract the two number to the right of the = sign
6) You now have your answer!
Tier 2 Intervention: A teacher is working with a small-group of five students twice a week for 15 minutes on addition skills.
Questions:
1) What is a quantitative change we can make to intensify this to a Tier 3 intervention?
2) What is a qualitative change we can make to intensify this to a Tier 3 intervention?
1) Frequency of intervention, duration of intervention, reduce size of group or one-on-one
2) Change teaching strategy for addition (incorporate concrete manipulatives), provide varied positive feedback, etc.
Read the following instructional activity for an addition lesson:
- Ask two volunteers to come to the front of the classroom.
- Give one student a two-digit number. Give the other student a one digit number. Instruct the students to use base-ten blocks to add their numbers together.
- Have the rest of the class use base-ten blocks to model the addition problem at their desks.
- Ask students to share some information. Great questions include: What is the sum of your addition problem? What strategies did you use to find the sum?
- Have the students independently complete a worksheet with five addition problems that include a mix of two-digit and one-digit numbers.
Question: How can this activity be differentiated? In other words, how can you adapt this activity for struggling or excelling learners?
Possible adaptations:
Struggling learners-
- Use of a number line
- Provide a worked example/model
- Frequent teacher check-ins or small-group support during independent practice
- Pair with an excelling learner for support
- Provided one problem at a time on worksheet
- Reduced problems on independent worksheet
Excelling learners-
- Complete without manipulatives
- Given more difficult two-digit numbers
- Pair with a struggling learner to explain their process
- Given more than five addition problems