AVPU stands for...
A - Alert
V - Verbal (Responds to verbal Stimuli)
P - Pain (Responds to Painful Stimuli)
U - Unresponsive (No physical response to anything you do)
The 3 phases of care are...
1. C.U.F. (Care Under Fire)
2. T.F.C. (Tactical Field Care)
3. C.C.E. (Combat Casualty Evacuation, CASEVAC/MEDEVAC)
If you can palpate a radial pulse (feel a pulse at the wrist) this tells you what about a patients blood pressure...
The systolic or "Top Number" of the blood pressure is > or = 80 torr.
What is the difference between a CC (Cubic Centimeter), ML (Millimeter), and MG (Milligram) if any...
A CC and ML are the same and refer to the measurement of actual fluid.
A MG or Milligram is the amount of Medication or "Dose"You get to the A in your S-MARCH-RV sequence. You decide the patient needs a Nasopharyngeal Airway (NPA), how do you appropriately measure it on your patient.
 Appropriately measuring an NPA is done by placing it at the tip of the nose and making sure it doesn't go past the earlobe. If it does you may cut it to fit.
Appropriately measuring an NPA is done by placing it at the tip of the nose and making sure it doesn't go past the earlobe. If it does you may cut it to fit.
Bag Valve Mask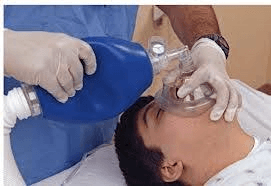
The only medical treatment performed in C.U.F. (Care Under Fire) is...
High Hasty Tourniquets if needed.
A normal respiratory rate range for an adult at rest is...
Between 12 and 20bpm (Breaths per minute)
What are the 2 medications given for an anaphylactic reaction...
0.3mg Epinephrine 1:1,000 (1 epi pen dose) IM or intramuscular
25-50mg Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) I.V./IO*Preferred method, or IM if IV/IO is unavailable
Your patient has a GSW high on the inside of the upper left leg, what is the appropriate treatment if your tourniquet will not reach...
Apply direct pressure above the injury, Pack the wound with Combat Gauze, Hold pressure on the Combat Gauze for 3 minutes to confirm bleeding is controlled, wrap the injury with a dressing and tape it to secure it.
A&Ox4 is assessing cognitive brain function by asking what 4 things...
Person - Do they know who they are or who you are
Place - Do they know where they are
Time - Do they know what day, month, or year it is
Event - Do they know what just happened
T.F.C. (Tactical Field Care) starts when...
Fire superiority has been gained and or the patient has been moved behind cover.
The average HR (Heart Rate) range for an adult at rest is...
Between 60-100bpm (beats per minute)
When using an Epi Pen where and how would you administer it...
Large Muscle Group i.e. Quads (Leg), Delts (Shoulder) or Glutes (Buttocks)
Take off the safety cap, push forcefully into the muscle group you choose to give it, and hold for approximately 10 seconds so all the medication is given.
You are managing a casualty with shrapnel to the left eye. They are in severe pain and cannot see out of the injured eye. 1.What is your treatment plan? 2. What is your pain control option? 3. What category on your 9-line medevac is this patient
1. Cover both eyes as they move in unison. by not covering the uninjured eye they may cause more damage by trying to look at objects with the good eye.
2. Fentanyl, Ketamine for sedation is a last resort as it may increase the pressure in the eye.
3. Urgent, Life/Limb/Eyesight category as well as you now have a blind patient still on the battlefield.
MIST on a 9-Line MEDEVAC request is giving what information...
M - Mechanism of Injury/Illness
I - Injury sustained
S - Symptoms and Vital Signs (Stable vs Unstable)
T - Treatments given (Tourniquets, IV/IO, Medications, etc...)
Explain the difference between a "High Hasty" and "Deliberate" Tourniquet...
A "High Hasty" Tourniquet is over the clothing, as high an tight as possible until bright red bleeding has stopped and typically preformed in the C.U.F. phase.
A "Deliberate" Tourniquet is placed 2-4 inches above the would but not on a joint, on the patients bare skin with tape placed on it and the time recorded from when it was placed.
Vital Signs need to be assessed how often on a stable patient vs an unstable patient (when the tactical situation permits)
Stable Patient - Every 15 - 30 Min
Unstable Patient - Every 5 Min (or immediately before a medication is given)
TXA (Tranexamic Acid) is given how often and at what dose.
TXA can be given initially after the injury up to the 1st 3 hours after
1000mg or 1gram is given in a 100cc bag of fluid over 10 minutes or a very slow IV pushA second does can be given up to 8 hours after the initial dose
What is the difference between a Role 1, Role 2, and Role 3 theater hospitals...
Role 1 - PA/Senior Medic Ran, No major surgical procedures done, No Blood Products, no patient holding facility, no imaging capabilities. (Sick Call Clinic)
Role 2 - Physicians, Nurses, Medics, Laboratory Surgical Capability, X- Ray and some imaging capabilities, usually a 4-12 bed patient holding facility, Blood Products Authorized (Emergency Room Facility)
Role 3 - All Trauma services offered as well as a long term care holding facility if needed. (Actual Hospital)
The Acronym S-M.A.R.C.H.-R.V. stands for...
S - Security
M - Massive hemorrhage/bleeding control
A - Airway (is it open, can they maintain it)
R - Respirations (are they breathing, = Rise/Fall of chest, Tension Pneumo?)
C - Circulation (Do they have a good pulse at the wrists "Radial Pulse", Do they require some sort of fluid, Do they Require TXA to help control bleeding)
H - Hypothermia (Are they packaged correctly in a blanket with heating pad, Do they need warm IV/IO Fluids)
R - Recovery Position (is the patient positioned injured side down if possible, are the positioned so if they vomit they won't choke)
V - Vital Signs (Baseline Vital Signs Documented, B/P, HR, RR, AVPU, GCS, Temp, and Pain Scale)
List the items that come standard in your issued IFAK (Individual First Aid Kit)
Chest Seal x 2
Gloves x 2 pair
Fox Eye Shield x 2
Compressed Gauze
Duct Tape
Permanent Marker
Emergency Trauma Bandage (E.T.B.)
Nasopharyngeal Airway (N.P.A.)
Combat Casualty Card (TC3 Card)
What 3 things does a GCS (Glasgow Coma Scale) assess?
Eye Opening - 4
Verbal Response - 5
Motor Response - 6
Minimum score of 3, Max Score of 15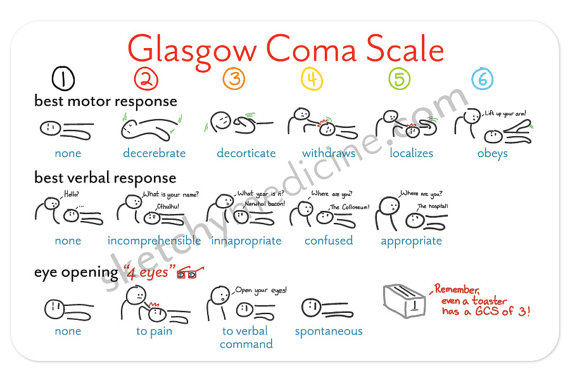
Looking at the picture below, if we have a 100kg patient (220lbs) (Robie-wan-kanobie) lets say, and we need to give him 1.5mg/kg of Ketamine, using a 10ML syringe, how many ML of would we administer into the syringe...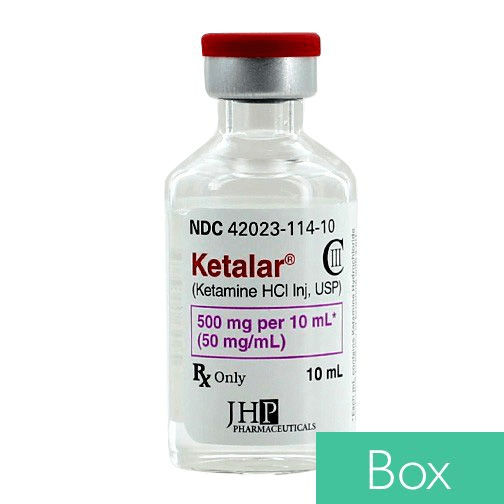
To Administer SSG Robles (100kg), 1.5mg/kg, we want 150mg of medication. There are 50mg/ml, so we need to give him 3ML of Ketamine to get a 150MG dose.
Explain all 9-lines of a 9-Line MEDEVAC Request...
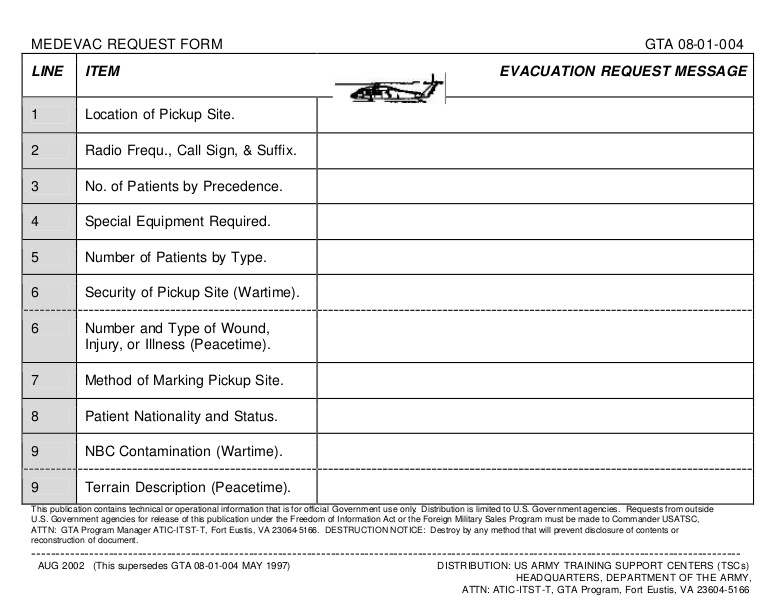 *Hint* Low Flying Pilots Eat Trees, Salsa Makes Nachos Nasty/Tasty
*Hint* Low Flying Pilots Eat Trees, Salsa Makes Nachos Nasty/Tasty