Tell me how accrual based accounting differ from cash-basis accounting (basic concept)?
Bonus: can you name the financial statement that particularly shows CASH-basis accounting?
Accrual Based: A picture of profitability based on management assumptions. Based on when Revenues are "earned" and expenses are incurred. This is what the public sees. GAAP-based accounting. Matching Revenues with expenses to provide investors with a picture of general profitability earned.
Cash Based: Profit is recorded only when cash is received or spent to generate the Revenues and expenses. Usually only seen by the IRS for tax purposes. Used for Tax book accounting. Provides actual CASH SPECIFIC COLLECTED profitability.
Bonus: The Cash Flow Statement takes accrual based net income and reconciles the impact of operations on CASH.
Explain Present Value and Future Value CONCEPTUALLY? (BASIC)
Bonus: What is the phrase used to describe these concepts?
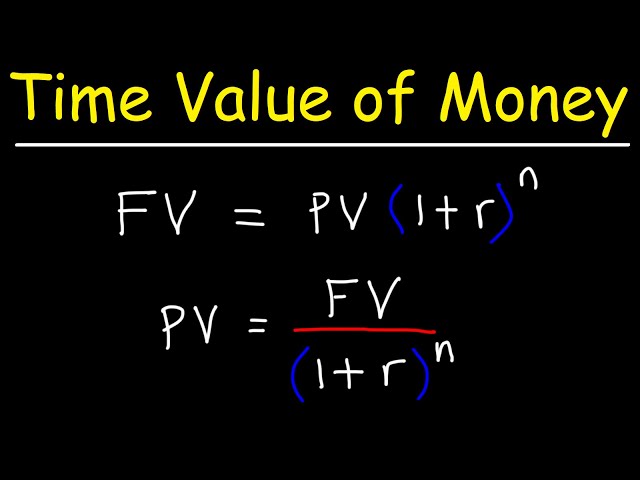
Bonus: Time value of Money concept (A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow)
($1B today is worth more than $1B 100 years from now!)
What are the 2 categories of valuation methodologies used?
Bonus: Give one example of each?
Intrinsic Valuation (value of the company internally based on the sum of its present value based on it's future free cash flow generation): DCF Model Analysis
Extrinsic/Relative Valuation (value derived by comparing to historical transactions and other companies): Comparable Transaction and Comparable Company Analysis
Other: Liquidation and LBO Model Analysis
Bonus: see above
Explain Net Working Capital conceptually?
BONUS: explain the change in networking capital conceptually
ANSWER: A financial metric used to evaluate a company’s near-term liquidity risk. It is calculated by subtracting a company’s current liabilities from its current assets.
BONUS ANSWER: Positive Net Working Capital signifies that a company is in the position to pay off its current/short-term liabilities/obligations. Negative Net Working Capital signifies that a company is not in a position to meet its short-term obligations so external financing might urgently be required.
It is ACTUALLY: current operating assets - current operating liabilities = NWC
Change in NWC = Prior Pd NWC - Ending NWC
What are equity capital markets, debt capital markets?
Equity Capital Markets:
Markets that a company obtains Asset financing by selling STOCKS. This is NON-obligatory form of financing, but the company needs to be cognizant of investor emotion and it's affect on the stock price volatility. Market/econonomic factors also have an affect on the stock's price. When you buy a stock, you are placing an ownership claim on a company's assets that entitles you to receiving a share of their profits (hopefully!)
Debt Capital Markets:
Markets where companies obtain asset financing by selling bonds, taking loans, commercial papers. Govts can issue T-bills here too. Generally attributed to RISK-FREE financing because obligations are backed by the US Govt. RISK FREE unless we are talking inflation risk, interest rate risk, default risk, etc. This form of financing has a SENIOR claim over Equity. Meaning if the business goes bankrupt, debt folks must be paid first (unless default risk) while the Equity folks are crying due to the loss in their IRAs/401Ks! OUCH!
Tell me about the basic revenue recognition principle used in accrual accounting (BASIC)
Revenues are recorded ONLY when they are earned.
This means that you can only record the receipt of revenue when the product and service was received or delivered to customers, REGARDLESS of whether cash was collected from the customer or not. Must be recognized in the same period as generation.
What is the CAPM CONCEPTUALLY? (BASIC)
Bonus: What is another term/phrase for the CAPM?

Bonus: Cost of Equity
What is the equation for Future Free Cash Flows? (simple lookup)
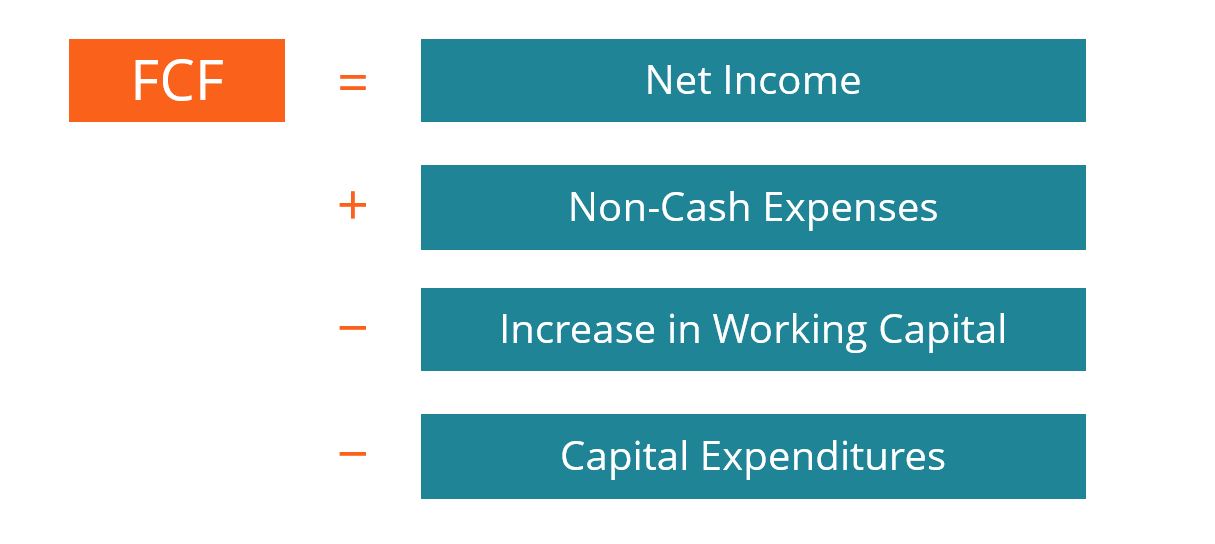
FCF = EBIT x (1-Tax Rate) + D&A - CAPEX - Changes in NWC
What are the three main categories of financial ratios used in analysis?
ANSWER: Liquidity ratios, profitability ratios, solvency ratios.
What is the market concept in relation to the federal reserve version of the discount rate?
In a DCF analysis, this is DIFFERENT! DO NOT CONFUSE THE TWO. In a DCF, it is projected WACC which accounts for the size, timing, and risk of future valued free cash flows a company hopes to generate
Tell me about the matching principle concept in accrual accounting (BASIC)
When Revenue is generated, you must record the expenses that were incurred, necessary, and associated directly with that product/service's revenue generation.
Must be recorded/recognized in the same period as when the revenue was earned.
What is the WACC CONCEPTUALLY? (BASIC)
Bonus: What is the connection between the CAPM and WACC?

Bonus: CAPM calculates the Cost of Equity Financing for a company. It is added along with the cost of debt to find the weighted average cost of financing using both debt and equity in the capital structure.
Can you define M&A, explain the difference between them?
Bonus: give 2 GENERAL reasons why companies might want to do an M&A? Hint: “Synergies”
A merger is when two companies join together
An acquisition is when one company buys another as it's subsidiary.
Bonus: Revenue Synergies and Cost Synergies
How can a high debt-to-equity ratio be interpreted?
ANSWER: Indicates a company is financed heavily by leverage compared to shareholder equity.
How does changes in interest rates generally affect the stock market, vs bond markets? ALL ELSE EQUAL
Bonus: Explain using an example
Generally, decreases in the interest rates have a positive effect on the stock market, as capital is cheaper if debt becomes cheaper, helping business performance. Bond prices of bonds already issued are driven down with increases in interest rates, in order to compensate for a lower coupon rate at the time of issuance.
Bonus: 2008-09 Financial Crisis (MBS and CDS crisis), 2021~2024 Interest Rate Hikes and cuts.
The Fed wants to cut interest rates strategically in a manner to achieve a "soft landing." This means they don't want to cut too aggressively to the extent where we end up in a recession.
Explain the BASIC concept of Depreciation & Amortization (D&A)
Bonus: Is depreciation cash-based or accrual-based accounting?
Depreciation is a recorded periodical loss in a TANGIBLE Long-term Asset's value. This is typically allocated equally for each year in a given period using straight-line method.
Amortization: Resetting the value of intangibles or bonds back to their face/par value. (depreciation for intangibles)
Bonus answer: depreciation is accrual-based because it's a NONcash expense....remember the difference between accrual and cash based accounting.
Explain the BASIC concept of Terminal Value in a DCF Analysis
Bonus: NAME TWO approaches used for doing this.

Walk me through the basic concept of an LBO using a real estate house flipping as an example?
Bonus: What field in Finance does this correspond to specifically?
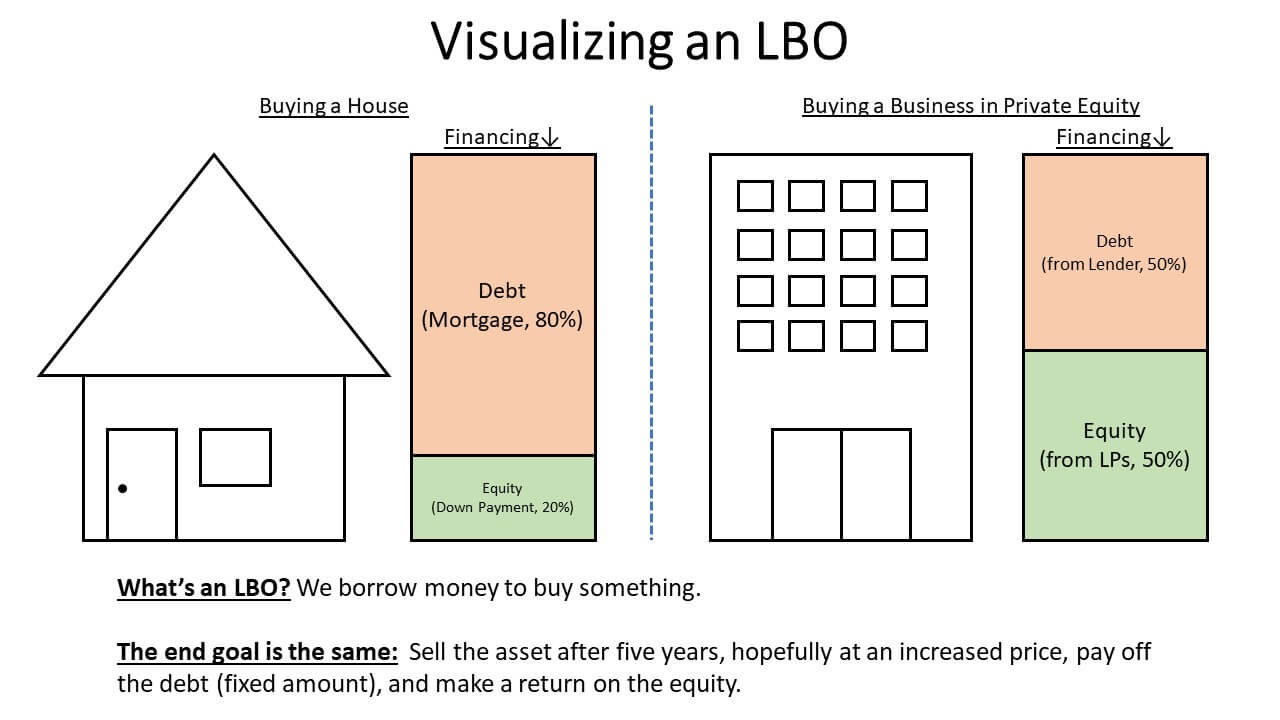
Bonus: Private Equity
What is the difference between the current ratio and the quick ratio?
ANSWER: Current ratio uses all current assets in its calculation while the quick ratio excludes inventory from its calculation.

Who controls interest rates in the US and how are they ACTUALLY controlled?
Hint: It is NOT like a stock price where it simply updates at next day opening as defined by the efficient market hypothesis. No one is sitting on a computer and just changing the rate in two seconds.
Bonus: What is the committee that meets to discuss the manipulation of interest rates and what's the name of the person who is their CHAIR?
The Federal Reserve uses the Interest on Reserve balances and the overnight reverse repo price to control the Effective Federal Funds Rate.
One thing to keep in mind about monetary policy/economics is that these changes take a while to take effect. The Fed may be cutting interest rates, but the economy is still in "STAGflation" or sticky inflation. This is why costs are still up and the job market hasn't really opened as much.
Bonus: FOMC and Jerome Powell - MAN this guy's mouth moves the markets (and ofc the unemployment reports)
WALK ME THROUGH the 3 Financial Statements? (SIMPLIFIED!) HINT: Income Statement, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flows Statement.
Bonus: Give a simple explanation of how they are linked together?
Income Statement: Revenue - Expenses = Net Income
Balance Sheet: Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity
Cash Flow Statement:
Net income + non cash adjustments (D&A or Gains and losses) + non cash Adjustments from Changes in NWC = Cash from Operations
(+/-) Cash from Investing
(+/-) Cash from financing
= Ending Cash for the year ended
Bonus Answer:
Net income from I/S is the starting line item on the CFS to calculate ending cash.
Ending Cash on CFS is the new Cash balance in the assets portion of the Balance Sheet at the end of the year.
Net income from I/S is used to update retained earnings in the equity portion of the Balance Sheet.
Walk me through a DCF Model Analysis and how it works? (SIMPLE WALKTHROUGH)
Bonus: Explain by using the step by step process and INTERPRET THE END RESULT OF THE MODEL
1. Forecast FCF for a time period (if company is mature use 5 years, If company is growth use 10)
2. Find the CAPM and WACC.
3. Calculate the Terminal Value using either Exit or Perp Approach.
4. Discount your Cash Flows back to the present using the PV equation.
5. Calculate the Implied Share price
Bonus step 6: Compare the implied share price to the current extrinsic open market value share price. This can determine whether your company is overvalued or undervalued!
What does accretion/dilution analysis tell you about the attractiveness of a transaction?
Bonus: Define and include pro forma EPS in your response and explain what it has to do with A/D Analysis. What is the formula for EPS?
Accretive: The sum of Pro forma EPS of two companies in an M&A deal (meaning projected earnings put together) are GREATER than the sum of the company earnings if they operated separately
Dilutive: The sum of Pro Form EPS of two companies in an M&A deal are LESSER than the sum of the company earnings if they operated separately
Bonus: see above
Double Bonus: Net income/average shares outstanding
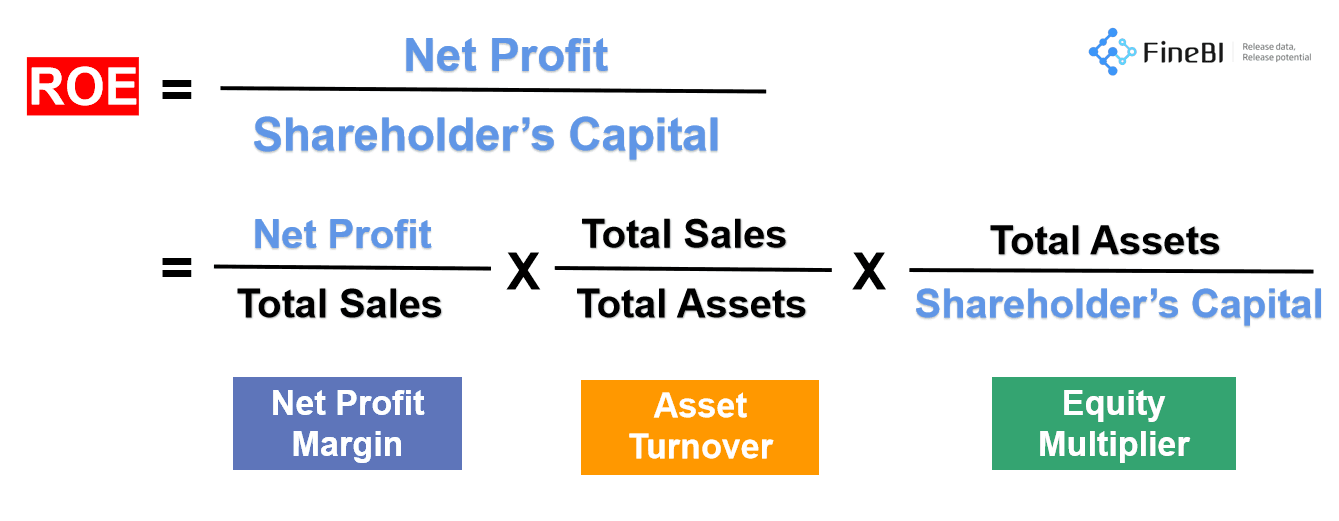
What is the DuPont Analysis Formula?
ANSWER: It breaks return on equity down into three parts.
(1)Profit Margin - expense control (2)Asset Turnover - asset utilization (3)Equity Multiplier - debt utilization.
What is a yield curve and why is it an important economic indicator?
Bonus: what is the name of payments annual or semi-annual payments
The yield curve is involved in the transmission of changes in monetary policy to a broad range of interest rates in the economy. When households, firms or governments borrow from a bank or from the market (by issuing a bond), their cost of borrowing will depend on the level and slope of the yield curve.
Bonus: Coupons