A piece with no discernable sections
Through composed
This technique was typical of Madrigals
word painting
Chord progressions used to end sections of music.
Cadences
The name given to chords without the third.
Implied.
Jaws
m2
The difference between a Motet and a Madrigal
Motet is sacred
Madrigal is secular.
Thomas Weelkes wrote what style of music?
Madrigals
The same rhythmic material imitated at different parts of the bar
rhythmic displacement
Name the type of cadence most commonly used in motets and masses.
Plagal - IV - I
Star Wars
P5
Mass are large scale and multi-movement, motets are shorter.
High register male voice used in lieu of female singers during the Renaissance
Castrato
The same melodic material alternated between instruments resulting in polyphony
canon
Name the MINOR modes
Dorian
Phrygian
Aeolian
Locrian
National Anthem
P4
The most common type of music through the Middle Ages
Gregorian Chant
When music directly imitates its lyrics
Word painting.
Chord V/V
Secondary dominant
Name of the progression I - V

m3
Name a key form for the Renaissance AND a key form for Middle Ages
Motet, Madrigal, Mass
Gregorian Chant
Hildegard von Bingen composed this type of music
Gregorian Chants
Chord V/V is used to:
modulate
Chord V - vi is a ___________ cadence.
interrupted
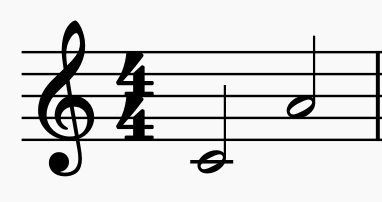
M6