Polyphonic form that uses counterpoint
Fugue
The Baroque Period was from ________ - _________.
1600-1750
Chord progressions used to end sections of music.
Cadences
Chromaticism was used to portray:
grief or sadness
Chord with three notes, 1 3 5
major triad
Theme A is played in the ______ key, theme B is played in the _______ key.
Tonic
dominant
In the Baroque Period, music became accessible to people from the _____________.
the same melodic material moved down a tone
descending sequence
Lyrics from an Opera
Libretto
Chord with three notes, 1 b3 5
minor triad
The final section of sonata form
The Classical Period began in ___________.
1750
A melody split into smaller sections
The minor key that shares the same key signature as a major key is called:
the relative minor
Chord with a major triad and a major 7:
1 3 5 7
Major 7
prelude
Classical music was written for _________ rather than the church
audiences
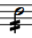
tremolo
acciaccatura and appoggiatura are examples of ___________.
ornamentation
Chord with a major triad and a minor seven:
1 3 5 b7
Dominant 7
The form of the first movement of a Classical symphony AND a Classical concerto
Sonata Form
Vivaldi composed this kind of music
programmatic
Modulation in a piece is clear when there are _________ on the score
accidentals
A chord progression used to establish a key
V - I
Three note chord with two minor thirds
diminished triad